Use CloudFront continuous deployment to safely test CDN configuration changes
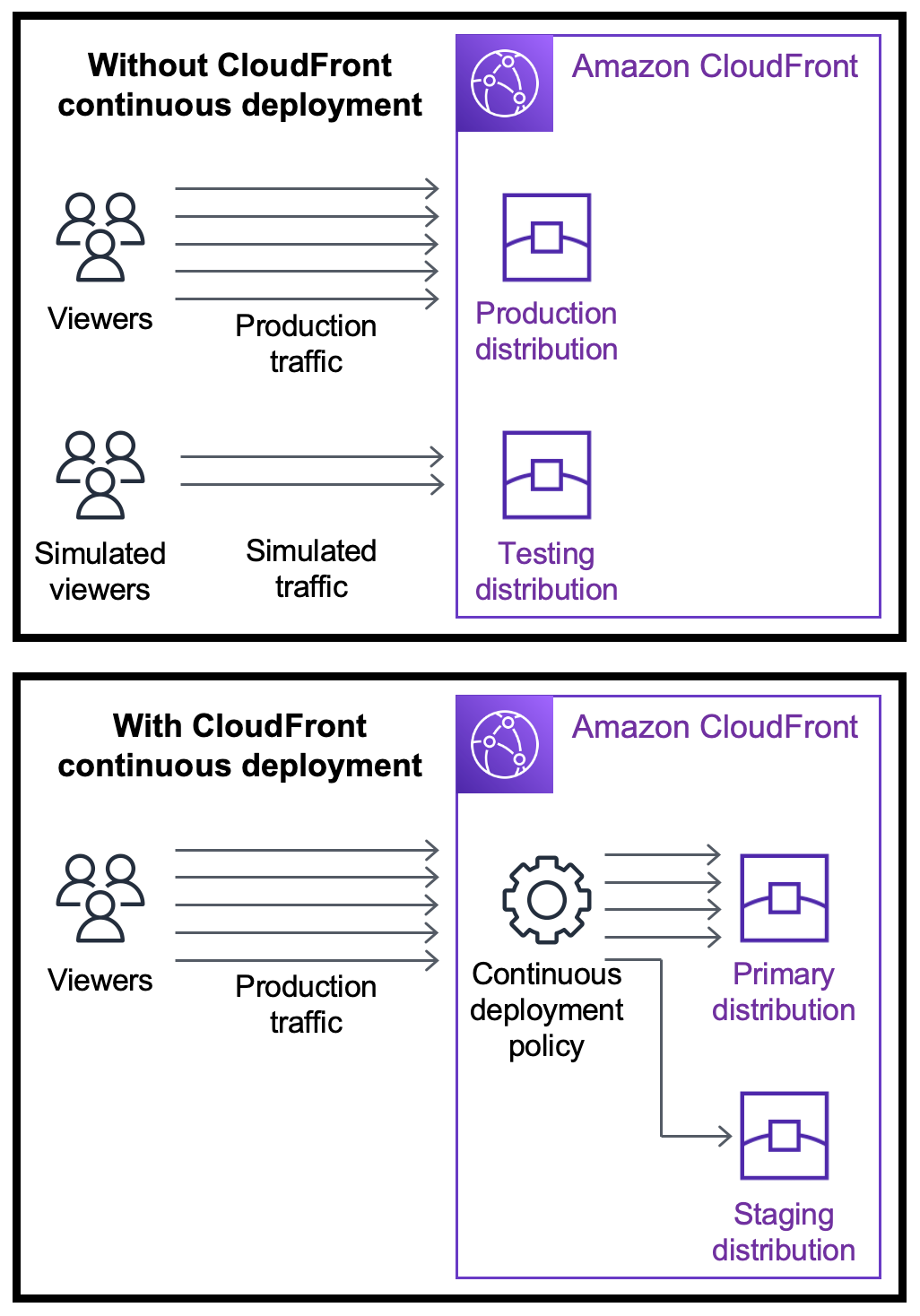
With Amazon CloudFront continuous deployment you can safely deploy changes to your CDN configuration by testing first with a subset of production traffic. You can use a staging distribution and a continuous deployment policy to send some traffic from real (production) viewers to the new CDN configuration and validate that it works as expected. You can monitor the performance of the new configuration in real time, and promote the new configuration to serve all traffic via the primary distribution when you're ready.
The following diagram shows the benefit of using CloudFront continuous deployment. Without it, you would have to test CDN configuration changes with simulated traffic. With continuous deployment you can test the changes with a subset of production traffic, then promote the changes to the primary distribution when you're ready.
Learn more about working with continuous deployment in the following topics.