How Amazon WorkMail uses AWS KMS
This topic discusses how Amazon WorkMail uses AWS KMS to encrypt email messages.
Topics
Amazon WorkMail overview
Amazon WorkMail is a secure, managed business email and calendaring service with support for existing desktop and mobile email clients. You can create an Amazon WorkMail organization and assign to it one or more email domains that you own. Then you can create mailboxes for the email users and distribution groups in the organization.
Amazon WorkMail transparently encrypts all messages in the mailboxes of all Amazon WorkMail organizations before the messages are written to disk and transparently decrypts the messages when users access them. There is no option to disable encryption. To protect the encryption keys that protect the messages, Amazon WorkMail is integrated with AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS).
Amazon WorkMail also provides an option for enabling users to send signed or encrypted email. This encryption feature does not use AWS KMS.
Amazon WorkMail encryption
In Amazon WorkMail, each organization can contain multiple mailboxes, one for each user in the organization. All messages, including email and calendar items, are stored in the user's mailbox.
To protect the contents of the mailboxes in your Amazon WorkMail organizations, Amazon WorkMail encrypts all mailbox messages before they are written to disk. No customer-provided information is stored in plaintext.
Each message is encrypted under a unique data encryption key. The message key is protected by a mailbox key, which is a unique encryption key that is used only for that mailbox. The mailbox key is encrypted under an AWS KMS key for the organization that never leaves AWS KMS unencrypted. The following diagram shows the relationship of the encrypted messages, encrypted message keys, encrypted mailbox key, and the KMS key for the organization in AWS KMS.
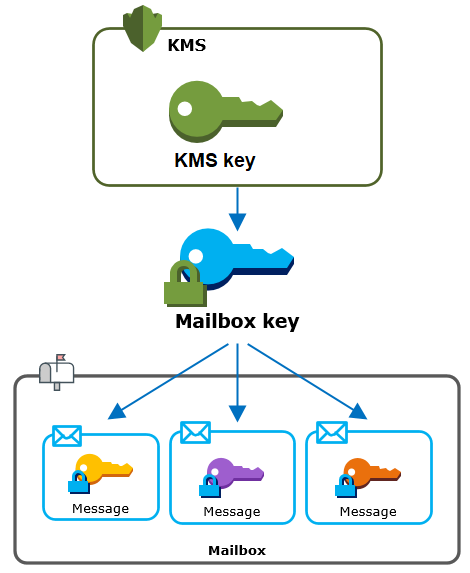
A KMS key for the organization
When you create an Amazon WorkMail organization, you can select an AWS KMS keyfor the organization. This KMS key protects all mailbox keys in that organization.
If you use the Quick
Setup procedure to create your organization, Amazon WorkMail uses the AWS managed key for Amazon WorkMail (aws/workmail) in your
AWS account. If you use the Standard Setup,
you can select the AWS managed key for Amazon WorkMail or a customer managed key that you own and manage. You can select the same KMS key or a
different KMS key for each of your organizations, but you cannot change the KMS key once
you have selected it.
Important
Amazon WorkMail supports only symmetric encryption KMS keys. You cannot use an asymmetric KMS key to encrypt data in Amazon WorkMail. For help determining whether a KMS key is symmetric or asymmetric, see Identifying asymmetric KMS keys.
To find the KMS key for your organization, use the AWS CloudTrail log entry that records calls to AWS KMS.
A unique encryption key for each mailbox
When you create a new mailbox, Amazon WorkMail generates a unique 256-bit Advanced Encryption
Standard
To protect the mailbox key, Amazon WorkMail calls AWS KMS to encrypt the mailbox key under the KMS key for the organization. Then it stores the encrypted mailbox key in the mailbox metadata.
Note
Amazon WorkMail uses a symmetric mailbox encryption key to protect message keys. Previously, Amazon WorkMail protected each mailbox with an asymmetric key pair. It used the public key to encrypt each message key and the private key to decrypt it. The private mailbox key was protected by the KMS key for the organization. Existing mailboxes might still use an asymmetric mailbox key pair. This change does not affect the security of the mailbox or its messages.
A unique encryption key for each message
When a message is added to the mailbox, Amazon WorkMail generates a unique 256-bit AES symmetric encryption key for the message outside of AWS KMS. It uses this message key to encrypt the message. Amazon WorkMail encrypts the message key under the mailbox key and stores the encrypted message key with the message. Then, it encrypts the mailbox key under the KMS key for the organization.
Creating a new mailbox
When Amazon WorkMail creates a new mailbox, it uses the following process to prepare the mailbox to hold encrypted messages.
-
Amazon WorkMail generates a unique 256-bit AES symmetric encryption key for the mailbox outside of AWS KMS.
-
Amazon WorkMail calls the AWS KMS Encrypt operation. It passes in the mailbox key and the identifier of the AWS KMS key for the organization. AWS KMS returns a ciphertext of the mailbox key encrypted under the KMS key.
-
Amazon WorkMail stores the encrypted mailbox key with the mailbox metadata.
Encrypting a mailbox message
To encrypt a message, Amazon WorkMail uses the following process.
