Workflow for orchestration
A central orchestrator agent uses an LLM to plan, decompose, and delegate subtasks to specialized worker agents or models, each with a specific role or domain expertise. This mirrors human team structures and supports emergent behavior across multiple agents.
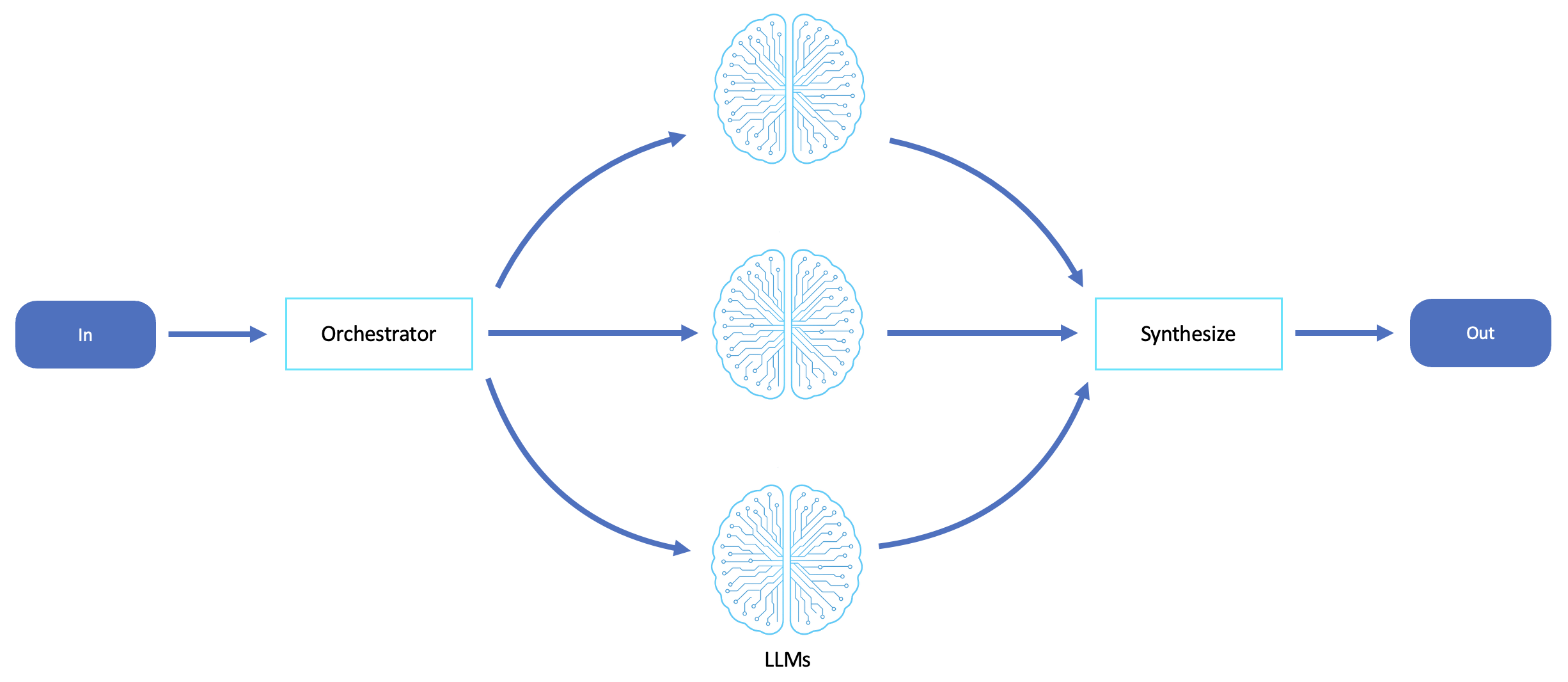
The orchestration workflow is ideal for scenarios that are complex, hierarchical, or multidisciplinary, requiring structured decomposition and specialized execution. It is particularly well-suited to tasks that require division of labor, where different subcomponents of a task are best handled by agents with distinct capabilities, knowledge, or toolsets.
This workflow is particularly effective when:
-
Tasks can be divided into subtasks that vary in scope, type, or reasoning (for example, plan, research, implement, and test).
-
An LLM or meta-agent must coordinate other agents, monitor progress, and synthesize results.
-
You want to modularize agent responsibilities, enabling scalability, reuse, and specialized tuning.
-
The system requires role-based behavior, mimicking how human teams (for example, project managers, developers, and reviewers) operate in collaboration.
Orchestration is ideal for multiturn planning agents, software development copilots, enterprise process agents, and autonomous project executors. It is especially useful when implementing multi-agent systems that require centralized task breakdown but distributed execution logic, enabling extensibility and more explainable behavior across agent layers.
Capabilities
-
Orchestrator performs goal meta-reasoning
-
Worker agents may include tool access, memory, or domain-specific prompting
-
Can be hierarchical (that is, multilevel task delegation)
Common use cases
-
Project managers, coordinating researchers, writers, and quality-assurance agents
-
Coding copilots that combine planning, executing, and testing
-
Agents that supervise toolchains or API access patterns