Simple single zone architecture with an internet gateway using AWS Network Firewall
This topic provides a high-level view of a simple VPC configuration using an internet gateway and AWS Network Firewall. It describes the basic route table modifications that are required to use the firewall.
Single zone architecture with internet gateway and no firewall
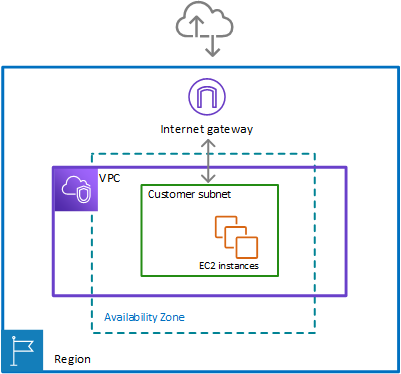
The following figure depicts a simple VPC configuration with a single customer subnet, and no firewall. The VPC has an internet gateway for internet access. All incoming and outgoing traffic routes through the internet gateway to the subnet.
Single zone architecture with internet gateway and the Network Firewall firewall
The following figure depicts a simple VPC configuration with the firewall and the subnet association in place. The VPC has an internet gateway for internet access. All incoming and outgoing traffic for the VPC routes through the firewall.
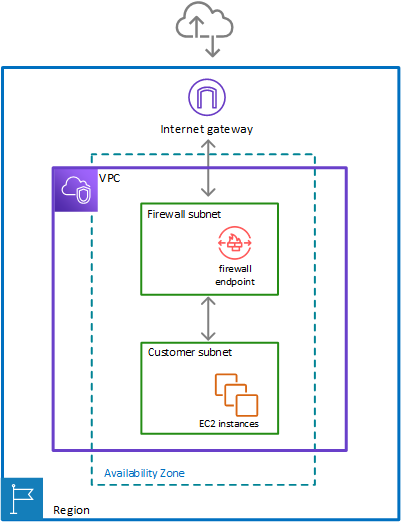
To include the firewall in your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud VPC, you need to modify the VPC route tables so that traffic between the customer subnets and the internet passes through the firewall, for both incoming and outgoing traffic.
Note
For information about managing route tables for your VPC, see Route tables in the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud User Guide.
Example route tables in the single zone architecture with no firewall
The following figure depicts the route tables that provide the correct flow of traffic for a single Availability Zone without a firewall:
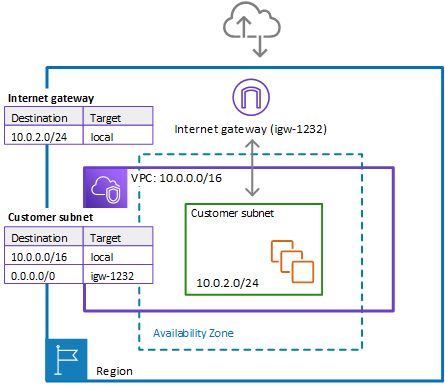
In the preceding figure, the route tables enforce the following traffic flows:
-
Internet gateway route table – Routes traffic that's destined for the customer subnet (range
10.0.2.0/24) tolocal. The customer subnet shows the private IP address range behind the publicly assigned address. The subnet has public addresses assigned, which are either auto-generated or assigned via Elastic IP address. Within a VPC, only private IP addresses are used for communication. -
Customer subnet route table – Routes traffic that's destined for anywhere inside the VPC (
10.0.0.0/16) to the local address. Routes traffic that's destined for anywhere else (0.0.0.0/0) to the internet gateway (igw-1232).
Example route tables in the single zone architecture with the firewall
The following figure depicts the same installation with the Network Firewall firewall added and the route tables changed to include the firewall. The route tables direct traffic between the customer subnet and the internet gateway through the firewall endpoint:
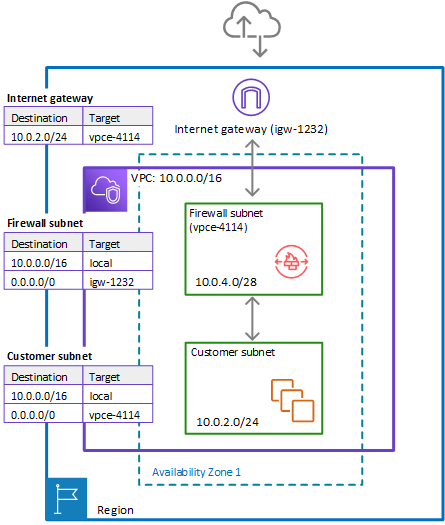
In the preceding figure, the route tables enforce the following traffic flows:
-
Internet gateway route table – Routes traffic that's destined for the customer subnet (range
10.0.2.0/24) to the firewall subnet (namedvpce-4114in the figure). The customer subnet shows the private IP address range behind the publicly assigned address. The subnet has public addresses assigned, which are either auto-generated or assigned via Elastic IP address. Within a VPC, only private IP addresses are used for communication. -
Firewall subnet route table – Routes traffic that's destined for anywhere inside the VPC (
10.0.0.0/16) to the local address. Routes traffic that's destined for anywhere else (0.0.0.0/0) to the internet gateway (igw-1232). -
Customer subnet route table – Routes traffic that's destined for anywhere inside the VPC (
10.0.0.0/16) to the local address. Routes traffic that's destined for anywhere else (0.0.0.0/0) to the firewall subnet (vpce-4114).Before the firewall inclusion, the customer subnet route table routed the
0.0.0.0/0traffic toigw-1232.