-
Amazon WorkMail generates a unique 256-bit AES symmetric key for the message. It uses the plaintext message key and the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm to encrypt the message outside of AWS KMS.
-
To protect the message key under the mailbox key, Amazon WorkMail needs to decrypt the mailbox key, which is always stored in its encrypted form.
Amazon WorkMail calls the AWS KMS Decrypt operation and passes in the encrypted mailbox key. AWS KMS uses the KMS key for the organization to decrypt the mailbox key and it returns the plaintext mailbox key to Amazon WorkMail.
-
Amazon WorkMail uses the plaintext mailbox key and the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm to encrypt the message key outside of AWS KMS.
-
Amazon WorkMail stores the encrypted message key in the metadata of the encrypted message so it is available to decrypt it.
Decrypting a mailbox message
To decrypt a message, Amazon WorkMail uses the following process.
-
Amazon WorkMail calls the AWS KMS Decrypt operation and passes in the encrypted mailbox key. AWS KMS uses the KMS key for the organization to decrypt the mailbox key and it returns the plaintext mailbox key to Amazon WorkMail.
-
Amazon WorkMail uses the plaintext mailbox key and the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm to decrypt the encrypted message key outside of AWS KMS.
-
Amazon WorkMail uses the plaintext message key to decrypt the encrypted message.
Caching mailbox keys
To improve performance and minimize calls to AWS KMS, Amazon WorkMail caches each plaintext mailbox key for each client locally for up to one minute. At the end of the caching period, the mailbox key is removed. If the mailbox key for that client is required during the caching period, Amazon WorkMail can get it from the cache instead of calling AWS KMS. The mailbox key is protected in the cache and is never written to disk in plaintext.
Authorizing use of the KMS key
When Amazon WorkMail uses an AWS KMS key in cryptographic operations, it acts on behalf of the mailbox administrator.
To use the AWS KMS key for a secret on your behalf, the administrator must have the following permissions. You can specify these required permissions in an IAM policy or key policy.
-
kms:Encrypt -
kms:Decrypt -
kms:CreateGrant
To allow the KMS key to be used only for requests that originate in Amazon WorkMail, you can use
the kms:ViaService condition key with the
workmail. value.<region>.amazonaws.com
You can also use the keys or values in the encryption context as a condition for using the KMS key for cryptographic operations. For example, you can use a string condition operator in an IAM or key policy document or use a grant constraint in a grant.
Key policy for the AWS managed key
The key policy for the AWS managed key for Amazon WorkMail gives users permission to use the KMS key for specified operations only when Amazon WorkMail makes the request on the user's behalf. The key policy does not allow any user to use the KMS key directly.
This key policy, like the policies of all AWS managed keys, is established by the service. You cannot change the key policy, but you can view it at any time. For details, see Viewing a key policy.
The policy statements in the key policy have the following effect:
-
Allow users in the account and Region to use the KMS key for cryptographic operations and to create grants, but only when the request comes from Amazon WorkMail on their behalf. The
kms:ViaServicecondition key enforces this restriction. -
Allows the AWS account to create IAM policies that allow users to view KMS key properties and revoke grants.
The following is a key policy for an example AWS managed key for Amazon WorkMail.
{ "Version" : "2012-10-17", "Id" : "auto-workmail-1", "Statement" : [ { "Sid" : "Allow access through WorkMail for all principals in the account that are authorized to use WorkMail", "Effect" : "Allow", "Principal" : { "AWS" : "*" }, "Action" : [ "kms:Decrypt", "kms:CreateGrant", "kms:ReEncrypt*", "kms:DescribeKey", "kms:Encrypt" ], "Resource" : "*", "Condition" : { "StringEquals" : { "kms:ViaService" : "workmail.us-east-1.amazonaws.com", "kms:CallerAccount" : "111122223333" } } }, { "Sid" : "Allow direct access to key metadata to the account", "Effect" : "Allow", "Principal" : { "AWS" : "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:root" }, "Action" : [ "kms:Describe*", "kms:List*", "kms:Get*", "kms:RevokeGrant" ], "Resource" : "*" } ] }
Using grants to authorize Amazon WorkMail
In addition to key policies, Amazon WorkMail uses grants to add permissions to the KMS key for each organization. To view the grants on the KMS key in your account, use the ListGrants operation.
Amazon WorkMail uses grants to add the following permissions to the KMS key for the organization.
-
Add the
kms:Encryptpermission to allow Amazon WorkMail to encrypt the mailbox key. -
Add the
kms:Decryptpermission to allow Amazon WorkMail to use the KMS key to decrypt the mailbox key. Amazon WorkMail requires this permission in a grant because the request to read mailbox messages uses the security context of the user who is reading the message. The request does not use the credentials of the AWS account. Amazon WorkMail creates this grant when you select a KMS key for the organization.
To create the grants, Amazon WorkMail calls CreateGrant on behalf of the user who created the organization. Permission to
create the grant comes from the key policy. This policy allows account users to call
CreateGrant on the KMS key for the organization when Amazon WorkMail makes the request
on an authorized user's behalf.
