Step 1: Set up your environment for trusts
In this section, you set up your Amazon EC2 environment, deploy your new forest, and prepare your VPC for trusts with AWS.
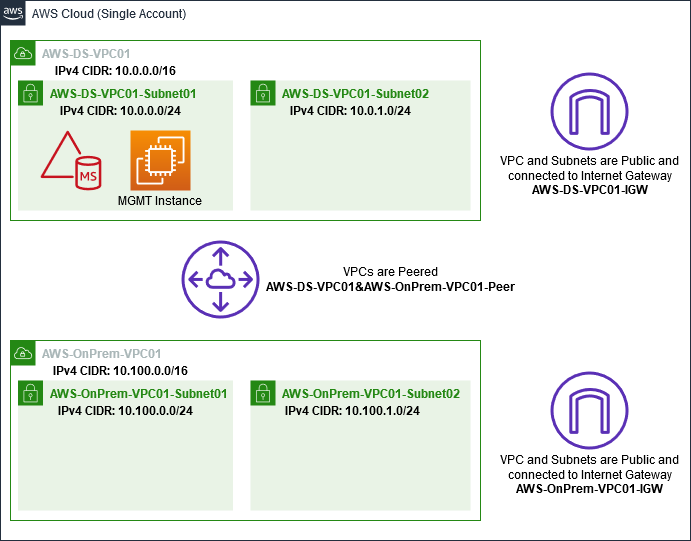
Create a Windows Server 2019 EC2 instance
Use the following procedure to create a Windows Server 2019 member server in Amazon EC2.
To create a Windows Server 2019 EC2 instance
Open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/
. -
In the Amazon EC2 console, choose Launch Instance.
-
On the Step 1 page, locate Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Base - ami-
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxin the list. Then choose Select. -
On the Step 2 page, select t2.large, and then choose Next: Configure Instance Details.
-
On the Step 3 page, do the following:
-
For Network, select vpc-
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxAWS-OnPrem-VPC01 (which you previously set up in the Base tutorial). -
For Subnet, select subnet-
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx| AWS-OnPrem-VPC01-Subnet01 | AWS-OnPrem-VPC01. -
For Auto-assign Public IP list, choose Enable (if the subnet setting is not set to Enable by default).
-
Leave the rest of the settings at their defaults.
-
Choose Next: Add Storage.
-
-
On the Step 4 page, leave the default settings, and then choose Next: Add Tags.
-
On the Step 5 page, choose Add Tag. Under Key type
example.local-DC01, and then choose Next: Configure Security Group. -
On the Step 6 page, choose Select an existing security group, select AWS On-Prem Test Lab Security Group (which you previously set up in the Base tutorial), and then choose Review and Launch to review your instance.
-
On the Step 7 page, review the page, and then choose Launch.
-
On the Select an existing key pair or create a new key pair dialog box, do the following:
-
Choose Choose an existing key pair.
-
Under Select a key pair, choose AWS-DS-KP (which you previously set up in the Base tutorial).
-
Select the I acknowledge... check box.
-
Choose Launch Instances.
-
-
Choose View Instances to return to the Amazon EC2 console and view the status of the deployment.
Promote your server to a domain controller
Before you can create trusts, you must build and deploy the first domain controller for a new forest. During this process you configure a new Active Directory forest, install DNS, and set this server to use the local DNS server for name resolution. You must reboot the server at the end of this procedure.
Note
If you want to create a domain controller in AWS that replicates with your on-premises network, you would first manually join the EC2 instance to your on-premises domain. After that you can promote the server to a domain controller.
To promote your server to a domain controller
-
In the Amazon EC2 console, choose Instances, select the instance you just created, and then choose Connect.
-
In the Connect To Your Instance dialog box, choose Download Remote Desktop File.
-
In the Windows Security dialog box, type your local administrator credentials for the Windows Server computer to login (for example,
administrator). If you do not yet have the local administrator password, go back to the Amazon EC2 console, right-click on the instance, and choose Get Windows Password. Navigate to yourAWS DS KP.pemfile or your personal.pemkey, and then choose Decrypt Password. -
From the Start menu, choose Server Manager.
-
In the Dashboard, choose Add Roles and Features.
-
In the Add Roles and Features Wizard, choose Next.
