Identifying asymmetric KMS keys
To determine if a particular KMS key is an asymmetric KMS key, find the key type or key spec. You can use the AWS KMS console or AWS KMS API.
Some of these methods also show you other aspects of the cryptographic configuration of a KMS key, including the key usage and the encryption or signing algorithms that the KMS key supports. You can view the cryptographic configuration of an existing KMS key, but you cannot change it.
For general information about viewing KMS keys, including sorting, filtering, and choosing columns for your console display, see Viewing KMS keys in the console.
Topics
Finding the key type in the KMS key table
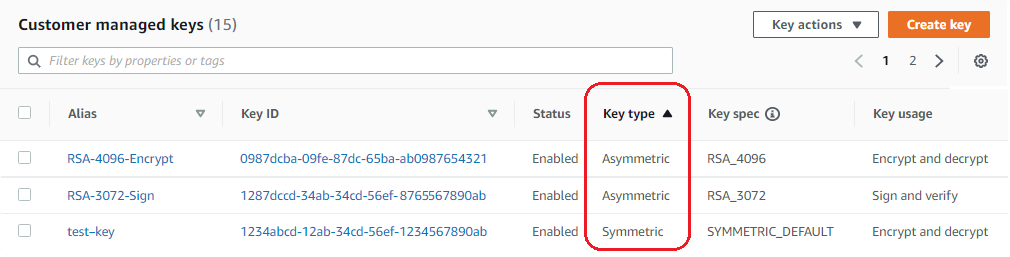
In the AWS KMS console, the Key type column shows whether each KMS key is symmetric or asymmetric. You can add a Key type column to the KMS key table on the Customer managed keys or AWS managed keys pages in the console.
To identify symmetric and asymmetric KMS keys in your KMS key table, use the following procedure.
-
Open the AWS KMS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/kms
. -
To change the AWS Region, use the Region selector in the upper-right corner of the page.
-
To view the keys in your account that you create and manage, in the navigation pane choose Customer managed keys. To view the keys in your account that AWS creates and manages for you, in the navigation pane, choose AWS managed keys.
-
The Key type columns shows whether each KMS key is symmetric or asymmetric. You can also sort and filter by the Key type value.
If the Key type column does not appear in your KMS key table, choose the gear icon in the upper right corner of the page, choose Key type, and then choose Confirm. You can also add the Key spec and Key usage columns.
Finding the key type on the details page
In the AWS KMS console, the details page for each KMS key includes a Cryptographic Configuration tab that displays the key type (symmetric or asymmetric) and other cryptographic details about the KMS key.
To identify symmetric and asymmetric KMS keys on the details page for a KMS key, use the following procedure.
-
Open the AWS KMS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/kms
. -
To change the AWS Region, use the Region selector in the upper-right corner of the page.
-
To view the keys in your account that you create and manage, in the navigation pane choose Customer managed keys. To view the keys in your account that AWS creates and manages for you, in the navigation pane, choose AWS managed keys.
-
Choose the alias or key ID of a KMS key.
-
Choose the Cryptographic configuration tab. The tabs are below the General configuration section.
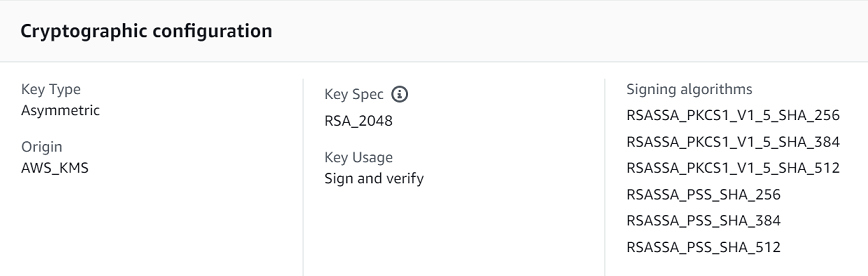
The Cryptographic configuration tab displays the Key Type, which indicates whether it is symmetric or asymmetric. It also displays other details about the KMS key, including the Key Usage, which tells whether a KMS key can be used for encryption and decryption or signing and verification. For asymmetric KMS keys, it displays the encryption algorithms or signing algorithms that the KMS key supports.
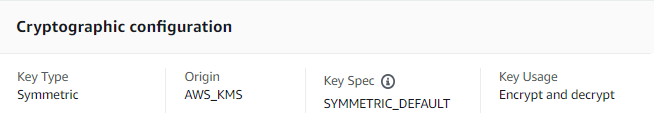
For example, the following is an example Cryptographic configuration tab for a symmetric encryption KMS key.
The following is an example Cryptographic configuration tab for an asymmetric RSA KMS key that's used for signing and verification.
Finding the key spec using the AWS KMS API
To determine whether a KMS key is symmetric or asymmetric, use the DescribeKey operation. The
KeySpec field in the response contains the key
spec of the KMS key. For a symmetric encryption KMS key, the value of
KeySpec is SYMMETRIC_DEFAULT. Other values indicate an
asymmetric KMS key or an HMAC KMS key.
Note
The CustomerMasterKeySpec member is deprecated. Instead, use KeySpec. To
prevent breaking changes, the DescribeKey response includes
KeySpec and CustomerMasterKeySpec members with the same
value.
For example, DescribeKey returns the following response for a symmetric encryption KMS key.
The KeySpec value is SYMMETRIC_DEFAULT.
{ "KeyMetadata": { "AWSAccountId": "111122223333", "KeyId": "0987dcba-09fe-87dc-65ba-ab0987654321", "Arn": "arn:aws:kms:us-west-2:111122223333:key/0987dcba-09fe-87dc-65ba-ab0987654321", "CreationDate": 1496966810.831, "Enabled": true, "Description": "", "KeyState": "Enabled", "Origin": "AWS_KMS", "KeyManager": "CUSTOMER", "MultiRegion": false, "KeySpec": "SYMMETRIC_DEFAULT", "CustomerMasterKeySpec": "SYMMETRIC_DEFAULT", "KeyUsage": "ENCRYPT_DECRYPT", "EncryptionAlgorithms": [ "SYMMETRIC_DEFAULT" ] } }
The DescribeKey response for an asymmetric RSA KMS key used in signing and
verification looks similar to this example. The KeySpec value is RSA_2048 and the KeyUsage is
SIGN_VERIFY. The SigningAlgorithms element lists the valid
signing algorithms for the KMS key.
{ "KeyMetadata": { "AWSAccountId": "111122223333", "KeyId": "1234abcd-12ab-34cd-56ef-1234567890ab", "Arn": "arn:aws:kms:us-west-2:111122223333:key/1234abcd-12ab-34cd-56ef-1234567890ab", "CreationDate": 1571767572.317, "CustomerMasterKeySpec": "RSA_2048", "Enabled": false, "Description": "", "KeyState": "Disabled", "Origin": "AWS_KMS", "MultiRegion": false, "KeyManager": "CUSTOMER", "KeySpec": "RSA_2048", "KeyUsage": "SIGN_VERIFY", "SigningAlgorithms": [ "RSASSA_PKCS1_V1_5_SHA_256", "RSASSA_PKCS1_V1_5_SHA_384", "RSASSA_PKCS1_V1_5_SHA_512", "RSASSA_PSS_SHA_256", "RSASSA_PSS_SHA_384", "RSASSA_PSS_SHA_512" ] } }