Troubleshoot SAML with Amazon Connect
This article explains how to troubleshoot and resolve some of the most common issues customers encounter when using SAML with Amazon Connect.
If you're troubleshooting your integration with other identity providers such as Okta, PingIdentify, Azure AD, and more, see
Amazon Connect SSO Setup Workshop
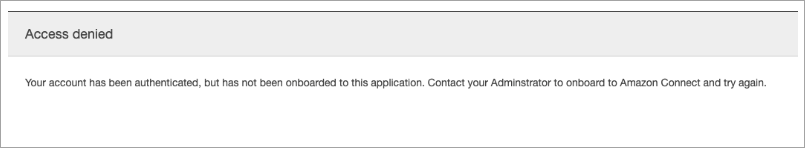
Error Message: Access Denied. Your account has been authenticated, but has not been onboarded to this application.
What does this mean?
This error means that the user has successfully authenticated using SAML into the AWS SAML login endpoint. However, the user could not be matched/found inside Amazon Connect. This usually indicates one of the following:
-
The username in Amazon Connect doesn't match the
RoleSessionNameSAML attribute specified in the SAML response returned by the identity provider. -
The user doesn't exist in Amazon Connect.
-
The user has two separate profiles assigned to them with SSO.
Resolution
Use the following steps to check the RoleSessionName SAML attribute specified in the SAML response returned by the identity provider, and then retrieve and compare with the login name in Amazon Connect.
-
Perform a HAR capture (HTTP ARchive) for the end-to-end login process. This captures the network requests from the browser side. Save the HAR file with your preferred file name, for example, saml.har.
For instructions, see How do I create a HAR file from my browser for an AWS Support case?
-
Use a text editor to find the SAMLResponse in the HAR file. Or, run the following commands:
$ grep -o "SAMLResponse=.*&" azuresaml.har | sed -E 's/SAMLResponse=(.*)&/\1/' > samlresponse.txt-
This searches for the SAMLresponse in the HAR file and saves it to a samlresponse.txt file.
-
The response is URL encoded and the contents are Base64 encoded.
-
-
Decode the URL response and then decode the Base64 contents using a third-party tool or a simple script. For example:
$ cat samlresponse.txt | python3 -c "import sys; from urllib.parse import unquote; print(unquote(sys.stdin.read()));" | base64 --decode > samlresponsedecoded.txtThis script uses a simple python command to decode the SAMLResponse from its original URL encoded format. Then it decodes the response from Base64 and outputs the SAML Response in plain text format.
-
Check the decoded response for the needed attribute. For example, the following image shows how to check
RoleSessionName:
-
Check whether the username returned in from the previous step exists as a user in your Amazon Connect instance:
$ aws connect list-users --instance-id [INSTANCE_ID] | grep $username
-
If the final grep does not return a result then this means that the user does not exist in your Amazon Connect instance or it has been created with a different case/capitalization.
-
If your Amazon Connect instance has many users, the response from the ListUsers API call maybe paginated. Use the
NextTokenreturned by the API to fetch the rest of the users. For more information, see ListUsers.
-
Example SAML Response
Following is an image from a sample SAML Response. In this case, the identity provider (IdP) is Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).

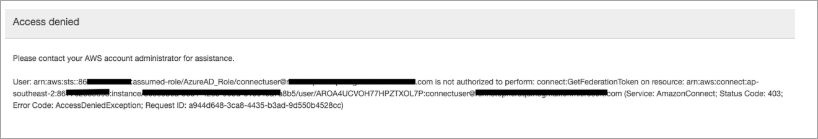
Error Message: Access denied, Please contact your AWS account administrator for assistance.
What does this mean?
The role that the user has assumed has successfully authenticated using SAML. However, the role doesn't have permission to call the GetFederationToken API for Amazon Connect. This call is required so the user can log in to your Amazon Connect instance using SAML.
Resolution
-
Attach a policy that has the permissions for
connect:GetFederationTokento the role found in the error message. Following is a sample policy: -
Use the IAM console to attach the policy. Or, use the attach-role-policy API, for example:
$ aws iam attach-role-policy —role-name [ASSUMED_ROLE] —policy_arn [POLICY_WITH_GETFEDERATIONTOKEN]
Error Message: Session Expired
If you see the Session expired message while logging in, you probably just need to refresh the session token. Go to your identity provider and log in. Refresh the Amazon Connect page. If you still get this message, contact your IT team.