The key policy also allows the account root to revoke the grant on the AWS managed key. However, if you revoke the grant, Amazon WorkMail cannot decrypt the encrypted data in your mailboxes.
Amazon WorkMail encryption context
An encryption context is a set of key-value pairs that contain arbitrary nonsecret data. When you include an encryption context in a request to encrypt data, AWS KMS cryptographically binds the encryption context to the encrypted data. To decrypt the data, you must pass in the same encryption context.
Amazon WorkMail uses the same encryption context format in all AWS KMS cryptographic operations. You can use the encryption context to identify a cryptographic operation in audit records and logs, such as AWS CloudTrail, and as a condition for authorization in policies and grants.
In its Encrypt and Decrypt requests to AWS KMS, Amazon WorkMail uses an
encryption context where the key is aws:workmail:arn and the value is the Amazon
Resource Name (ARN) of the organization.
"aws:workmail:arn":"arn:aws:workmail:region:account ID:organization/organization ID"For example, the following encryption context includes an example organization ARN in the
US East (Ohio) (us-east-2) Region.
"aws:workmail:arn":"arn:aws:workmail:us-east-2:111122223333:organization/m-68755160c4cb4e29a2b2f8fb58f359d7"Monitoring Amazon WorkMail interaction with AWS KMS
You can use AWS CloudTrail and Amazon CloudWatch Logs to track the requests that Amazon WorkMail sends to AWS KMS on your behalf.
Encrypt
When you create a new mailbox, Amazon WorkMail generates a mailbox key and calls AWS KMS to encrypt the mailbox key. Amazon WorkMail sends an Encrypt request to AWS KMS with the plaintext mailbox key and an identifier for the KMS key of the Amazon WorkMail organization.
The event that records the Encrypt operation is similar to the following
example event. The user is the Amazon WorkMail service. The parameters include the KMS key ID
(keyId) and the encryption context for the Amazon WorkMail organization. Amazon WorkMail also
passes in the mailbox key, but that is not recorded in the CloudTrail log.
{ "eventVersion": "1.05", "userIdentity": { "type": "AWSService", "invokedBy": "workmail.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com" }, "eventTime": "2019-02-19T10:01:09Z", "eventSource": "kms.amazonaws.com", "eventName": "Encrypt", "awsRegion": "eu-west-1", "sourceIPAddress": "workmail.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com", "userAgent": "workmail.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com", "requestParameters": { "encryptionContext": { "aws:workmail:arn": "arn:aws:workmail:eu-west-1:111122223333:organization/m-c6981ff7642446fa8772ba99c690e455" }, "keyId": "arn:aws:kms:eu-west-1:111122223333:key/1a2b3c4d-5e6f-1a2b-3c4d-5e6f1a2b3c4d" }, "responseElements": null, "requestID": "76e96b96-7e24-4faf-a2d6-08ded2eaf63c", "eventID": "d5a59c18-128a-4082-aa5b-729f7734626a", "readOnly": true, "resources": [ { "ARN": "arn:aws:kms:eu-west-1:111122223333:key/1a2b3c4d-5e6f-1a2b-3c4d-5e6f1a2b3c4d", "accountId": "111122223333", "type": "AWS::KMS::Key" } ], "eventType": "AwsApiCall", "recipientAccountId": "111122223333", "sharedEventID": "d08e60f1-097e-4a00-b7e9-10bc3872d50c" }
Decrypt
When you add, view, or delete a mailbox message, Amazon WorkMail asks AWS KMS to decrypt the mailbox key. Amazon WorkMail sends an Decrypt request to AWS KMS with the encrypted mailbox key and an identifier for the KMS key of the Amazon WorkMail organization.
The event that records the Decrypt operation is similar to the following
example event. The user is the Amazon WorkMail service. The parameters include the encrypted mailbox
key (as a ciphertext blob), which is not recorded in the log, and the encryption context for
the Amazon WorkMail organization. AWS KMS derives the ID of the KMS key from the ciphertext.
{ "eventVersion": "1.05", "userIdentity": { "type": "AWSService", "invokedBy": "workmail.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com" }, "eventTime": "2019-02-20T11:51:10Z", "eventSource": "kms.amazonaws.com", "eventName": "Decrypt", "awsRegion": "eu-west-1", "sourceIPAddress": "workmail.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com", "userAgent": "workmail.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com", "requestParameters": { "encryptionContext": { "aws:workmail:arn": "arn:aws:workmail:eu-west-1:111122223333:organization/m-c6981ff7642446fa8772ba99c690e455" } }, "responseElements": null, "requestID": "4a32dda1-34d9-4100-9718-674b8e0782c9", "eventID": "ea9fd966-98e9-4b7b-b377-6e5a397a71de", "readOnly": true, "resources": [ { "ARN": "arn:aws:kms:eu-west-1:111122223333:key/1a2b3c4d-5e6f-1a2b-3c4d-5e6f1a2b3c4d", "accountId": "111122223333", "type": "AWS::KMS::Key" } ], "eventType": "AwsApiCall", "recipientAccountId": "111122223333", "sharedEventID": "241e1e5b-ff64-427a-a5b3-7949164d0214" }