5-I framework for an AI-powered software development experience
The 5-I framework provides a structured approach for software development teams to effectively integrate generative AI into their development practices. It helps you establish a robust foundation for using generative AI throughout the SDLC. It also helps you set up the right development practices, workflows, and mindsets to fully harness the potential of generative AI.
This section contains the following topics:
Framework overview
The 5-I framework is built around five key dimensions: Investigate, Integrate, Interact, Iterate, and Impact. Each dimension represents a critical area where generative AI significantly enhances the software development process. By strategically integrating generative AI across these dimensions, the framework addresses the evolving needs of modern software development. It can reduce cognitive load and amplify creative potential. It recognizes that the ideal development experience is not just about tools—it's about creating an environment where AI seamlessly enhances human capabilities at every stage.
The following diagram shows the five dimensions of AI-powered software development. For each dimension, it shows where you can integrate generative AI in order to drive efficiency and innovation.
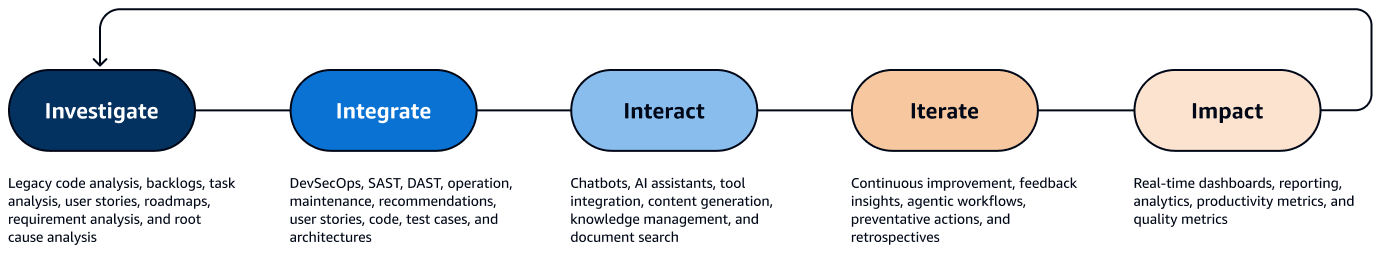
The following are the five dimensions in the framework:
-
Investigate – Enhance every analytical task in your software development process with generative AI. Use generative AI to understand requirements, process vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and generate insights that might be beyond human capacity or would take significantly longer to produce. These insights help you make more informed decisions, quickly identify improvement opportunities, and more efficiently deliver high-quality software. Generative AI can be an intelligent partner for the analytical processes throughout the SDLC. By harnessing generative AI, you apply in-depth analysis to critical areas, such as requirements gathering, legacy codebase examination, and product backlog optimization. For example, product owners can use generative AI to analyze user journeys or requirements before creating user stories. Development teams can uncover inefficiencies and identify optimization opportunities in existing codebases. DevOps engineers can apply root cause analysis to quickly diagnose performance issues or security vulnerabilities, which can improve reliability.
-
Integrate – Integrate generative AI to automate a wide range of tasks and processes across the entire SDLC. This includes automatically generating code snippets, test cases, architectural designs, user stories, and deployment pipelines. By automating these typically manual tasks, teams can focus on more strategic and innovative work, which drives faster time to market and high-quality applications. The Integrate dimension represents a paradigm shift in software development, where AI becomes an integral part of the development process. It works alongside your software development team to enhance productivity, improve quality, and drive innovation. This results in faster time to market. It challenges your software development teams to regularly assess their processes and workflows by asking at each step: "Can this be automated?"
-
Interact – Use generative AI-powered assistants to provide your team with instant, contextual support across a range of tasks and queries. These intelligent assistants act as knowledgeable collaborators that draw from a vast repository of information. They can answer coding questions, offer design suggestions, explain standard operating procedures, and help troubleshoot complex issues. Integrating these AI assistants into the development workflow boosts productivity and fosters a more collaborative, problem-solving environment.
-
Iterate – Use generative AI to enable rapid, data-driven adjustments throughout the SDLC. You can continuously analyze data from sources such as customer feedback, usage patterns, market trends, and team performance metrics in order to make informed decisions quickly. This adaptability refines your software development from a static, predefined process into a fluid, responsive approach. It manifests in various ways, including dynamic prioritization of backlogs, flexible resource allocation, adaptive testing strategies, evolving documentation, and responsive deployment processes. For example, product managers can use AI-generated insights to reorder their backlogs, integrating new customer requirements and market trends in near real time. DevOps engineers can adapt deployment plans and infrastructure configurations based on performance analytics, making sure that applications remain resilient and optimized. Development teams can translate feedback from sprint retrospectives into actionable improvements for the next iteration, driving a culture of continuous process enhancement.
-
Impact – Apply generative AI to assess the effectiveness and performance of your software development process. By using AI-powered analytics and metrics, you gain deeper insights into development efficiency, code quality, user engagement, and overall application performance. This data-driven approach helps you make informed decisions, optimize your development workflows, and continuously improve the quality and user experience of your applications. When assessing software team productivity, generative AI analyzes various data points, such as code commit frequency, issue resolution times, release velocity, feature delivery rates, and more. It can also evaluate the quality of code reviews, the effectiveness of collaboration tools, and the impact of different development practices on the overall team output. By correlating these metrics with project outcomes, the AI identifies patterns and trends that human analysts might miss, and they can provide actionable insights that boost team productivity. Furthermore, generative AI can help you benchmark team performance against industry standards or historical data, offering personalized recommendations for improvement. It can also predict potential bottlenecks or risks in the development process so that you can take proactive measures.
Integrating with the software development lifecycle
The SDLC consists of multiple phases, which can differ from organization to organization. Commonly, these phases include the following: requirements and planning, design and architecture, implementation, testing, deployment, and operation and maintenance.
The following table maps the dimensions of the 5-I framework to the SDLC phases and provides the level of integration for each dimension.
| Framework dimension | Requirements and planning | Design and architecture | Implementation | Testing | Deployment | Operation and maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investigate | High | Low | Low | Low | Low | Medium |
| Integrate | Medium | Medium | High | Medium | High | High |
| Interact | High | High | High | Medium | Medium | High |
| Iterate | Medium | Low | Low | Low | Low | Medium |
| Impact | High | Medium | High | Low | High | High |
The levels of integration vary from high to low. The mapping reveals key focus areas for each dimension. For instance, Investigate shows high intensity in the requirements and planning phase. Integrate demonstrates high intensity in the implementation, deployment, and operation and maintenance phases.
By using this mapping, you can prioritize your efforts effectively. We recommend that you focus on high, then medium, and then low. Make sure that you adopt a balanced and impactful approach that enhances the software development experience with generative AI.