Creating a blue/green deployment in Amazon Aurora
RDS copies the blue environment's topology and features to a staging area. If the blue DB instance has read replicas, they are copied as replicas of the green instance. The allocated storage of all green replicas matches the green primary instance, while other storage parameters are inherited from the blue replicas.
When you create a blue/green deployment, you specify the DB cluster to copy in the deployment. The DB cluster you choose is the production DB cluster, and it becomes the DB cluster in the blue environment. RDS copies the blue environment's topology to a staging area, along with its configured features. The DB cluster is copied to the green environment, and RDS configures replication from the DB cluster in the blue environment to the DB cluster in the green environment. RDS also copies all of the DB instances in the DB cluster.
Topics
Preparing for a blue/green deployment
There are certain steps you must take before you create a blue/green deployment, depending on the engine that your Aurora DB cluster is running.
Topics
Preparing an Aurora MySQL DB cluster for a blue/green deployment
Before you create a blue/green deployment for an Aurora MySQL DB cluster, the cluster must be
associated with a custom DB cluster parameter group with binary logging
(binlog_format) turned on. Binary logging is required for replication from
the blue environment to the green environment. While any binlog format works, we recommend
ROW to reduce the risk of replication inconsistencies. For information about
creating a custom DB cluster parameter group and setting parameters, see DB cluster parameter groups for Amazon Aurora DB clusters.
Note
Enabling binary logging increases the number of write disk I/O operations to the DB cluster.
You can monitor IOPS usage with the VolumeWriteIOPs CloudWatch metric.
After you enable binary logging, make sure to reboot the DB cluster so that your changes take effect. Blue/green deployments require that the writer instance be in sync with the DB cluster parameter group, otherwise creation fails. For more information, see Rebooting a DB instance within an Aurora cluster.
In addition, we recommend changing the binary log retention period to a value other than
NULL to prevent binary log files from being purged. For more information, see
Setting and showing binary log configuration.
Preparing an Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster for a blue/green deployment
Before you create a blue/green deployment for an Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster, make sure to do the following.
-
Associate the cluster with a custom DB cluster parameter group that has logical replication (
rds.logical_replication) enabled. Logical replication is required for replication from the blue environment to the green environment.When you enable logical replication, you also need to tune certain cluster parameters, such as
max_replication_slots,max_logical_replication_workers, andmax_worker_processes. For instructions to enable logical replication and tune these parameters, see Setting up logical replication for your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster.In addition, make sure that the
synchronous_commitparameter is set toon.After you configure the required parameters, reboot the DB cluster so that your changes take effect. Blue/green deployments require that the writer instance be in sync with the DB cluster parameter group, otherwise creation fails. For more information, see Rebooting a DB instance within an Aurora cluster.
-
Confirm that your DB cluster is running a version of Aurora PostgreSQL that's compatible with Blue/Green Deployments. For a list of compatible versions, see Blue/Green Deployments with Aurora PostgreSQL.
-
Make sure that all tables in the DB cluster have a primary key. PostgreSQL logical replication doesn't allow UPDATE or DELETE operations on tables that don't have a primary key.
Preparing an Aurora Global Database DB cluster for a blue/green deployment
Before creating a blue/green deployment for your Aurora Global Database DB cluster, note the following points:
-
All operations must be initiated from the same Region as the writer cluster of the Global Database.
-
Parameter group configuration:
-
The Green environment uses either a new parameter group you specify or the same parameter group as the blue cluster (default).
-
Custom parameter groups are copied to the green environment.
-
If a specified parameter group doesn't exist in the secondary region, the default parameter group in the secondary region is used for the green environment.
-
Specifying changes when creating a blue/green deployment
You can make the following changes to the DB cluster in the green environment when you create the blue/green deployment.
You can make other modifications to the DB cluster and its DB instances in the green environment after it is deployed. For example, you might specify a higher engine version or a different parameter group.
For information about modifying a DB cluster, see Modifying an Amazon Aurora DB cluster.
Specify a higher engine version
You can specify a higher engine version if you want to test a DB engine upgrade. Upon switchover, the database is upgraded to the major or minor DB engine version that you specify.
Specify a different DB parameter group
Specify a DB cluster parameter group that is different from the one used by the DB cluster. You can test how parameter changes affect the DB cluster in the green environment or specify a parameter group for a new major DB engine version in the case of an upgrade.
If you specify a different DB cluster parameter group, the specified parameter group is associated with the DB cluster in the green environment. If you don't specify a different DB cluster parameter group, the DB cluster in the green environment is associated with the same parameter group as the blue DB cluster.
Creating a blue/green deployment
You can create a blue/green deployment using the AWS Management Console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API.
To create a blue/green deployment
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Databases, and then choose the DB cluster that you want to copy to a green environment.
-
Choose Actions, Create blue/green deployment.
The Create blue/green deployment page appears.
