Run commands on your Windows instance at launch
When you launch a Windows instance using Amazon EC2, you can pass user data to the instance that can be used to perform automated configuration tasks, or to run scripts after the instance starts. Instance user data is treated as opaque data; it is up to the instance to interpret it. User data is processed by EC2Launch v2 on Windows Server 2022, EC2Launch on Windows Server 2016 and 2019, and EC2Config on Windows Server 2012 R2 and earlier.
For examples of the assembly of a UserData property in a AWS CloudFormation template, see
Base64 Encoded UserData Property and Base64 Encoded UserData Property with AccessKey and SecretKey.
For information about running commands on your Linux instance at launch, see Running commands on your Linux instance at launch in the Amazon EC2 User Guide for Linux Instances.
For an example of running commands on an instance within an Auto Scaling that work with lifecycle hooks, see Tutorial: Configure user data to retrieve the target lifecycle state through instance metadata in the Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling User Guide.
Contents
User data scripts
For EC2Config or EC2Launch to run scripts, you must enclose the script within a special tag when you add it to user data. The tag that you use depends on whether the commands run in a Command Prompt window (batch commands) or use Windows PowerShell.
If you specify both a batch script and a Windows PowerShell script, the batch script runs first and the Windows PowerShell script runs next, regardless of the order in which they appear in the instance user data.
If you use an AWS API, including the AWS CLI, in a user data script, you must use an instance profile when launching the instance. An instance profile provides the appropriate AWS credentials required by the user data script to make the API call. For more information, see Instance profiles. The permissions you assign to the IAM role depend on which services you are calling with the API. For more information, see IAM roles for Amazon EC2.
Script type
Syntax for batch scripts
Specify a batch script using the script tag. Separate the commands using line
breaks as shown in the following example.
<script> echo Current date and time >> %SystemRoot%\Temp\test.log echo %DATE% %TIME% >> %SystemRoot%\Temp\test.log </script>
By default, user data scripts run one time when you launch the instance.
To run the user data scripts every time you reboot or start the instance, add
<persist>true</persist> to the user data.
<script> echo Current date and time >> %SystemRoot%\Temp\test.log echo %DATE% %TIME% >> %SystemRoot%\Temp\test.log </script> <persist>true</persist>
EC2Launch v2 agent
To run an XML user data script as a detached process with the EC2Launch v2
executeScript task in the UserData stage,
add the following tag to your user data.
<detach>true</detach>
Note
The detach tag is not supported on previous launch agents.
<script> echo Current date and time >> %SystemRoot%\Temp\test.log echo %DATE% %TIME% >> %SystemRoot%\Temp\test.log </script> <detach>true</detach>
Syntax for Windows PowerShell scripts
The AWS Windows AMIs include the AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell
Specify a Windows PowerShell script using the <powershell> tag.
Separate the commands using line breaks. The <powershell> tag is
case-sensitive.
For example:
<powershell> $file = $env:SystemRoot + "\Temp\" + (Get-Date).ToString("MM-dd-yy-hh-mm") New-Item $file -ItemType file </powershell>
By default, the user data scripts are run one time when you launch the instance.
To run the user data scripts every time you reboot or start the instance, add
<persist>true</persist> to the user data.
<powershell> $file = $env:SystemRoot + "\Temp\" + (Get-Date).ToString("MM-dd-yy-hh-mm") New-Item $file -ItemType file </powershell> <persist>true</persist>
EC2Launch v2 agent
To run an XML user data script as a detached process with the EC2Launch v2
executeScript task in the UserData stage,
add the following tag to your user data.
<detach>true</detach>
Note
The detach tag is not supported on previous launch agents.
<powershell> $file = $env:SystemRoot + "\Temp\" + (Get-Date).ToString("MM-dd-yy-hh-mm") New-Item $file -ItemType file </powershell> <detach>true</detach>
Syntax for YAML configuration scripts
If you are using EC2Launch v2 to run scripts, you can use the YAML format. To view configuration tasks, details, and examples for EC2Launch v2, see EC2Launch v2 task configuration.
Specify a YAML script with the executeScript task.
Example YAML syntax to run a PowerShell script
version: 1.0 tasks: - task: executeScript inputs: - frequency: always type: powershell runAs: localSystem content: |- $file = $env:SystemRoot + "\Temp\" + (Get-Date).ToString("MM-dd-yy-hh-mm") New-Item $file -ItemType file
Example YAML syntax to run a batch script
version: 1.1 tasks: - task: executeScript inputs: - frequency: always type: batch runAs: localSystem content: |- echo Current date and time >> %SystemRoot%\Temp\test.log echo %DATE% %TIME% >> %SystemRoot%\Temp\test.log
Base64 encoding
If you're using the Amazon EC2 API or a tool that does not perform base64 encoding of
the user data, you must encode the user data yourself. If not, an error is logged
about being unable to find script or powershell tags to
run. The following is an example that encodes using Windows PowerShell.
