Traffic Mirroring example configuration scenarios
This section consists of step-by-step instructions you can use to configure Traffic Mirroring for the following scenarios:
To mirror traffic from multiple network interfaces, see
VPC Traffic Mirroring Source Automation Application
Example: Mirror inbound TCP traffic to a single monitoring appliance
Consider the scenario where you want to mirror inbound TCP traffic on an instance, and send it to a single monitoring appliance. You need the following traffic mirror resources for this example.
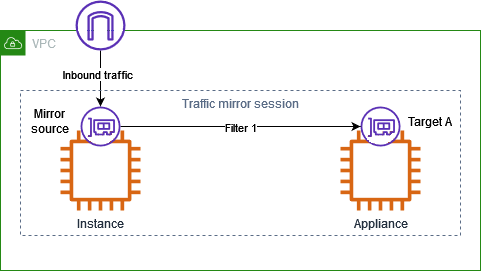
Resources
-
A traffic mirror target for the appliance (Target A)
-
A traffic mirror filter with a traffic mirror rule for the TCP inbound traffic (Filter 1)
-
A traffic mirror session that has the following:
-
A traffic mirror source
-
A traffic mirror target for the appliance
-
A traffic mirror filter with a traffic mirror rule for the TCP inbound traffic
-
Step 1: Create a traffic mirror target
Create a traffic mirror target (Target A) for the monitoring appliance. Depending on your configuration, the target is one of the following types:
-
The network interface of the monitoring appliance
-
The Network Load Balancer when the appliance is deployed behind one
-
The Gateway Load Balancer endpoint when the appliance is deployed behind a Gateway Load Balancer
For more information, see Create or delete a traffic mirror target.
Step 2: Create a traffic mirror filter
Create a traffic mirror filter (Filter 1) that has the following inbound rule. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror filter.
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule action | Accept |
| Protocol | TCP |
| Source port range | |
| Destination port range | |
| Source CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Destination CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Description | TCP Rule |
Step 3: Create a traffic mirror session
Create and configure a traffic mirror session with the following options. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror session.
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Mirror source | The network interface of the instance that you want to monitor. |
| Mirror target | Target A |
| Filter | Filter 1 |
Example: Mirror inbound TCP and UDP traffic to multiple appliances
Consider the scenario where you want to mirror inbound TCP and UDP traffic on an instance. But you want to send the TCP traffic to one appliance (Appliance A), and the UDP traffic to a second appliance (Appliance B). You need the following traffic mirror entities for this example.
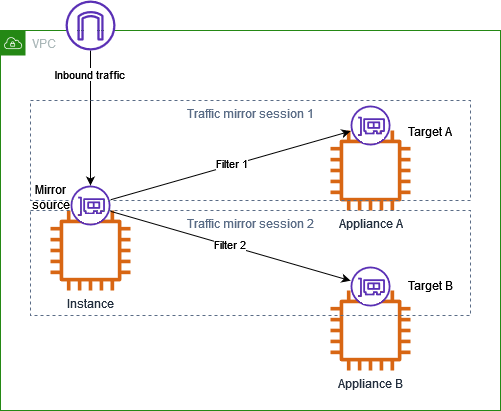
Resources
-
A traffic mirror target for Appliance A (Target A)
-
A traffic mirror target for Appliance B (Target B)
-
A traffic mirror filter with a traffic mirror rule for the TCP inbound traffic (Filter 1)
-
A traffic mirror filter with a traffic mirror rule for the UDP inbound traffic (Filter 2)
-
A traffic mirror session that has the following:
-
A traffic mirror source
-
A traffic mirror target (Target A) for Appliance A
-
A traffic mirror filter (Filter 1) with a traffic mirror rule for the TCP inbound traffic
-
-
A traffic mirror session that has the following:
-
A traffic mirror source
-
A traffic mirror target (Target B) for Appliance B
-
A traffic mirror filter (Filter 2) with a traffic mirror rule for the UDP inbound traffic
-
Step 1: Create a traffic mirror target for Appliance A
Create a traffic mirror target for Appliance A (Target A). Depending on your configuration, the target is one of the following types:
-
The network interface of the monitoring appliance
-
The Network Load Balancer when the appliance is deployed behind one
-
The Gateway Load Balancer endpoint when the appliance is deployed behind a Gateway Load Balancer
For more information, see Create or delete a traffic mirror target.
Step 2: Create a traffic mirror target for Appliance B
Create a traffic mirror target (Target B) for Appliance B. Depending on your configuration, the target is one of the following types:
-
The network interface of the monitoring appliance
-
The Network Load Balancer when the appliance is deployed behind one
-
The Gateway Load Balancer endpoint when the appliance is deployed behind a Gateway Load Balancer
For more information, see Create or delete a traffic mirror target.
