AWS Data Pipeline is no longer available to new customers. Existing customers of AWS Data Pipeline can continue to use the service as normal. Learn more
Executing Work on Existing Resources Using Task Runner
You can install Task Runner on computational resources that you manage, such as an Amazon EC2 instance, or a physical server or workstation. Task Runner can be installed anywhere, on any compatible hardware or operating system, provided that it can communicate with the AWS Data Pipeline web service.
This approach can be useful when, for example, you want to use AWS Data Pipeline to process data that is stored inside your organization’s firewall. By installing Task Runner on a server in the local network, you can access the local database securely and then poll AWS Data Pipeline for the next task to run. When AWS Data Pipeline ends processing or deletes the pipeline, the Task Runner instance remains running on your computational resource until you manually shut it down. The Task Runner logs persist after pipeline execution is complete.
To use Task Runner on a resource that you manage, you must first download Task Runner, and then install it on your computational resource, using the procedures in this section.
Note
You can only install Task Runner on Linux, UNIX, or macOS. Task Runner is not supported on the Windows operating system.
To use Task Runner 2.0, the minimum Java version needed is 1.7.
To connect a Task Runner that you've installed to the pipeline activities it should
process, add a workerGroup field to the object, and configure
Task Runner to poll for that worker group value. You do this by passing the worker
group string as a parameter (for example, --workerGroup=wg-12345) when you
run the Task Runner JAR file.
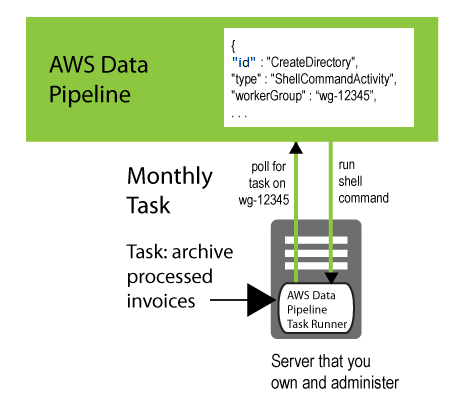
{ "id" : "CreateDirectory", "type" : "ShellCommandActivity", "workerGroup" : "wg-12345", "command" : "mkdir new-directory" }
Installing Task Runner
This section explains how to install and configure Task Runner and its prerequisites. Installation is a straightforward manual process.
To install Task Runner
-
Task Runner requires Java versions 1.6 or 1.8. To determine whether Java is installed, and the version that is running, use the following command:
java -versionIf you do not have Java 1.6 or 1.8 installed on your computer, download one of these versions from http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/index.html
. Download and install Java, and then proceed to the next step. -
Download
TaskRunner-1.0.jarfrom https://s3.amazonaws.com/datapipeline-us-east-1/us-east-1/software/latest/TaskRunner/TaskRunner-1.0.jarand then copy it into a folder on the target computing resource. For Amazon EMR clusters running EmrActivitytasks, install Task Runner on the master node of the cluster. -
When using Task Runner to connect to the AWS Data Pipeline web service to process your commands, users need programmatic access to a role that has permissions to create or manage data pipelines. For more information, see Granting programmatic access.
-
Task Runner connects to the AWS Data Pipeline web service using HTTPS. If you are using an AWS resource, ensure that HTTPS is enabled in the appropriate routing table and subnet ACL. If you are using a firewall or proxy, ensure that port 443 is open.
Starting Task Runner
In a new command prompt window that is set to the directory where you installed Task Runner, start Task Runner with the following command.
java -jar TaskRunner-1.0.jar --config ~/credentials.json--workerGroup=myWorkerGroup--region=MyRegion--logUri=s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/foldername
The --config option points to your credentials file.
The --workerGroup option specifies the name of your worker group,
which must be the same value as specified in your pipeline for tasks to be
processed.
The --region option specifies the service region from which to pull
tasks to execute.
The --logUri option is used for pushing your compressed logs to a location in Amazon S3.
When Task Runner is active, it prints the path to where log files are written in the terminal window. The following is an example.
Logging to /Computer_Name/.../output/logs
Task Runner should be run detached from your login shell. If you are using a terminal application to connect to your computer, you may need to use a utility like nohup or screen to prevent the Task Runner application from exiting when you log out. For more information about command line options, see Task Runner Configuration Options.
Verifying Task Runner Logging
The easiest way to verify that Task Runner is working is to check whether it is
writing log files. Task Runner writes hourly log files to the directory,
output/logs, under the directory where Task Runner is
installed. The file name is Task Runner.log.YYYY-MM-DD-HH, where
HH runs from 00 to 23, in UDT. To save storage space, any log files older than eight
hours are compressed with GZip.