$UserData = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes($Script))
The following is an example that decodes using PowerShell.
$Script = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String($UserData))
For more information about base64 encoding, see https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4648.txt
User data execution
By default, all AWS Windows AMIs have user data execution enabled for the initial launch. You can specify that user data scripts are run the next time the instance reboots or restarts. Alternatively, you can specify that user data scripts are run every time the instance reboots or restarts.
Note
User data is not enabled to run by default after the initial launch. To enable user data to run when you reboot or start the instance, see Subsequent reboots or starts.
User data scripts are run from the local administrator account when a random password is generated. Otherwise, user data scripts are run from the System account.
Instance launch
Scripts in the instance user data are run during the initial launch of the
instance. If the persist tag is found, user data execution is enabled
for subsequent reboots or starts. The log files for EC2Launch v2, EC2Launch, and
EC2Config contain the output from the standard output and standard error
streams.
EC2Launch v2
The log file for EC2Launch v2 is
C:\ProgramData\Amazon\EC2Launch\log\agent.log.
Note
The C:\ProgramData folder might be hidden. To view the
folder, you must show hidden files and folders.
The following information is logged when the user data is run:
-
Info: Converting user-data to yaml format– If the user data was provided in XML format -
Info: Initialize user-data state– The start of user data execution -
Info: Frequency is: always– If the user data task is running on every boot -
Info: Frequency is: once– If the user data task is running just once -
Stage: postReadyUserData execution completed– The end of user data execution
EC2Launch
The log file for EC2Launch is
C:\ProgramData\Amazon\EC2-Windows\Launch\Log\UserdataExecution.log.
The C:\ProgramData folder might be hidden. To view the
folder, you must show hidden files and folders.
The following information is logged when the user data is run:
-
Userdata execution begins– The start of user data execution -
<persist> tag was provided: true– If the persist tag is found -
Running userdata on every boot– If the persist tag is found -
<powershell> tag was provided.. running powershell content– If the powershell tag is found -
<script> tag was provided.. running script content– If the script tag is found -
Message: The output from user scripts– If user data scripts are run, their output is logged
EC2Config
The log file for EC2Config is C:\Program
Files\Amazon\Ec2ConfigService\Logs\Ec2Config.log. The following
information is logged when the user data is run:
-
Ec2HandleUserData: Message: Start running user scripts– The start of user data execution -
Ec2HandleUserData: Message: Re-enabled userdata execution– If the persist tag is found -
Ec2HandleUserData: Message: Could not find <persist> and </persist>– If the persist tag is not found -
Ec2HandleUserData: Message: The output from user scripts– If user data scripts are run, their output is logged
Subsequent reboots or starts
When you update instance user data, user data scripts are not run automatically when you reboot or start the instance. However, you can enable user data execution so that user data scripts are run one time when you reboot or start the instance, or every time you reboot or start the instance.
If you choose the Shutdown with Sysprep option, user data scripts are run the next time the instance starts or reboots, even if you did not enable user data execution for subsequent reboots or starts. The user data scripts will not be executed on subsequent reboots or starts.
To enable user data execution with EC2Launch v2 (Preview AMIs)
-
To run a task in user data on first boot, set
frequencytoonce. -
To run a task in user data on every boot, set
frequencytoalways.
To enable user data execution with EC2Launch (Windows Server 2016 or later)
-
Connect to your Windows instance.
-
Open a PowerShell command window and run the following command:
C:\ProgramData\Amazon\EC2-Windows\Launch\Scripts\InitializeInstance.ps1 -Schedule -
Disconnect from your Windows instance. To run updated scripts the next time the instance is started, stop the instance and update the user data. For more information, see View and update the instance user data.
To enable user data execution with EC2Config (Windows Server 2012 R2 and earlier)
-
Connect to your Windows instance.
-
Open
C:\Program Files\Amazon\Ec2ConfigService\Ec2ConfigServiceSetting.exe. -
For User Data, select Enable UserData execution for next service start.
-
Disconnect from your Windows instance. To run updated scripts the next time the instance is started, stop the instance and update the user data. For more information, see View and update the instance user data.
User data and the console
You can specify instance user data when you launch the instance. If the root volume of the instance is an EBS volume, you can also stop the instance and update its user data.