Step 3: Create a traffic mirror filter with a rule for TCP traffic
Create a traffic mirror filter (Filter 1) with the following inbound rule for TCP traffic. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror filter
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule action | Accept |
| Protocol | TCP |
| Source port range | |
| Destination port range | |
| Source CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Destination CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Description | TCP Rule |
Step 4: Create a traffic mirror filter with a rule for UDP traffic
Create a traffic mirror filter (Filter 2) with the following inbound rule for UDP traffic. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror filter
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule action | Accept |
| Protocol | UDP |
| Source port range | |
| Destination port range | |
| Source CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Destination CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Description | UDP Rule |
Step 5: Create a traffic mirror session for the TCP traffic
Create and configure a traffic mirror session with the following options. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror session.
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Mirror source | The network interface of the instance that you want to monitor. |
| Mirror target | Target A |
| Filter | Filter 1 |
| Session number | 1 |
Step 6: Create a traffic mirror session for the UDP traffic
Create and configure a traffic mirror session with the following options. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror session.
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Mirror source | The network interface of the instance that you want to monitor. |
| Mirror target | Target B |
| Filter | Filter 2 |
| Session number | 2 |
Example: Mirror non-local VPC traffic
Consider the scenario where you want to monitor traffic leaving your VPC or traffic whose source is outside your VPC. In this case, you will mirror all traffic except traffic passing within your VPC and send it to a single monitoring appliance. You need the following traffic mirror resources:
-
A traffic mirror target for the appliance (Target A)
-
A traffic mirror filter that has two sets of rules for outbound and inbound traffic. For outbound traffic, it will reject all packets which have a destination IP in the VPC CIDR block and accept all other outbound packets. For inbound traffic, it will reject all packets which have a source IP in the VPC CIDR block and accept all other inbound packets.
-
A traffic mirror session that has the following:
-
A traffic mirror source
-
A traffic mirror target for the appliance (Target A)
-
A traffic mirror filter with a traffic mirror rule for the TCP inbound traffic (Filter F)
-
In this example, the VPC CIDR block is 10.0.0.0/16.
Step 1: Create a traffic mirror target
Create a traffic mirror target (Target A) for the monitoring appliance. Depending on your configuration, the target is one of the following types:
-
The network interface of the monitoring appliance
-
The Network Load Balancer when the appliance is deployed behind one
-
The Gateway Load Balancer endpoint when the appliance is deployed behind a Gateway Load Balancer
For more information, see Create or delete a traffic mirror target.
Step 2: Create a traffic mirror filter
Create a traffic mirror filter (Filter F) that has the following rules. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror filter.
Outbound traffic mirror filter rules
Create the following outbound rules:
-
Reject all outbound packets which have a destination IP in the VPC CIDR block
-
Accept all other outbound packets (destination CIDR block 0.0.0.0/0)
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule number | 10 |
| Rule action | Reject |
| Protocol | All |
| Source port range | |
| Destination port range | |
| Source CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Destination CIDR block | 10.0.0.0/16 |
| Description | Reject all intra-VPC traffic |
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule number | 20 |
| Rule action | Accept |
| Protocol | All |
| Source port range | |
| Destination port range | |
| Source CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Destination CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Description | Accept all outbound traffic |
Inbound traffic mirror filter rules
Create the following inbound rules:
-
Reject all inbound packets which have a source IP in the VPC CIDR block
-
Accept all other inbound packets (source CIDR block 0.0.0.0/0)
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule number | 10 |
| Rule action | Reject |
| Protocol | All |
| Source port range | |
| Destination port range | |
| Source CIDR block | 10.0.0.0/16 |
| Destination CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Description | Reject all intra-VPC traffic |
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule number | 20 |
| Rule action | Accept |
| Protocol | All |
| Source port range | |
| Destination port range | |
| Source CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Destination CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Description | Accept all inbound traffic |
Step 3: Create a traffic mirror session
Create and configure a traffic mirror session with the following options. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror session.
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Mirror source | The network interface of the instance that you want to monitor. |
| Mirror target | Target A |
| Filter | Filter F |
Example: Mirror traffic to appliances behind a Gateway Load Balancer via Gateway Load Balancer endpoints
You can deploy a Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) and Gateway Load Balancer endpoint (GWLBe) to securely send mirror traffic across VPC and accounts. The GWLBe is a VPC endpoint that provides private connectivity between VPC with the mirror sources and the monitoring appliances deployed behind the GWLB.
