Overview of a typical IT operating model
An operating model serves as the cornerstone of successful IT service delivery in any
organization. It's the blueprint that defines how an organization creates and delivers
value through its operations. At its core, an operating model aligns people, processes,
and various technologies with business strategy. (For more information about operating
models, see Defining the IT
Operating Model
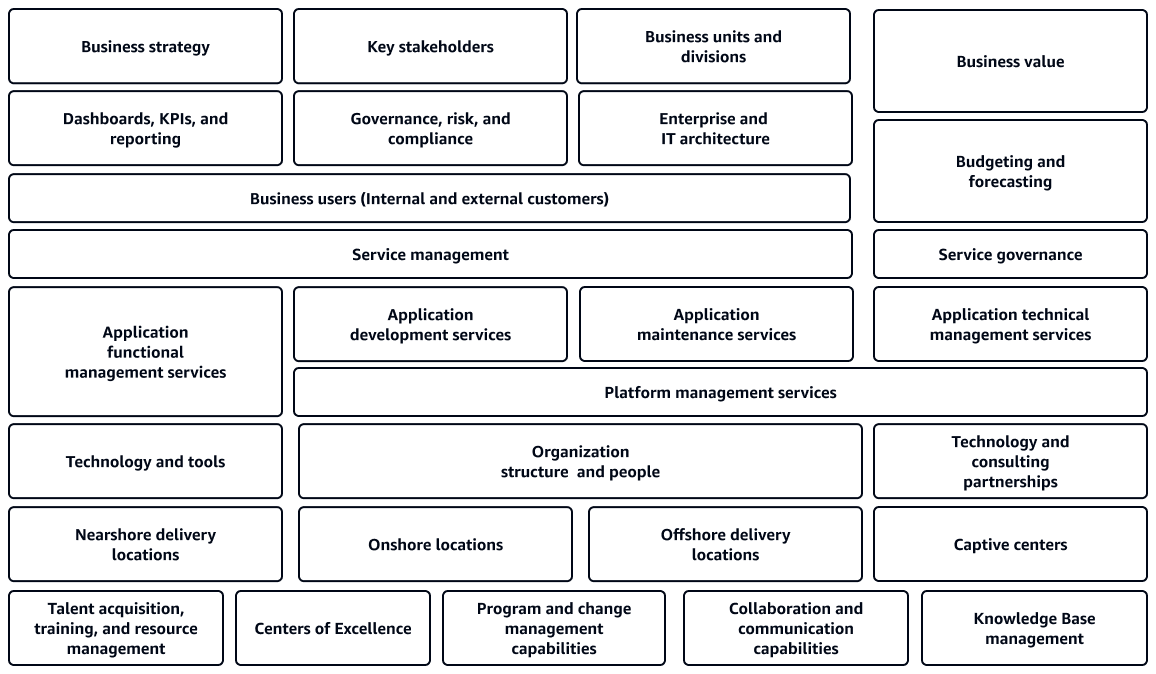
As shown in the following diagram, a typical IT operating model encompasses multiple key components:
-
Organizational structure and roles
-
Key stakeholders
-
Business units and divisions
-
Business users (internal and external customers)
-
People roles
-
Technology and consulting partnerships
-
-
Governance and decision-making frameworks
-
Enterprise and IT architecture
-
Core processes and workflows
-
Business strategy
-
Business value
-
Budgeting and forecasting
-
Application functional management services
-
Application development services
-
Application maintenance services
-
Application technology management services
-
Platform management services
-
-
Technology and tools
-
Performance metrics
-
Dashboards, key performance indicators (KPIs), and reporting
-
-
Organization capabilities
-
Program and change management
-
Collaboration and communication
-
Knowledge base management
-
-
Culture and ways of working
-
Talent acquisition, training, and resource management
-
Center of Excellence (COE)
-
Nearshore delivery locations
-
Offshore locations
-
Offshore delivery locations
-
Captive centers
-
A well-designed operating model does more than explain day-to-day operations. It's a strategic asset driving competitive advantage. The operating model enables organizations to respond quickly to market changes, innovate effectively, and deliver greater customer value. A key strength of a well-designed operating model is adaptability. Your organization's operating model must flex to support its chosen practices while maintaining consistency and efficiency. This ability to adapt applies whether you use traditional waterfall methodologies, agile frameworks, or a hybrid approach for your ADM.