Step 3: Test Connectivity to the Oracle DB Instance and Create the Sample Schema
After the AWS CloudFormation stack has been created, test the connection to the Oracle DB instance by using SQL Workbench/J and then create the HR sample schema.
-
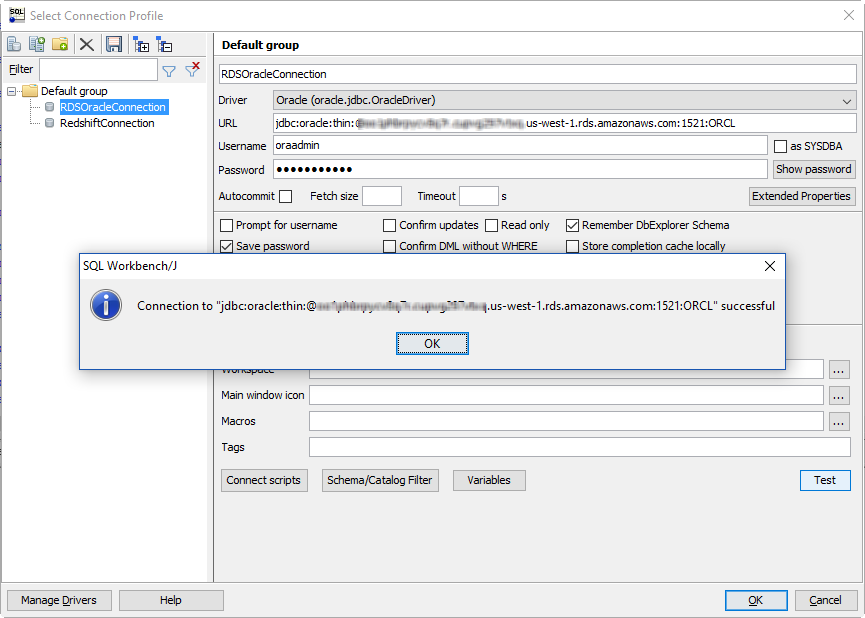
In SQL Workbench/J, choose File, then choose Connect window. Create a new connection profile using the following information.
Parameter Action New profile name
Enter
RDSOracleConnection.Driver
Choose
Oracle (oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver).URL
Use the OracleJDBCConnectionString value you recorded when you examined the output details of the DMSdemo stack in a previous step.
Username
Enter
oraadmin.Password
Enter
oraadmin123. -
Test the connection by choosing Test. Choose OK to close the dialog box, then choose OK to create the connection profile.
Note
If your connection is unsuccessful, ensure that the IP address you assigned when creating the AWS CloudFormation template is the one you are attempting to connect from. This issue is the most common one when trying to connect to an instance.
-
Create the SH schema you will use for migration using a custom
Oraclesalesstarschema.sqlSQL script. To obtain this script, do the following:-
Download the following archive to your computer:
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/dms/latest/sbs/samples/dms-sbs-RDSOracle2Redshift.zip -
Extract the
Oraclesalesstarschema.sqlSQL script from the archive. -
Copy and paste the
Oraclesalesstarschema.sqlfile into your current directory.-
Open the SQL script in a text editor. Copy the entire script.
-
In SQL Workbench/J, paste the SQL script in the Default.wksp window showing Statement 1.
-
Choose SQL, then choose Execute All.
-
-
-
Verify the object types and count in SH Schema were created successfully by running the following SQL query.
Select OBJECT_TYPE, COUNT(*) from dba_OBJECTS where owner='SH' GROUP BY OBJECT_TYPE;
The results of this query should be similar to the following.
OBJECT_TYPE | COUNT(*) ----------------+--------- INDEX PARTITION | 40 TABLE PARTITION | 8 TABLE | 5 INDEX | 15
-
Verify the total number of tables and number of rows for each table by running the following SQL query.
Select table_name, num_rows from dba_tables where owner='SH' order by 1;
The results of this query should be similar to the following.
TABLE_NAME | NUM_ROWS -----------+--------- CHANNELS | 5 CUSTOMERS | 8 PRODUCTS | 66 PROMOTIONS | 503 SALES | 553
-
Verify the integrity in tables. Check the number of sales made in different channels by running the following SQL query.
Select b.channel_desc,count(*) from SH.SALES a,SH.CHANNELS b where a.channel_id=b.channel_id group by b.channel_desc order by 1;
The results of this query should be similar to the following.
CHANNEL_DESC | COUNT(*) -------------+--------- Direct Sales | 710 Internet | 52 Partners | 344
Note
The preceding examples are representative of validation queries. When you perform actual migrations, you should develop similar queries to validate the schema and the data integrity.