The following diagram shows a deployment of a GWLB for traffic mirroring utilizing GWLBe interfaces. The GWLB is deployed in a centralized Service VPC with multiple appliances as targets. The GWLB is set up for each Availability Zone that the customer wants to monitor traffic, and it can configure their GWLB with cross-zone load balancing as an option to protect against single Availability Zone failures. In the spoke VPCs, GWLBe interfaces are deployed in each spoke VPC. These endpoints are connected to the GWLB to send traffic from the spoke VPC to the Service VPC.
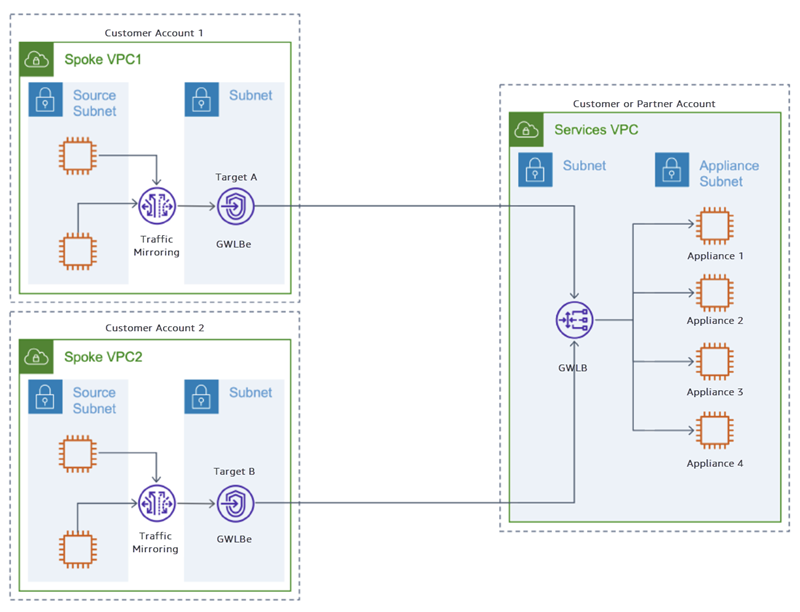
Consider the scenario where you want to mirror inbound TCP traffic on an instance and then send it to a Gateway Load Balancer via a Gateway Load Balancer endpoint. You need the following Traffic Mirroring entities for this example:
-
A Traffic Mirroring target for the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint (Target A) in Spoke VPC1
-
A Traffic Mirroring target for the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint (Target B) in Spoke VPC2
-
A Traffic Mirroring filter with a Traffic Mirroring rule for the TCP inbound traffic (Filter 1) for the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint
-
A Traffic Mirroring session for Spoke VPC1 that has the following:
-
A Traffic Mirroring source
-
A Traffic Mirroring target (Target A) for the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint
-
A Traffic Mirroring filter (Filter 1) with a Traffic Mirroring rule for the TCP inbound traffic
-
-
A Traffic Mirroring session for Spoke VPC2 that has the following:
-
A Traffic Mirroring source
-
A Traffic Mirroring target (Target B) for the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint
-
A Traffic Mirroring filter (Filter 1) with a Traffic Mirroring rule for the TCP inbound traffic
-
Step 1: Create a traffic mirror target in Spoke VPC1
Create a traffic mirror target (Target A) for the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint in Spoke VPC1. For more information, see Create or delete a traffic mirror target.
The Gateway Load Balancer endpoint will be the target when the monitoring appliances are deployed behind a Gateway Load Balancer.
Step 2: Create a traffic mirror target in Spoke VPC2
Create a traffic mirror target (Target B) for the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint in Spoke VPC1. For more information, see Create or delete a traffic mirror target.
The Gateway Load Balancer endpoint will be the target when the monitoring appliances are deployed behind a Gateway Load Balancer.
Step 3: Create a traffic mirror filter rule
Create a traffic mirror filter (Filter 1) that has the following inbound rule. For more information on creating a filter, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror filter.
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule action | Accept |
| Protocol | TCP |
| Source port range | |
| Destination port range | |
| Source CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Destination CIDR block | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Description | TCP Rule |
Step 4: Create a traffic mirror session in Spoke VPC1
Create and configure a traffic mirror session with the following options. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror session.
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Mirror source | The network interface of the instance that you want to monitor. |
| Mirror target | Target A |
| Filter | Filter 1 |
Step 5: Create a traffic mirror session in Spoke VPC2
Create and configure a traffic mirror session with the following options. For more information, see Create, modify, or delete a traffic mirror session.
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Mirror source | The network interface of the instance that you want to monitor. |
| Mirror target | Target B |
| Filter | Filter 1 |