-
On the Select installation type page, choose Role-based or feature-based installation, and then choose Next.
-
On the Select destination server page, make sure that the local server is selected, and then choose Next.
-
On the Select server roles page, select Active Directory Domain Services. In the Add Roles and Features Wizard dialog box, verify that the Include management tools (if applicable) check box is selected. Choose Add Features, and then choose Next.
-
On the Select features page, choose Next.
-
On the Active Directory Domain Services page, choose Next.
-
On the Confirm installation selections page, choose Install.
-
Once the Active Directory binaries are installed, choose Close.
-
When Server Manager opens, look for a flag at the top next to the word Manage. When this flag turns yellow, the server is ready to be promoted.
-
Choose the yellow flag, and then choose Promote this server to a domain controller.
-
On the Deployment Configuration page, choose Add a new forest. In Root domain name, type
example.local, and then choose Next. -
On the Domain Controller Options page, do the following:
-
In both Forest functional level and Domain functional level, choose Windows Server 2016.
-
Under Specify domain controller capabilities, verify that both DNS server and Global Catalog (GC) are selected.
-
Type and then confirm a Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) password. Then choose Next.
-
-
On the DNS Options page, ignore the warning about delegation and choose Next.
-
On the Additional options page, make sure that EXAMPLE is listed as the NetBios domain name.
-
On the Paths page, leave the defaults, and then choose Next.
-
On Review Options page, choose Next. The server now checks to make sure all the prerequisites for the domain controller are satisfied. You may see some warnings displayed, but you can safely ignore them.
-
Choose Install. Once the installation is complete, the server reboots and then becomes a functional domain controller.
Configure your VPC
The following three procedures guide you through the steps to configure your VPC for connectivity with AWS.
To configure your VPC outbound rules
-
In the AWS Directory Service console
, make a note of the AWS Managed Microsoft AD directory ID for corp.example.com that you previously created in the Base tutorial. Open the Amazon VPC console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Security Groups.
-
Search for your AWS Managed Microsoft AD directory ID. In the search results, select the item with the description AWS created security group for d-
xxxxxxdirectory controllers.Note
This security group was automatically created when you initially created your directory.
-
Choose the Outbound Rules tab under that security group. Choose Edit, choose Add another rule, and then add the following values:
-
For Type, choose All Traffic.
-
For Destination, type
0.0.0.0/0. -
Leave the rest of the settings at their defaults.
-
Select Save.
-
To verify kerberos preauthentication is enabled
-
On the example.local domain controller, open Server Manager.
-
On the Tools menu, choose Active Directory Users and Computers.
-
Navigate to the Users directory, right-click on any user and select Properties, and then choose the Account tab. In the Account options list, scroll down and ensure that Do not require Kerberos preauthentication is not selected.
-
Perform the same steps for the corp.example.com domain from the corp.example.com-mgmt instance.
To configure DNS conditional forwarders
Note
A conditional forwarder is a DNS server on a network that is used to forward DNS queries according to the DNS domain name in the query. For example, a DNS server can be configured to forward all the queries it receives for names ending with widgets.example.com to the IP address of a specific DNS server or to the IP addresses of multiple DNS servers.
-
Open the AWS Directory Service console
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Directories.
-
Select the directory ID of your AWS Managed Microsoft AD.
-
Take note of the fully qualified domain name (FQDN), corp.example.com, and the DNS addresses of your directory.
-
Now, return to your example.local domain controller, and then open Server Manager.
-
On the Tools menu, choose DNS.
-
In the console tree, expand the DNS server of the domain for which you are setting up the trust, and navigate to Conditional Forwarders.
-
Right-click Conditional Forwarders, and then choose New Conditional Forwarder.
-
In DNS domain, type
corp.example.com. -
Under IP addresses of the primary servers, choose <Click here to add ...>, type the first DNS address of your AWS Managed Microsoft AD directory (which you made note of in the previous procedure), and then press Enter. Do the same for the second DNS address. After typing the DNS addresses, you might get a "timeout" or "unable to resolve" error. You can generally ignore these errors.
-
Select the Store this conditional forwarder in Active Directory, and replicate as follows check box. In the drop-down menu, choose All DNS servers in this Forest, and then choose OK.