Detect drift on individual stack resources
You can detect drift on specific resources within a stack, rather than the entire stack. This is especially useful when you only need to determine if specific resources now match their expected template configurations again.
When performing drift detection on a resource, CloudFormation also updates the overall
stack drift status and the Last drift check time, if
applicable. For example, suppose a stack has a drift status of
IN_SYNC. You have CloudFormation perform drift detection on one or
more resources contained in that stack, and CloudFormation detects that one or more of those
resources has drifted. CloudFormation updates the stack drift status to
DRIFTED. Conversely, suppose you have a stack with a drift
status of DRIFTED because of a single drifted resource. If you set
that resource back to its expected property values, and then detect drift on the
resource again, CloudFormation will update both resource drift status and stack drift status
to IN_SYNC without requiring you to detect drift on the entire
stack again.
To detect drift on an individual resource using the AWS Management Console
Open the AWS CloudFormation console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation
. -
From the list of stacks, select the stack that contains the resource. CloudFormation displays the stack details for that stack.
-
In the left navigation pane, under Stacks, choose Stack actions, and then choose Detect drift.
-
Under Resource drift status, choose the resource and then select Detect drift for resource.
CloudFormation performs drift detection on the selected resource. If successful, CloudFormation updates the resource's drift status, and the overall stack drift status, if necessary. CloudFormation also updates time stamp for when drift detection was last performed on the resource, and the stack as a whole. If the resource has been modified, CloudFormation displays detailed drift information about the expected and current property values of the resource.
-
Review the drift detection results for the resource.
-
To view the details on a modified resource.
-
With the modified resource selected, select View drift details.
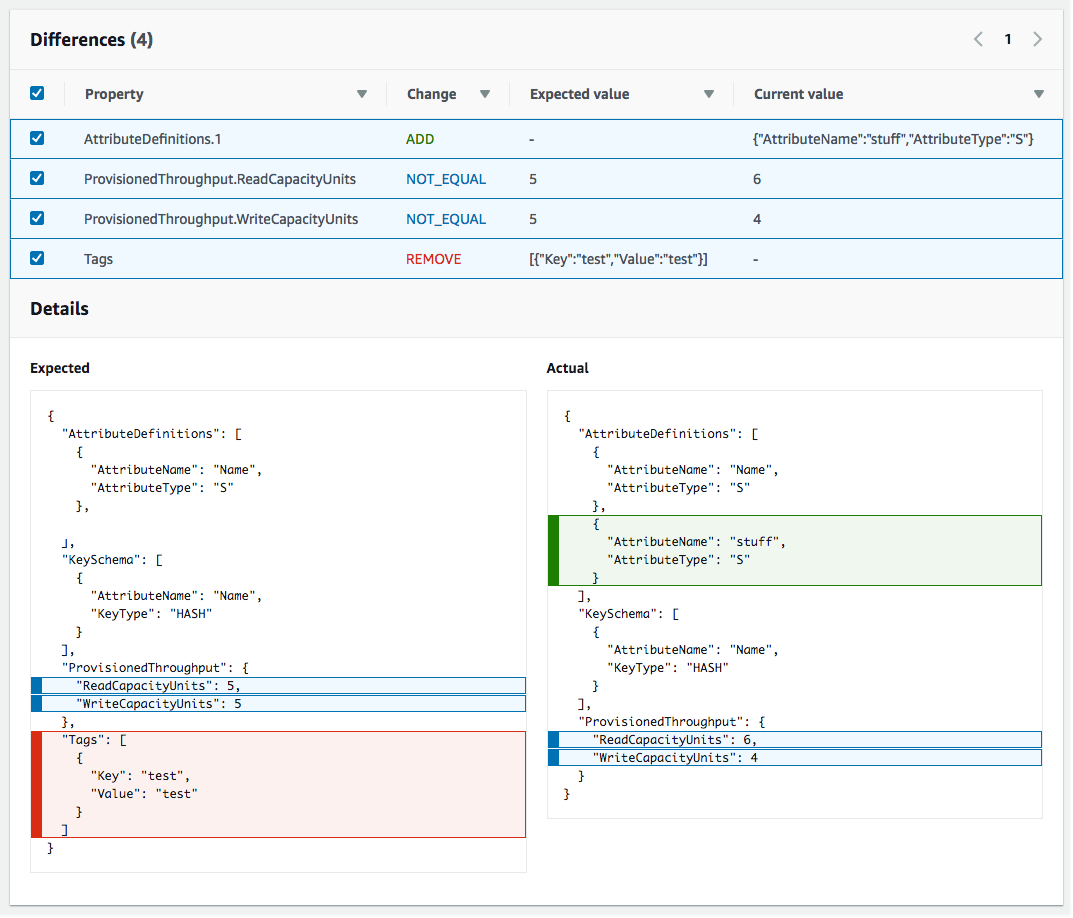
CloudFormation displays the drift details for that resource, including the resource's expected and current property values, and any differences between the two.