Specify instance user data at launch
Follow the procedure for launching an instance. The User data field is located in the Advanced details section of the launch instance wizard. Enter your PowerShell script in the User data field, and then complete the instance launch procedure.
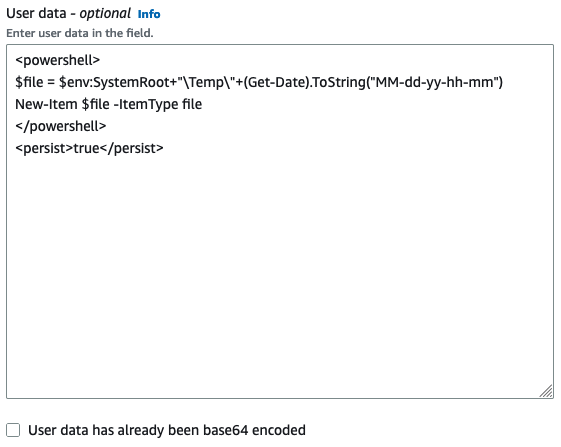
In the following screenshot of the User data field, the example script
creates a file in the Windows temporary folder, using the current date and time in
the file name. When you include <persist>true</persist>,
the script is run every time you reboot or start the instance. If you leave the
User data has already been base64 encoded check box empty,
the Amazon EC2 console performs the base64 encoding for you.
View and update the instance user data
You can view the instance user data for any instance, and you can update the instance user data for a stopped instance.
To update the user data for an instance using the console
-
Open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Instances.
-
Select the instance and choose Actions, Instance state, Stop instance.
Warning
When you stop an instance, the data on any instance store volumes is erased. To keep data from instance store volumes, be sure to back it up to persistent storage.
-
When prompted for confirmation, choose Stop. It can take a few minutes for the instance to stop.
-
With the instance still selected, choose Actions, Instance settings, Edit user data. You can't change the user data if the instance is running, but you can view it.
-
In the Edit user data dialog box, update the user data, and then choose Save. To run user data scripts every time you reboot or start the instance, add
<persist>true</persist>, as shown in the following example: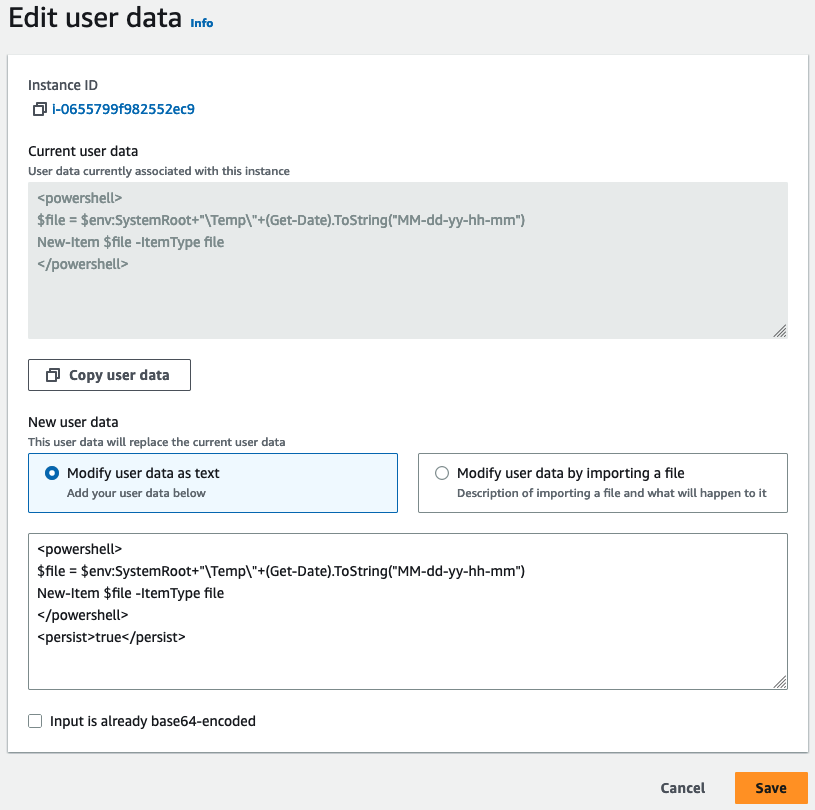
-
Start the instance. If you enabled user data execution for subsequent reboots or starts, the updated user data scripts are run as part of the instance start process.
User data and the Tools for Windows PowerShell
You can use the Tools for Windows PowerShell to specify, modify, and view the user data for your instance. For information about viewing user data from your instance using instance metadata, see Retrieve instance user data from your instance. For information about user data and the AWS CLI, see User data and the AWS CLI in the Amazon EC2 User Guide for Linux Instances.