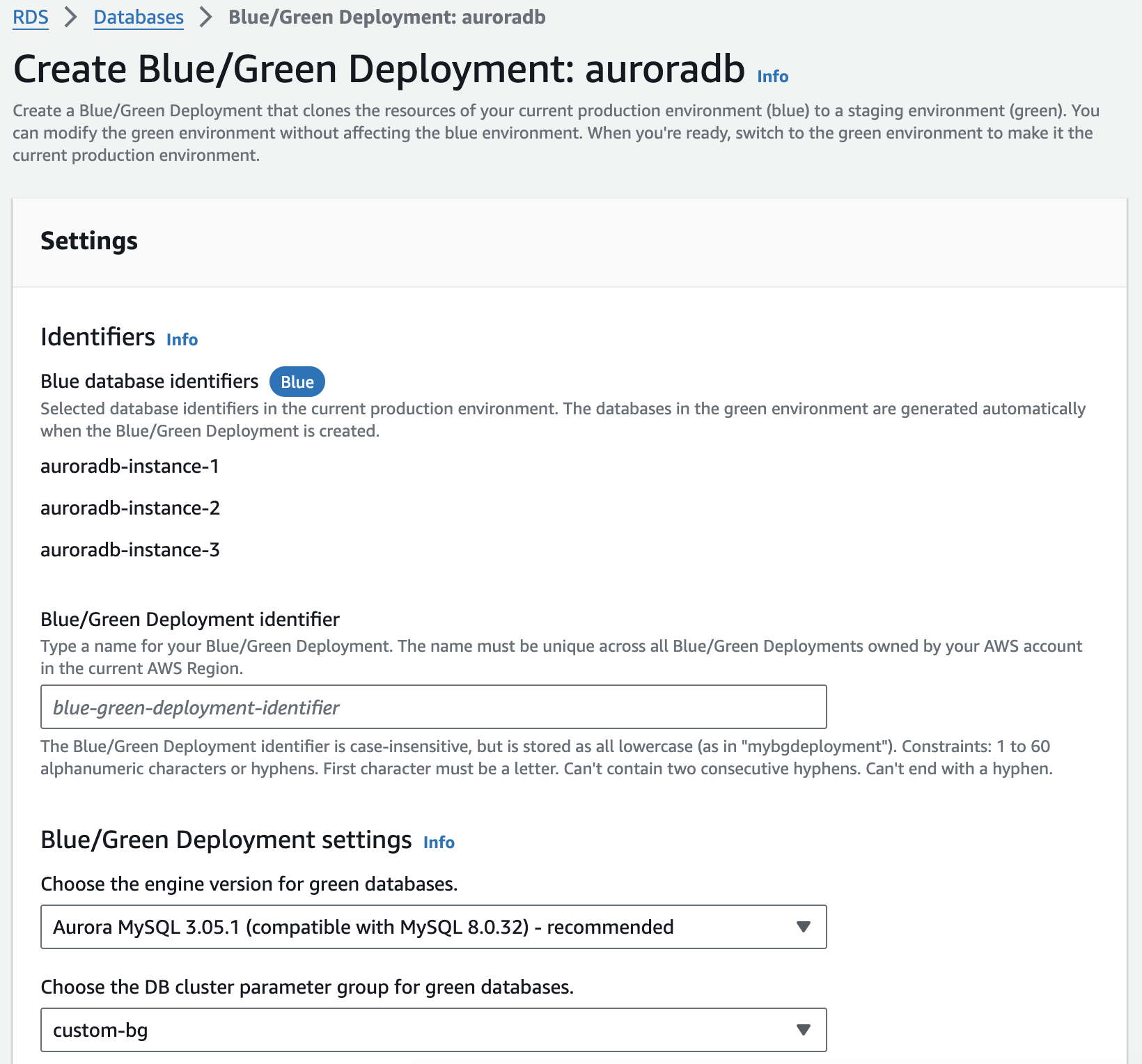
-
Review the blue database identifiers. Make sure that they match the DB instances that you expect in the blue environment. If they don't, choose Cancel.
-
For Blue/green deployment name, enter a name for your blue/green deployment.
-
In the remaining sections, specify the settings for the green environment. For information about each setting, see Settings for creating blue/green deployments.
You can make other modifications to the databases in the green environment after it is deployed.
-
Choose Create.
To create a blue/green deployment using the AWS CLI, use the create-blue-green-deployment command. For information about all available options, see Settings for creating blue/green deployments.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-blue-green-deployment \ --blue-green-deployment-nameaurora-blue-green-deployment\ --source arn:aws:rds:us-east-2:123456789012:cluster:auroradb\ --target-engine-version8.0\ --target-db-cluster-parameter-group-namemydbclusterparametergroup
For Windows:
aws rds create-blue-green-deployment ^ --blue-green-deployment-nameaurora-blue-green-deployment^ --source arn:aws:rds:us-east-2:123456789012:cluster:auroradb^ --target-engine-version8.0^ --target-db-cluster-parameter-group-namemydbclusterparametergroup
To create a blue/green deployment by using the Amazon RDS API, use the CreateBlueGreenDeployment operation. For information about each
option, see Settings for creating blue/green
deployments.
Settings for creating blue/green deployments
The following table explains the settings that you can choose when you create a blue/green deployment. For more information about the AWS CLI options, see create-blue-green-deployment. For more information about the RDS API parameters, see CreateBlueGreenDeployment.
| Console setting | Setting description | CLI option and RDS API parameter |
|---|---|---|
|
Blue/Green Deployment identifier |
A name for the blue/green deployment. |
CLI option:
API parameter:
|
| Blue database identifier |
The identifier of the cluster that you want to copy to the green environment. When using the CLI or API, specify the cluster Amazon Resource Name (ARN). |
CLI option:
API parameter:
|
| DB cluster parameter group for green databases | A parameter group to associate with the databases in the green environment. |
CLI option:
API parameter:
|
|
Engine version for green databases |
Upgrade the cluster in the green environment to the specified DB engine version. If you choose an Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster, review and acknowledge the logical replication limitations. For more information, see Logical replication-specific limitations for blue/green deployments. |
CLI option:
RDS API parameter:
|