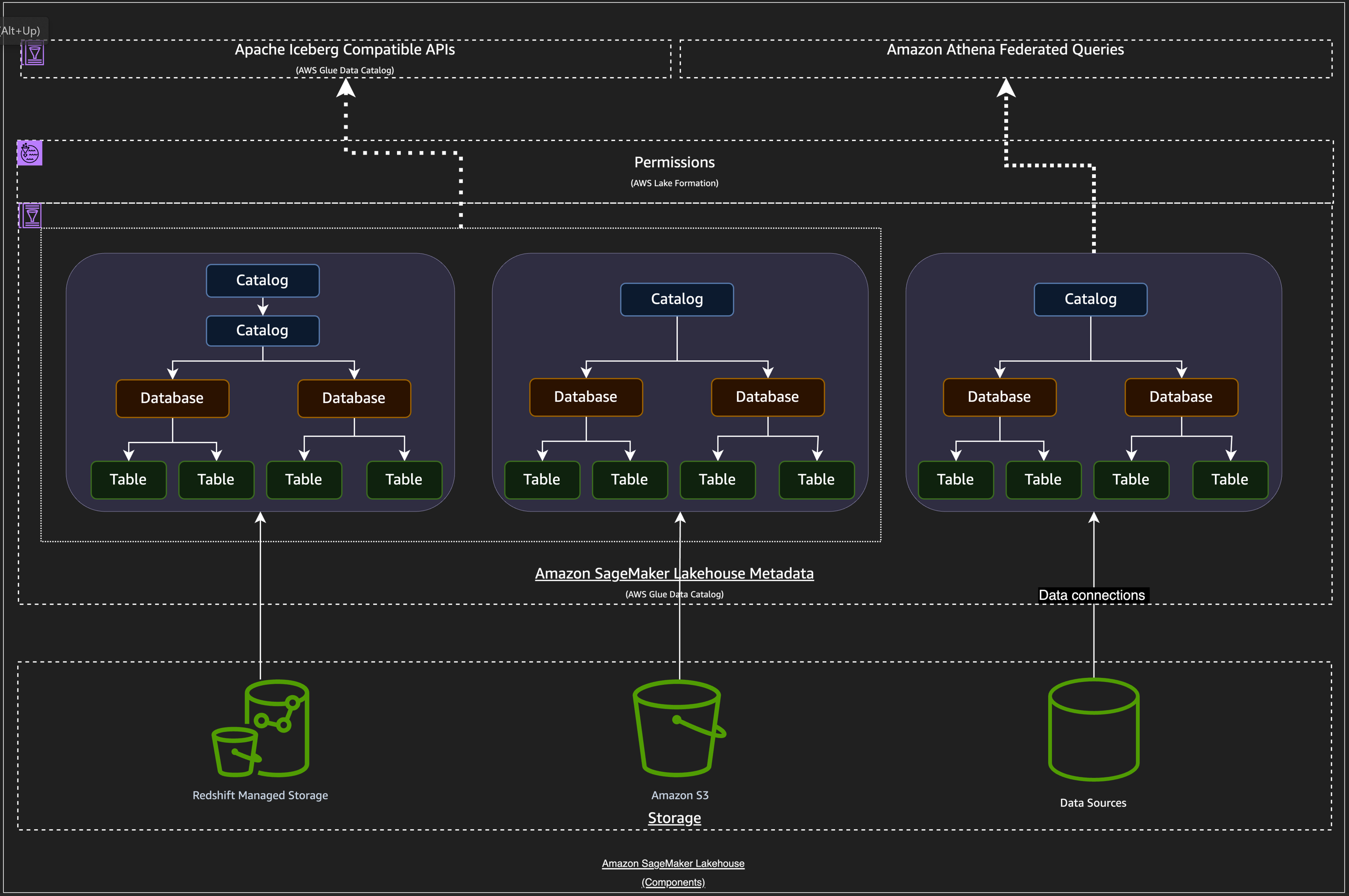
How the lakehouse architecture of Amazon SageMaker works
The lakehouse architecture is accessible from Amazon SageMaker Unified Studio. It organizes data from various sources into logical containers called catalogs. Each catalog represents data from existing sources like Amazon Redshift data warehouses, Amazon S3 data lakes, databases, or enterprise applications. You can also create new catalogs in the lakehouse to store data in S3 or Redshift Managed Storage (RMS).
You can access the data as Apache Iceberg tables and query it using any Iceberg-compatible
engine, such as Apache Spark
The lakehouse architecture is built on AWS Glue Data Catalog and AWS Lake Formation in your AWS account. With thelakehouse architecture, you can access and query your existing data in Amazon Redshift data warehouses and store new data in RMS from any Apache Iceberg compatible engine.
The following diagram shows how the lakehouse architecture works. Catalogs contain databases, which then contain tables. Types of storage sources for data that goes into catalogs include Redshift Managed Storage, Amazon S3, and data sources that you connect to with data connections.