Query Apache logs stored in Amazon S3
You can use Amazon Athena to query Apache HTTP Server log files
Fields in the common log format include the client IP address, client ID, user ID, request received timestamp, text of the client request, server status code, and size of the object returned to the client.
The following example data shows the Apache common log format.
198.51.100.7 - Li [10/Oct/2019:13:55:36 -0700] "GET /logo.gif HTTP/1.0" 200 232 198.51.100.14 - Jorge [24/Nov/2019:10:49:52 -0700] "GET /index.html HTTP/1.1" 200 2165 198.51.100.22 - Mateo [27/Dec/2019:11:38:12 -0700] "GET /about.html HTTP/1.1" 200 1287 198.51.100.9 - Nikki [11/Jan/2020:11:40:11 -0700] "GET /image.png HTTP/1.1" 404 230 198.51.100.2 - Ana [15/Feb/2019:10:12:22 -0700] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 30 198.51.100.13 - Saanvi [14/Mar/2019:11:40:33 -0700] "GET /intro.html HTTP/1.1" 200 1608 198.51.100.11 - Xiulan [22/Apr/2019:10:51:34 -0700] "GET /group/index.html HTTP/1.1" 200 1344
Create a table in Athena for Apache logs
Before you can query Apache logs stored in Amazon S3, you must create a table schema for Athena so that it can read the log data. To create an Athena table for Apache logs, you can use the Grok SerDe. For more information about using the Grok SerDe, see Writing grok custom classifiers in the AWS Glue Developer Guide.
To create a table in Athena for Apache web server logs
Open the Athena console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/athena/
. -
Paste the following DDL statement into the Athena Query Editor. Modify the values in
LOCATION 's3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/to point to your Apache logs in Amazon S3.apache-log-folder/'CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE apache_logs ( client_ip string, client_id string, user_id string, request_received_time string, client_request string, server_status string, returned_obj_size string ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'com.amazonaws.glue.serde.GrokSerDe' WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ( 'input.format'='^%{IPV4:client_ip} %{DATA:client_id} %{USERNAME:user_id} %{GREEDYDATA:request_received_time} %{QUOTEDSTRING:client_request} %{DATA:server_status} %{DATA: returned_obj_size}$' ) STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat' OUTPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat' LOCATION 's3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/apache-log-folder/'; -
Run the query in the Athena console to register the
apache_logstable. When the query completes, the logs are ready for you to query from Athena.
Example queries
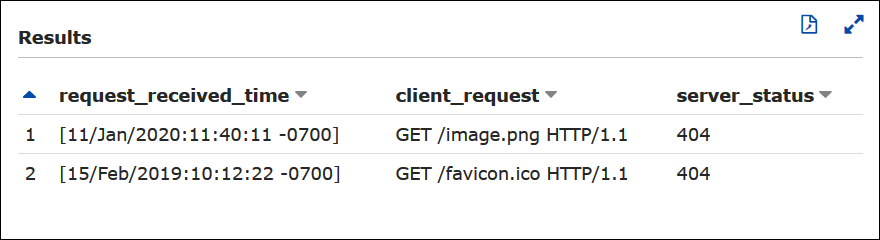
Example – Filter for 404 errors
The following example query selects the request received time, text of the
client request, and server status code from the apache_logs table.
The WHERE clause filters for HTTP status code 404
(page not found).
SELECT request_received_time, client_request, server_status FROM apache_logs WHERE server_status = '404'
The following image shows the results of the query in the Athena Query Editor.
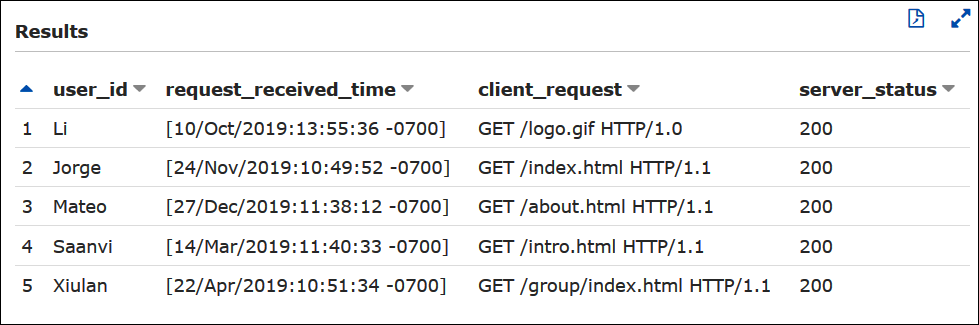
Example – Filter for successful requests
The following example query selects the user ID, request received time, text
of the client request, and server status code from the apache_logs
table. The WHERE clause filters for HTTP status code
200 (successful).
SELECT user_id, request_received_time, client_request, server_status FROM apache_logs WHERE server_status = '200'
The following image shows the results of the query in the Athena Query Editor.
Example – Filter by timestamp
The following example queries for records whose request received time is greater than the specified timestamp.
SELECT * FROM apache_logs WHERE request_received_time > 10/Oct/2023:00:00:00