To highlight a difference, in the Differences section select the property name.
-
Added properties are highlighted in green in the Current column of the Details section.
-
Deleted properties are highlighted in red in the Expected column of the Details section.
-
Properties whose value have been changed are highlighted in yellow in the both Expected and Current columns.
-
-
-
To detect drift on an individual resource using the AWS CLI
-
Important
Review the Last drift check time for the stack resource and confirm that it's earlier than the timestamp shown in the resource drift results to prevent the use of stale data.
To detect drift on an individual resource using the AWS CLI, use the detect-stack-resource-drift command. Specify the logical ID of the resource and the stack in which it's contained.
The following example runs a drift detection operation on a specific stack resources,
my-drifted-resource. The response returns information that confirms the resource has been modified, including details about two of its properties whose values have been changed.aws cloudformation detect-stack-resource-drift \ --stack-namemy-stack-with-resource-drift\ --logical-resource-idmy-drifted-resourceOutput:
{ "StackResourceDrift": { "StackId": "arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-1:099908667365:stack/my-stack-with-resource-drift/489e5570-df85-11e7-a7d9-50example", "ActualProperties": "{\"ReceiveMessageWaitTimeSeconds\":0,\"DelaySeconds\":120,\"RedrivePolicy\":{\"deadLetterTargetArn\":\"arn:aws:sqs:us-east-1:099908667365:my-stack-with-resource-drift-DLQ-1BCY7HHD5QIM3\",\"maxReceiveCount\":12},\"MessageRetentionPeriod\":345600,\"MaximumMessageSize\":262144,\"VisibilityTimeout\":60,\"QueueName\":\"my-stack-with-resource-drift-Queue-494PBHCO76H4\"}", "ResourceType": "AWS::SQS::Queue", "Timestamp": "2018-03-26T18:54:28.462Z", "PhysicalResourceId": "https://sqs.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/099908667365/my-stack-with-resource-drift-Queue-494PBHCO76H4", "StackResourceDriftStatus": "MODIFIED", "ExpectedProperties": "{\"ReceiveMessageWaitTimeSeconds\":0,\"DelaySeconds\":20,\"RedrivePolicy\":{\"deadLetterTargetArn\":\"arn:aws:sqs:us-east-1:099908667365:my-stack-with-resource-drift-DLQ-1BCY7HHD5QIM3\",\"maxReceiveCount\":10},\"MessageRetentionPeriod\":345600,\"MaximumMessageSize\":262144,\"VisibilityTimeout\":60,\"QueueName\":\"my-stack-with-resource-drift-Queue-494PBHCO76H4\"}", "PropertyDifferences": [ { "PropertyPath": "/DelaySeconds", "ActualValue": "120", "ExpectedValue": "20", "DifferenceType": "NOT_EQUAL" }, { "PropertyPath": "/RedrivePolicy/maxReceiveCount", "ActualValue": "12", "ExpectedValue": "10", "DifferenceType": "NOT_EQUAL" } ], "LogicalResourceId": "my-drifted-resource" } }