Tutorial: Connect an Amazon EC2 instance to an Amazon RDS database
Tutorial objective
The objective of this tutorial is to learn how to configure a secure connection between an Amazon EC2 instance and an Amazon RDS database by using the AWS Management Console.
There are different options for configuring the connection. In this tutorial, we explore the following three options:
-
Option 1: Automatically connect an instance to an RDS database using the EC2 console
Use the automatic connection feature in the EC2 console to automatically configure the connection between your EC2 instance and your RDS database to allow traffic between the EC2 instance and the RDS database.
-
Option 2: Automatically connect an instance to an RDS database using the RDS console
Use the automatic connection feature in the RDS console to automatically configure the connection between your EC2 instance and your RDS database to allow traffic between the EC2 instance and the RDS database.
-
Option 3: Manually connect an instance to an RDS database by creating security groups
Configure the connection between your EC2 instance to your RDS database by manually configuring and assigning the security groups to reproduce the configuration that is automatically created by the automatic connection feature in Option 1 and Option 2.
Context
As context for why you'd want to configure a connection between your EC2 instance and an RDS database, let's consider the following scenario: Your website presents a form to your users to fill in. You need to capture the form data in a database. You can host your website on an EC2 instance that's been configured as a web server, and you can capture the form data in an RDS database. The EC2 instance and the RDS database need to be connected to each other so that the form data can go from the EC2 instance to the RDS database. This tutorial explains how to configure that connection. Note that this is just one example of a use case for connecting an EC2 instance and an RDS database.
Architecture
The following diagram shows the resources that are created and the architectural configuration that results from completing all the steps in this tutorial.
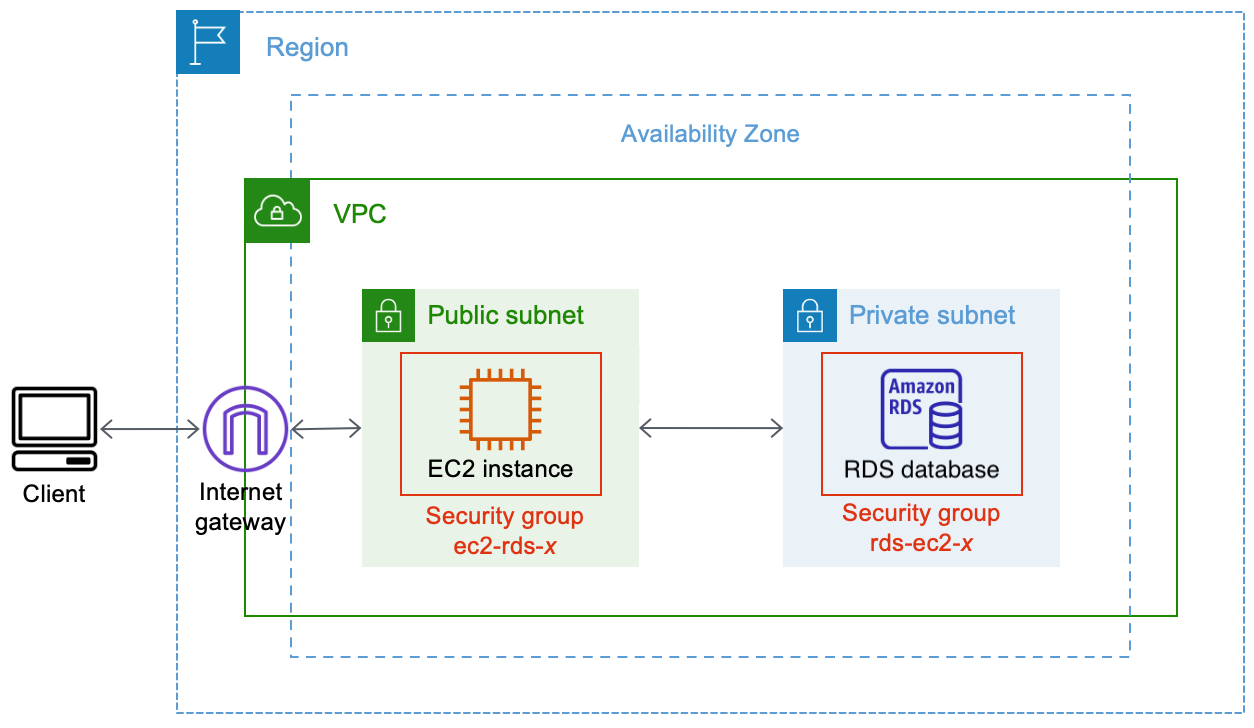
The diagram illustrates the following resources that you'll create:
-
You'll create an EC2 instance and an RDS database in the same AWS Region, VPC, and Availability Zone.