Example: Specify instance user data at launch
Create a text file with the instance user data. To run user data scripts every
time you reboot or start the instance, add
<persist>true</persist>, as shown in the following
example.
<powershell> $file = $env:SystemRoot + "\Temp\" + (Get-Date).ToString("MM-dd-yy-hh-mm") New-Item $file -ItemType file </powershell> <persist>true</persist>
To specify instance user data when you launch your instance, use the New-EC2Instance command. This
command does not perform base64 encoding of the user data for you. Use the following
commands to encode the user data in a text file named
script.txt.
PS C:\>$Script = Get-Content -Rawscript.txtPS C:\>$UserData = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes($Script))
Use the -UserData parameter to pass the user data to the
New-EC2Instance command.
PS C:\>New-EC2Instance -ImageIdami-abcd1234-MinCount1-MaxCount1-InstanceTypem3.medium\ -KeyNamemy-key-pair-SubnetIdsubnet-12345678-SecurityGroupIdssg-1a2b3c4d\ -UserData $UserData
Example: Update instance user data for a stopped instance
You can modify the user data of a stopped instance using the Edit-EC2InstanceAttribute command.
Create a text file with the new script. Use the following commands to encode the user
data in the text file named new-script.txt.
PS C:\>$NewScript = Get-Content -Rawnew-script.txtPS C:\>$NewUserData = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes($NewScript))
Use the -UserData and -Value parameters to specify the user
data.
PS C:\>Edit-EC2InstanceAttribute -InstanceIdi-1234567890abcdef0-Attribute userData -Value $NewUserData
Example: View instance user data
To retrieve the user data for an instance, use the Get-EC2InstanceAttribute command.
PS C:\>(Get-EC2InstanceAttribute -InstanceIdi-1234567890abcdef0-Attribute userData).UserData
The following is example output. Note that the user data is encoded.
PHBvd2Vyc2hlbGw+DQpSZW5hbWUtQ29tcHV0ZXIgLU5ld05hbWUgdXNlci1kYXRhLXRlc3QNCjwvcG93ZXJzaGVsbD4=Use the following commands to store the encoded user data in a variable and then decode it.
PS C:\>$UserData_encoded = (Get-EC2InstanceAttribute -InstanceIdi-1234567890abcdef0-Attribute userData).UserDataPS C:\>[System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String($UserData_encoded))
The following is example output.
<powershell>
$file = $env:SystemRoot + "\Temp\" + (Get-Date).ToString("MM-dd-yy-hh-mm")
New-Item $file -ItemType file
</powershell>
<persist>true</persist>Example: Rename the instance to match the tag value
You can use the Get-EC2Tag
command to read the tag value, rename the instance on first boot to match the tag
value, and reboot. To run this command successfully, you must have a role with
ec2:DescribeTags permissions attached to the instance because tag
information is retrieved by the API call. For more information on settings
permissions by using IAM roles, see Attaching an IAM Role to an Instance.
Note
This script fails on Windows Server versions prior to 2008.
<powershell>
$instanceId = (invoke-webrequest http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id -UseBasicParsing).content
$nameValue = (get-ec2tag -filter @{Name="resource-id";Value=$instanceid},@{Name="key";Value="Name"}).Value
$pattern = "^(?![0-9]{1,15}$)[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,15}$"
#Verify Name Value satisfies best practices for Windows hostnames
If ($nameValue -match $pattern)
{Try
{Rename-Computer -NewName $nameValue -Restart -ErrorAction Stop}
Catch
{$ErrorMessage = $_.Exception.Message
Write-Output "Rename failed: $ErrorMessage"}}
Else
{Throw "Provided name not a valid hostname. Please ensure Name value is between 1 and 15 characters in length and contains only alphanumeric or hyphen characters"}
</powershell>You can also rename the instance using tags in instance metadata, if your instance is configured to access tags from the instance metadata.
Note
This script fails on Windows Server versions prior to 2008.
<powershell>
$nameValue = Get-EC2InstanceMetadata -Path /tags/instance/Name
$pattern = "^(?![0-9]{1,15}$)[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,15}$"
#Verify Name Value satisfies best practices for Windows hostnames
If ($nameValue -match $pattern)
{Try
{Rename-Computer -NewName $nameValue -Restart -ErrorAction Stop}
Catch
{$ErrorMessage = $_.Exception.Message
Write-Output "Rename failed: $ErrorMessage"}}
Else
{Throw "Provided name not a valid hostname. Please ensure Name value is between 1 and 15 characters in length and contains only alphanumeric or hyphen characters"}
</powershell>