Setting up a standard channel
When you followed the guidelines for implementing pipeline redundancy in a MediaLive channel, you might have decided that you might want to implement pipeline redundancy. In this case, make sure that you set up the inputs as standard-class inputs and set up the channel as a standard channel.
Follow these guidelines when you plan the workflow:
-
Make sure that the upstream system can provide you with two instances of the source content. See Assess source formats and packaging.
-
When you create inputs, set up all the inputs as standard-class inputs.
Some inputs are always set up as standard-class inputs. For all other inputs, set the Input class field to Standard input.
-
When you create the channel, do the following:
-
Set up the channel as a standard channel. See Complete channel and input details.
-
At the step to attach inputs to the channel, attach only standard-class inputs. If you try to attach a single-class input to a standard channel, you won't be able to create the channel.
-
-
Contact the upstream system and request that they provide two content sources.
How pipeline redundancy works
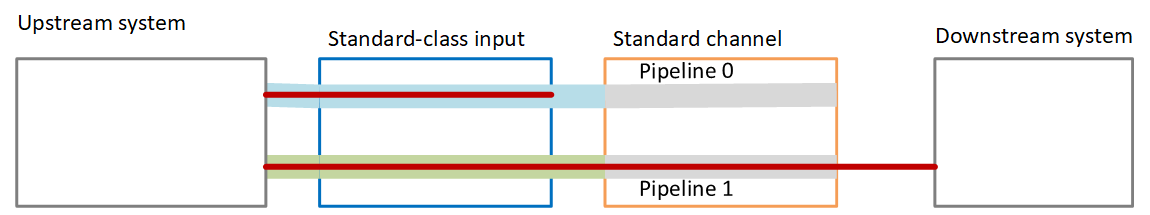
When you set up a standard channel, the channel has two pipelines—pipeline 0 and pipeline 1. Each input also contains two pipelines. A content source is connected to each pipeline.
As this diagram illustrates, the upstream system provides two instances of the content to the input. One instance goes to the pipeline that is indicated by the blue line, the other goes to the pipeline indicated by the green line. Each of these lines is attached to one of the two pipelines in the channel. The channel produces two identical instances of the output for the downstream system. The downstream system chooses to handle one instance (the output from blue pipeline) and to ignore the other instance (the output from the green pipeline).
Failure handling
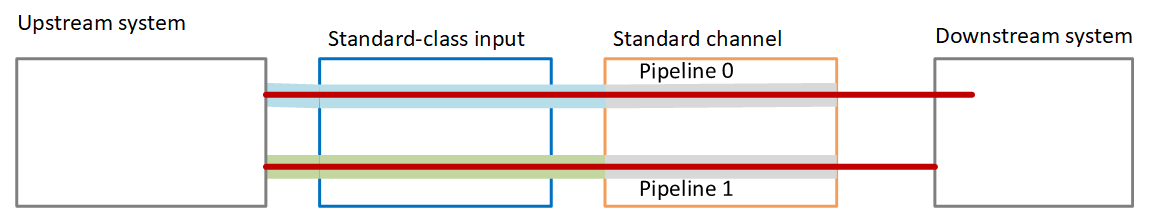
There might be a problem that causes a pipeline to stop functioning.
-
If the failed pipeline is the pipeline that the downstream system is handling (for example, the blue pipeline), the downstream system can switch to the other output.
-
After a few minutes, the failed pipeline automatically restarts and produces output. The downstream system can continue to handle the output from the green pipeline, or it can go back to the blue pipeline. That decision has no impact on MediaLive.
In this diagram, notice that the upstream system is still sending source content to the blue pipeline, which indicates that the upstream system is working but pipeline 0 has failed. The downstream system has started handling pipeline 1 instead, using the source content from the green pipeline.