Monitoring
Prometheus, a graduated CNCF project
The high level architecture of Prometheus metrics collection is shown below:
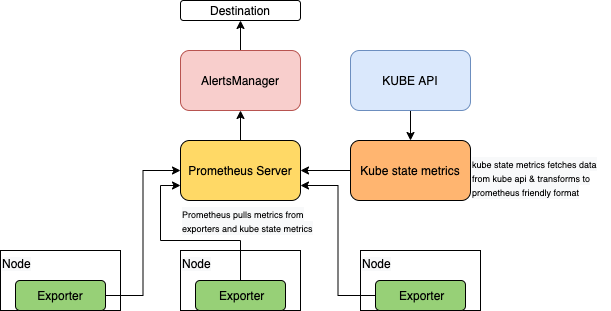
Prometheus uses a pull mechanism and scrapes metrics from targets using exporters and from the Kubernetes API using the kube state metrics
An exporter lets you consume third party metrics as Prometheus formatted metrics. A Prometheus exporter is typically deployed on each node. For a complete list of exporters please refer to the Prometheus exporters
In a mixed node EKS cluster with Windows nodes when you use the stable Prometheus helm chart
In order to setup Prometheus monitoring for Windows nodes, you need to download and install the WMI exporter on the Windows server itself and then setup the targets inside the scrape configuration of the Prometheus configuration file.
The releases page
You can check out the scheduling best practices section of this guide which suggests the use of taints/tolerations or RuntimeClass to selectively deploy node exporter only to linux nodes, while the Windows exporter is installed on Windows nodes as you bootstrap the node or using a configuration management tool of your choice (example chef, Ansible, SSM etc).
Note that, unlike the linux nodes where the node exporter is installed as a daemonset , on Windows nodes the WMI exporter is installed on the host itself. The exporter will export metrics such as the CPU usage, the memory and the disk I/O usage and can also be used to monitor IIS sites and applications, the network interfaces and services.
The windows_exporter will expose all metrics from enabled collectors by default. This is the recommended way to collect metrics to avoid errors. However, for advanced use the windows_exporter can be passed an optional list of collectors to filter metrics. The collect[] parameter, in the Prometheus configuration lets you do that.
The default install steps for Windows include downloading and starting the exporter as a service during the bootstrapping process with arguments, such as the collectors you want to filter.
> Powershell Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/prometheus-community/windows_exporter/releases/download/v0.13.0/windows_exporter-0.13.0-amd64.msi -OutFile <DOWNLOADPATH> > msiexec /i <DOWNLOADPATH> ENABLED_COLLECTORS="cpu,cs,logical_disk,net,os,system,container,memory"
By default, the metrics can be scraped at the /metrics endpoint on port 9182. At this point, Prometheus can consume the metrics by adding the following scrape_config to the Prometheus configuration
scrape_configs: - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090'] ... - job_name: "wmi_exporter" scrape_interval: 10s static_configs: - targets: ['<windows-node1-ip>:9182', '<windows-node2-ip>:9182', ...]
Prometheus configuration is reloaded using
> ps aux | grep prometheus > kill HUP <PID>
A better and recommended way to add targets is to use a Custom Resource Definition called ServiceMonitor, which comes as part of the Prometheus operator
The ServiceMonitor, which declaratively specifies how groups of Kubernetes services should be monitored, is used to define an application you wish to scrape metrics from within Kubernetes. Within the ServiceMonitor we specify the Kubernetes labels that the operator can use to identify the Kubernetes Service which in turn identifies the Pods, that we wish to monitor.
In order to leverage the ServiceMonitor, create an Endpoint object pointing to specific Windows targets, a headless service and a ServiceMontor for the Windows nodes.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Endpoints metadata: labels: k8s-app: wmiexporter name: wmiexporter namespace: kube-system subsets: - addresses: - ip: NODE-ONE-IP targetRef: kind: Node name: NODE-ONE-NAME - ip: NODE-TWO-IP targetRef: kind: Node name: NODE-TWO-NAME - ip: NODE-THREE-IP targetRef: kind: Node name: NODE-THREE-NAME ports: - name: http-metrics port: 9182 protocol: TCP --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service ##Headless Service metadata: labels: k8s-app: wmiexporter name: wmiexporter namespace: kube-system spec: clusterIP: None ports: - name: http-metrics port: 9182 protocol: TCP targetPort: 9182 sessionAffinity: None type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1 kind: ServiceMonitor ##Custom ServiceMonitor Object metadata: labels: k8s-app: wmiexporter name: wmiexporter namespace: monitoring spec: endpoints: - interval: 30s port: http-metrics jobLabel: k8s-app namespaceSelector: matchNames: - kube-system selector: matchLabels: k8s-app: wmiexporter
For more details on the operator and the usage of ServiceMonitor, checkout the official operator