-
You'll create the EC2 instance in a public subnet.
-
You'll create the RDS database in a private subnet.
When you use the RDS console to create the RDS database and automatically connect the EC2 instance, the VPC, DB subnet group, and public access settings for the database are automatically selected. The RDS database is automatically created in a private subnet within the same VPC as the EC2 instance.
-
Internet users can connect to the EC2 instance by using SSH or HTTP/HTTPS via an Internet gateway.
-
Internet users cannot connect directly to the RDS database; only the EC2 instance is connected to the RDS database.
-
When you use the automatic connection feature to allow traffic between the EC2 instance and the RDS database, the following security groups are automatically created and added:
-
Security group ec2-rds-
xis created and added to the EC2 instance. It has one outbound rule that references the rds-ec2-xsecurity group as its destination. This allows traffic from the EC2 instance to reach the RDS database with the rds-ec2-xsecurity group. -
Security group rds-ec2-
xis created and added to the RDS database. It has one inbound rule that references the ec2-rds-xsecurity group as its source. This allows traffic from the EC2 instance with the ec2-rds-xsecurity group to reach the RDS database.
By using separate security groups (one for the EC2 instance, and one for the RDS database), you have better control over the security of the instance and the database. If you were to use the same security group on both the instance and the database, and then modified the security group to suit, say, only the database, the modification would affect both the instance and the database. In other words, if you were to use one security group, you could unintentionally modify the security of a resource (either the instance or the database) because you'd forgotten that the security group was attached to it.
The security groups that are automatically created also respect least privilege as they only allow the mutual connection for this workload on the database port by creating a workload-specific security group pair.
-
Considerations
Consider the following when you complete the tasks in this tutorial:
-
Two consoles – You will use the following two consoles for this tutorial:
-
Amazon EC2 console – You will use the EC2 console to launch instances, to automatically connect an EC2 instance to an RDS database, and for the manual option to configure the connection by creating the security groups.
-
Amazon RDS console – You will use the RDS console to create an RDS database and to automatically connect an EC2 instance to an RDS database.
-
-
One VPC – To use the automatic connection feature, your EC2 instance and your RDS database must be in the same VPC.
If you were to manually configure the connection between your EC2 instance and your RDS database, you could launch your EC2 instance in one VPC and your RDS database in another VPC; however, you’d need to set up additional routing and VPC configuration. This scenario is not covered in this tutorial.
-
One AWS Region – The EC2 instance and RDS database must be located in the same Region.
-
Two security groups – The connectivity between the EC2 instance and the RDS database is configured by two security groups—a security group for your EC2 instance, and a security group for your RDS database.
When you use the automatic connection feature in the EC2 console or RDS console to configure the connectivity (Option 1 and Option 2 of this tutorial), the security groups are automatically created and assigned to the EC2 instance and RDS database.
If you do not use the automatic connection feature, you'll need to manually create and assign the security groups. You do this in Option 3 of this tutorial.
Time to complete the tutorial
30 minutes
You can complete the entire tutorial in one sitting, or you can complete it one task at a time.
Costs
By completing this tutorial, you might incur costs for the AWS resources that you create.
You can use Amazon EC2 under the Free Tier
If your EC2 instance and your RDS database are in different Availability Zones, you will
incur data transfer fees. To avoid incurring these fees, the EC2 instance and the RDS
database must be in the same Availability Zone. For information about data transfer
fees, see Data
Transfer
To prevent incurring costs after you've completed the tutorial, make sure to delete the resources if they are no longer needed. For the steps to delete the resources, see Task 4 (Optional): Clean up.