Create an Amazon ECS blue/green deployment through AWS CloudFormation
You can use AWS CloudFormation to manage Amazon ECS blue/green deployments through CodeDeploy. You generate your deployment by defining your green and blue resources and specifying the traffic routing and stabilization settings to use in AWS CloudFormation. This topic covers the differences between Amazon ECS blue/green deployments that are managed by CodeDeploy and deployments that are managed by AWS CloudFormation.
For step-by-step instructions on using AWS CloudFormation to manage your Amazon ECS blue/green deployments, see Automate ECS blue/green deployments through CodeDeploy using AWS CloudFormation in the AWS CloudFormation User Guide.
Note
Managing Amazon ECS blue/green deployments with AWS CloudFormation is not available in the Asia Pacific (Osaka) region.
Differences between Amazon ECS blue/green deployments through CodeDeploy and AWS CloudFormation
The AWS CloudFormation stack template models Amazon ECS task-related resources and infrastructure, and also the configuration options for deployments. So there are differences between the standard Amazon ECS blue/green deployments and blue/green deployments that are created through AWS CloudFormation.
Unlike standard Amazon ECS blue/green deployments, you don't model or manually create the following:
-
You don't create an AWS CodeDeploy application by specifying a name that uniquely represents what you want to deploy.
-
You don't create an AWS CodeDeploy deployment group.
-
You don't specify an application specification file (AppSpec file). The information normally managed with the AppSpec file, such as the weighted configuration options or lifecycle events, is managed by the
AWS::CodeDeploy::BlueGreenhook.
This table summarizes the differences in the high-level workflow between deployment types.
| Function | Standard blue/green deployments | Blue/green deployments through AWS CloudFormation |
|---|---|---|
| Specify the Amazon ECS cluster, Amazon ECS service, Application Load Balancer or Network Load Balancer, Production listener, test listener, and two target groups. | Create a CodeDeploy deployment group that specifies these resources. | Create an AWS CloudFormation template to model these resources. |
| Specify the change to be deployed. | Create a CodeDeploy application. | Create an AWS CloudFormation template that specifies the container image. |
| Specify the Amazon ECS task definition, container name, and container port. | Create an AppSpec file that specifies these resources. | Create an AWS CloudFormation template to model these resources. |
| Specify the deployment traffic shifting options and lifecycle event hooks. | Create an AppSpec file that specifies these options. | Create an AWS CloudFormation template that uses the
AWS::CodeDeploy::BlueGreen hook parameters to
specify these options. |
|
CloudWatch alarms. |
Create a CloudWatch alarm that triggers a rollback. |
Configure a CloudWatch alarm at the AWS CloudFormation stack level that triggers a rollback. |
| Rollback/redeployment. | Specify rollback and redeployment options. | Cancel the stack update in AWS CloudFormation. |
Monitoring Amazon ECS blue/green deployments through AWS CloudFormation
You can monitor blue/green deployments through AWS CloudFormation and CodeDeploy. For information about monitoring through AWS CloudFormation, see Monitoring blue/green events in AWS CloudFormation in the AWS CloudFormation User Guide.
To view deployment status of blue/green deployments in CodeDeploy
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the CodeDeploy console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/codedeploy
. Note
Sign in with the same user that you set up in Getting started with CodeDeploy.
-
In Deployments, the deployment that was triggered by the AWS CloudFormation stack update appears. Choose the deployment to view the Deployment history.
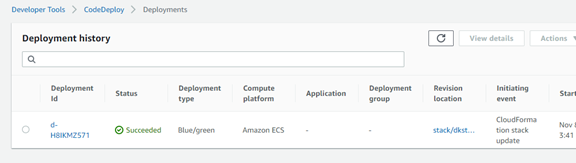
-
Choose the deployment to view the traffic shifting status. Note that the application and deployment group are not created.
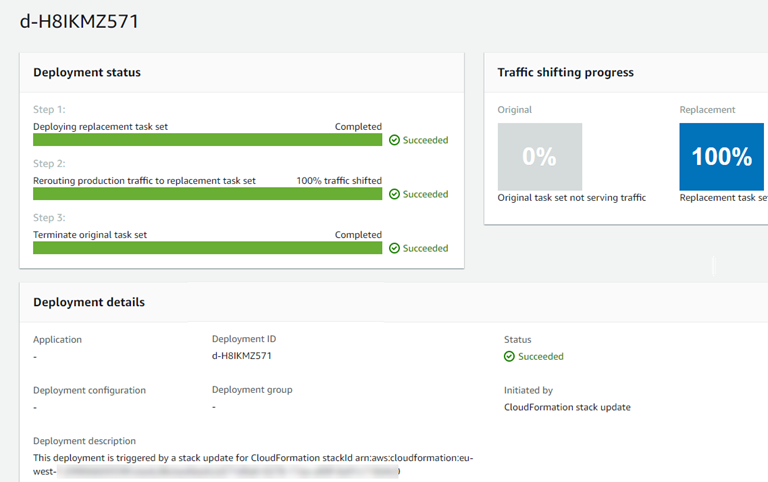
-
The following apply for rolling back or stopping the deployment:
-
The successful deployment appears in CodeDeploy and shows that the deployment was initiated by AWS CloudFormation.
-
If you want to stop and roll back the deployment, you must cancel the stack update in AWS CloudFormation.
-