Using CloudWatch outlier detection
When you enable outlier detection for a metric, CloudWatch applies statistical and machine learning algorithms. These algorithms continuously analyze metrics of systems and applications, determine normal baselines, and surface anomalies with minimal user intervention.
The algorithms generate an outlier detection model. The model generates a range of expected values that represent normal metric behavior.
You can enable outlier detection using the AWS Management Console, the AWS CLI, CloudFormation, or the AWS SDK. You can enable outlier detection on metrics vended by AWS and also on custom metrics. In an account set up as a monitoring account for CloudWatch cross-account observability, you can create anomaly detectors on metrics in source accounts in addition to metrics in the monitoring account.
You can use the model of expected values in two ways:
Create outlier detection alarms based on a metric's expected value. These types of alarms don't have a static threshold for determining alarm state. Instead, they compare the metric's value to the expected value based on the outlier detection model.
You can choose whether the alarm is triggered when the metric value is above the band of expected values, below the band, or both.
For more information, see Create a CloudWatch alarm based on anomaly detection.
When viewing a graph of metric data, overlay the expected values onto the graph as a band. This makes it visually clear which values in the graph are out of the normal range. For more information, see Creating a graph.
You can also retrieve the upper and lower values of the model's band by using the
GetMetricDataAPI request with theANOMALY_DETECTION_BANDmetric math function. For more information, see GetMetricData.
In a graph with outlier detection, the expected range of values is shown as a gray band. If the metric's actual value goes beyond this band, it is shown as red during that time.
Outlier detection algorithms account for the seasonality and trend changes of metrics. The seasonality changes could be hourly, daily, or weekly, as shown in the following examples.

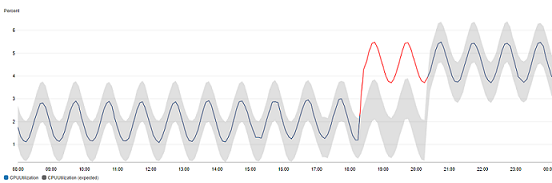
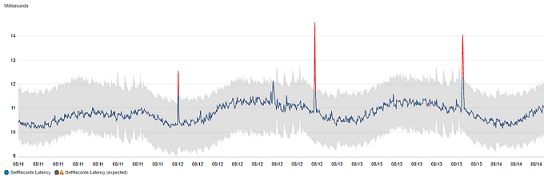
The longer-range trends could be downward or upward.
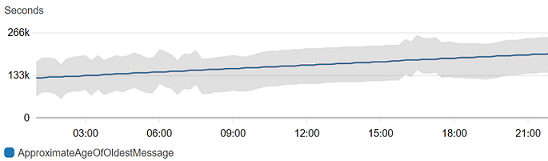
Outlier detection also works well with metrics with flat patterns.

How CloudWatch outlier detection works
When you enable outlier detection for a metric, CloudWatch applies machine learning algorithms to the metric's past data to create a model of the metric's expected values. The model assesses both trends and hourly, daily, and weekly patterns of the metric. The algorithm trains on up to two weeks of metric data, but you can enable outlier detection on a metric even if the metric does not have a full two weeks of data.
You specify a value for the outlier detection threshold that CloudWatch uses along with the model to determine the "normal" range of values for the metric. A higher value for the outlier detection threshold produces a thicker band of "normal" values.
The machine learning model is specific to a metric and a statistic. For example, if you
enable outlier detection for a metric using the AVG statistic, the model is
specific to the AVG statistic.
When CloudWatch creates a model for many common metrics from AWS services, it ensures that the band doesn’t
extend outside of logical values. For example, the band for MemoryUtilization of an EC2 instance will stay between 0 and 100, and the bands
tracking CloudFront Requests, which can't be negative, will never extend below zero.
After you create a model, CloudWatch outlier detection continually evaluates the model and makes adjustments to it to ensure that it is as accurate as possible. This includes re-training the model to adjust if the metric values evolve over time or have sudden changes, and also includes predictors to improve the models of metrics that are seasonal, spiky, or sparse.
After you enable outlier detection on a metric, you can choose to exclude specified time periods of the metric from being used to train the model. This way, you can exclude deployments or other unusual events from being used for model training, ensuring the most accurate model is created.
Using outlier detection models for alarms incurs charges on your AWS account. For more information, see Amazon CloudWatch
Pricing
Outlier detection on metric math
Outlier detection on metric math is a feature that you can use to create outlier detection alarms on the output metric math expressions. You can use these expressions to create graphs that visualize outlier detection bands. The feature supports basic arithmetic functions, comparison and logical operators, and most other functions. For information about functions that are not supported, see Using metric math in the Amazon CloudWatch User Guide.
You can create outlier detection models based on metric math expressions similar to how you already create outlier detection models. From the CloudWatch console, you can apply outlier detection to metric math expressions and select outlier detection as a threshold type for these expressions.
Note
Outlier detection on metric math only can be enabled and edited in the latest version of the metrics user interface. When you create anomaly detectors based on metric math expressions in the new version of the interface, you can view them in the old version, but not edit them.
For information about how to create, edit, and delete alarms and models for outlier detection and metric math, see the following sections:
You also can create, delete, and discover outlier detection models based on metric math
expressions
using
the CloudWatch API with PutAnomalyDetector, DeleteAnomalyDetector,
and DescribeAnomalyDetectors. For information about these API actions, see the
following sections in the Amazon CloudWatch API Reference.
For information about how outlier detection alarms are priced, see Amazon CloudWatch pricing