This whitepaper is for historical reference only. Some content might be outdated and some links might not be available.
Service Fulfillment
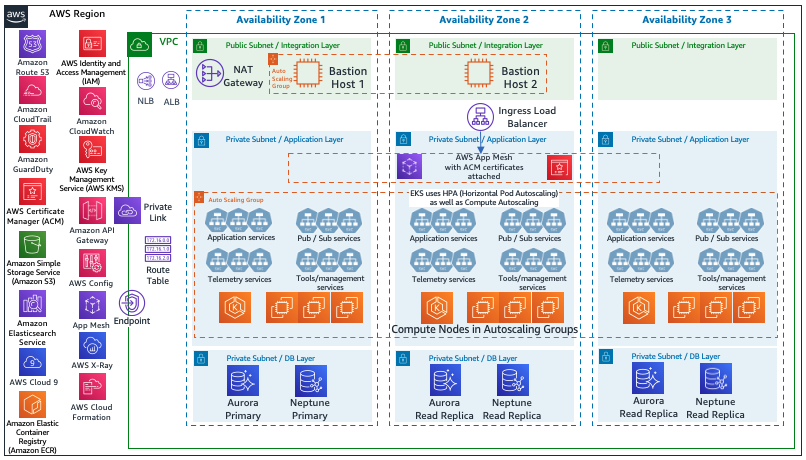
This section presents a service fulfillment architecture on AWS that provides
flexibility, scalability, reliability, and the integration points to enable the customer
journey. As depicted by the following reference architecture, the proposed architecture
enables you to seamlessly integrate with order management, service orchestration, service
assurance, and domain managers across multiple networks and service domains. Services such as
Amazon API Gateway, AWS App Mesh, and Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) provide you with the ability to develop service fulfillment
applications that are fully integrated with service orchestration applications and service
assurance applications, enabling you to eliminate functional duplication and choose
delimitation based on a given technology, network, and service type. For example, Amazon Aurora provides you with a MySQL and
PostgreSQL-compatible relational database that can host inventory data used both in service
fulfillment and orchestration. While your fulfilment can act as a central location of the inventory data
for network services, Amazon Aurora enables you to define read-replicas. This enables you to
support low-latency reading of network services for your service orchestration to speed up
decision-making while providing APIs to govern provisioning requests at the fulfillment level.
Amazon EKS provides you with the ability to run
Kubernetes applications that scale. To achieve high availability and resiliency, the pods are
distributed across multiple AZs. AWS' purpose-built database services for Graph DB, NoSQL,
and RDBMS, can further help you achieve your goals. An ingress gateway fronts the
communication to and between your applications and uses the AWS native service AWS App Mesh to provide application networking, and
offer end-to-end visibility and high availability.
AWS Step Functions allows you to seamlessly integrate service fulfillment applications with order
management applications, allowing you to execute a multitude of events (such as dependency
verification, dates, location validation, breaking tasks into sub-tasks, and executing the
configuration on an individual network function).
Dynamic service inventory management is done by using Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) and graph databases
to depict the relationship of a service, its status, and the underlying provisioned resources.
Fulfilment tracking in near real-time is enabled by Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) and Amazon Simple Queue Service(SQS). It
provides you with the mechanisms to control how fulfillment operations interact within the
service fulfilment stack as well as between other applications in the OSS Stack.