Managing a Multi-AZ deployment for RDS Custom for Oracle
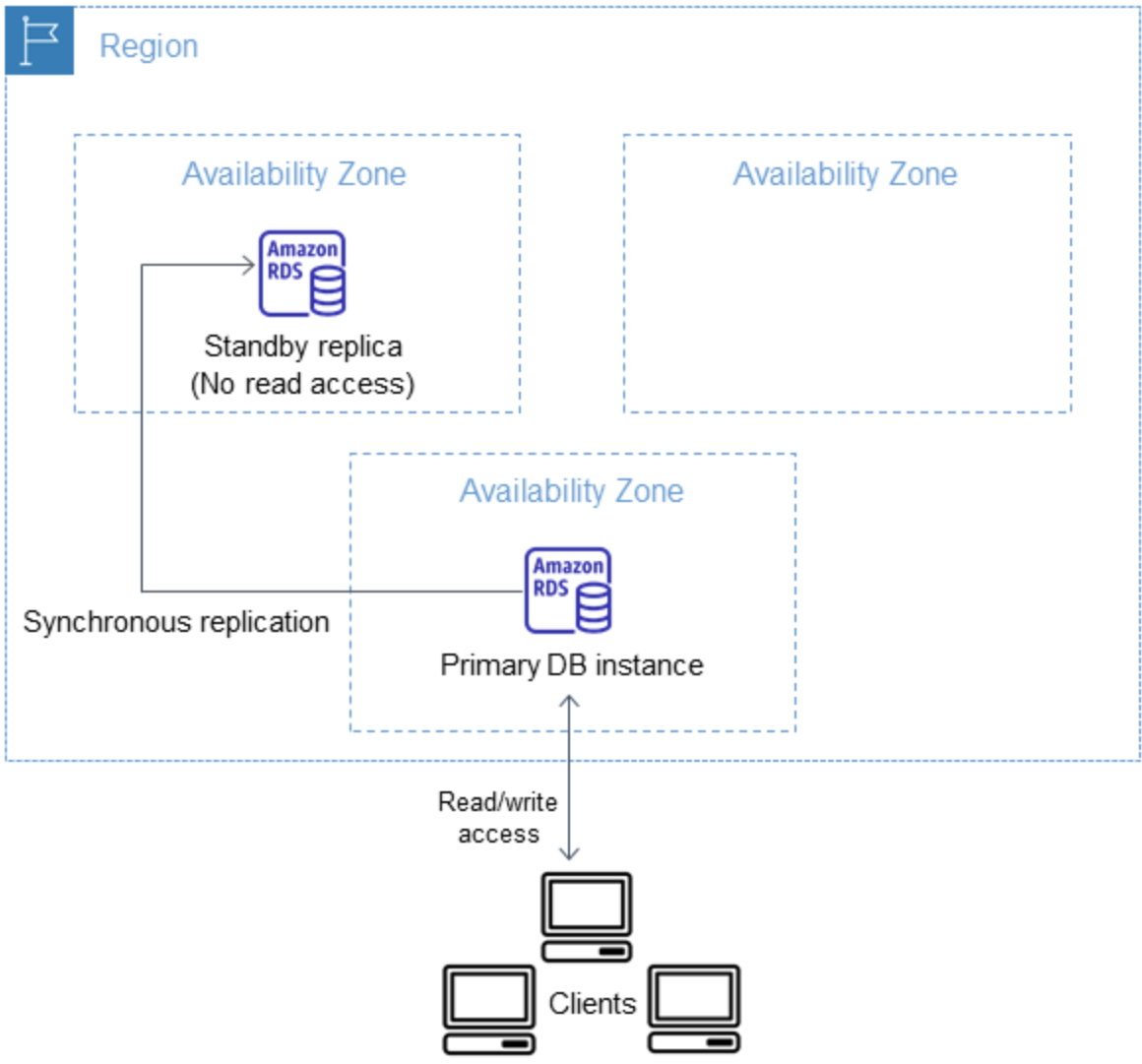
In a Multi-AZ DB instance deployment for RDS Custom for Oracle, Amazon RDS automatically provisions and maintains a synchronous standby replica in a different Availability Zone (AZ). The primary DB instance is synchronously replicated across Availability Zones to a standby replica to provide data redundancy.
A Multi-AZ DB instance deployment enhances availability during planned system maintenance. If planned database maintenance or unplanned service disruption occurs, Amazon RDS automatically fails over to the up-to-date standby DB instance. Database operations can resume quickly without manual intervention. The primary and standby instances use the same endpoint, whose physical network address transitions to the standby replica as part of the failover process. You don't need to reconfigure your application when a failover occurs.
The following diagram shows the Multi-AZ architecture for RDS Custom for Oracle:
The Amazon RDS console shows the Availability Zone of the standby replica (the secondary AZ).
You can also use the describe-db-instances CLI command or the
DescribeDBInstances API operation to find the secondary AZ.
Region and version availability for a Multi-AZ deployment for RDS Custom for Oracle
Multi-AZ deployments for RDS Custom for Oracle are supported for the following releases for both Enterprise Edition (EE) and Standard Edition 2 (SE2):
-
Oracle Database 19c
-
Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2)
-
Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1)
Note
Multi-AZ deployments for RDS Custom for Oracle aren't supported on Oracle Database 18c.
Multi-AZ deployments for RDS Custom for Oracle are available in all Regions where RDS Custom for Oracle is available. For more information on Region availability of Multi-AZ deployments for RDS Custom for Oracle, see Supported Regions and DB engines for RDS Custom for Oracle.
Limitations for a Multi-AZ deployment in RDS Custom for Oracle
Multi-AZ deployments with RDS Custom for Oracle have the following limitations:
-
If your DB instance was created before June 30, 2025, you can't convert from a Single-AZ to Multi-AZ deployment. Your underlying Custom Engine Version (CEV) was built with an older service-provided AMI that lacks Multi-AZ support. You must migrate your database to a new DB instance using a CEV that you create with a service-provided AMI after June 30, 2025. For details, see Migration steps for DB instances using CEVs created before June 30, 2025.
-
You can't create cross-Region Multi-AZ deployments.
-
You can't configure the standby DB instance to accept database read activity.
-
When you use a Custom Engine Version (CEV) with a Multi-AZ deployment, your standby DB instance uses the same CEV. The standby DB instance can't use a different CEV.
-
You can't create a read replica on a Multi-AZ deployment instance and you also cannot modify the primary instance of the read replica to have a Multi-AZ deployment.
-
RDS Custom for Oracle DB instances with Multi-AZ deployment can have increased write and commit latency compared to a Single-AZ deployment. This increase can happen because of the synchronous data replication between DB instances. You might have a change in latency if your deployment fails over to the standby replica, although AWS is engineered with low-latency network connectivity between Availability Zones.
Creating a Multi-AZ deployment in RDS Custom for Oracle
To create an RDS Custom for Oracle DB instance with a Multi-AZ deployment, follow the steps in Setting up your environment for Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle to set up your environment with the prerequisites.
Important
To simplify setup, we recommend that you use the latest CloudFormation template file provided in the network setup instructions. For more information, see Deploying RDS Custom for Oracle with AWS CloudFormation.
You can create an RDS Custom for Oracle instance with a Multi-AZ deployment by choosing the
Multi-AZ option during the database instance creation in the
Amazon RDS console. Alternatively, you can specify the --multi-az parameter in
the Amazon RDS create-db-instance command in the AWS CLI.