This whitepaper is for historical reference only. Some content might be outdated and some links might not be available.
Design considerations for running Active Directory on EC2 instances
If you cannot use AWS Managed Microsoft AD and you have Windows workloads you want to deploy on AWS, you can still run Active Directory on EC2 instances in AWS. Depending on the number of Regions where you are deploying your solution, your Active Directory design may slightly differ. The following section provides a deployment guide and recommendation on how you can deploy Active Directory on EC2 instances in AWS.
Single Region deployment
This deployment scenario is applicable if you are operating in a single Region or you do not need Active Directory to be in more than a single Region. The deployment options or architecture patterns are not significantly different whether you are operating in a single VPC or multiple VPCs. If you are using multiple VPCs, you must ensure that network connectivity between the VPCs is available through VPC peering, VPN, or AWS Transit Gateway.
The following diagrams depict how Active Directory can be deployed in a single Region in a single VPC or multiple VPCs.
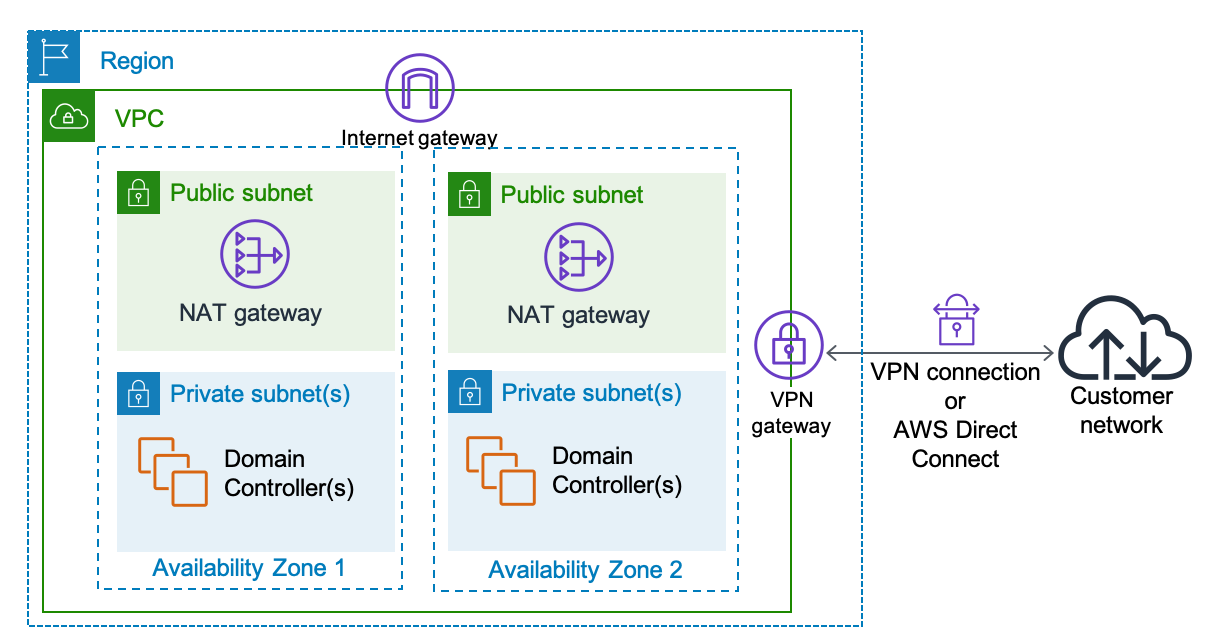
Figure 7: Deploying Active Directory on EC2 instances in a single Region for single VPC

Figure 8: Deploying Active Directory on EC2 instances in a single Region for multiple VPCs
Consider the following points when deploying Active Directory in this architecture:
-
We recommend deploying at least two domain controllers (DCs) in a Region. These domain controllers should be placed in different AZs for availability reasons.
-
DCs and other non-internet facing servers should be placed in private subnets.
-
If you require additional DCs due to performance, you can add more DCs to existing AZs or deploy to another available AZ.
-
Configure VPCs in a Region as a single Active Directory site and define Active Directory subnets accordingly. This configuration ensures that all of your clients correctly select the closest available DC.
-
If you have multiple VPCs, you can centralize the Active Directory services in one of the existing VPCs or create a shared services VPC to centralize the domain controllers.
-
You must ensure you have highly available network connectivity between VPCs, such as VPC peering. If you are connecting the VPCs using VPNs or other methods, ensure connectivity is highly available.
-
If you want to use your self-managed Active Directory credentials to access AWS Services or third-party services, you can integrate your self-managed AD with AWS IAM and AWS Single Sign-On using AWS AD Connector or AWS Managed AD through a trust relationship. In these cases, AD Connector or AWS Managed AD must be deployed in the management account of your organization.
Multi-region/global deployment of self-managed AD
If you are operating in more than one Region and require Active Directory to be available in these Regions, use the multi-region/global deployment scenario. Within each of the Regions, use the guidelines for single Region deployment as all of the single Region best practices still apply.
The following diagrams depict how Active Directory can be deployed
in multiple Regions. In this example, we are showing Active
Directory deployed in three Regions that are interconnected to
each other using cross-Region VPC peering. In addition, these
Regions are also connected to the corporate network using
AWS Direct Connect

Figure 9: Deploying Active Directory on EC2 instances in multiple Regions with multiple VPCs
Consider the following recommendations when deploying Active Directory in this architecture:
-
Deploy at least two domain controllers in each Region. These domain controllers should be placed in different AZs for availability reasons.
-
Configure VPCs in a region as a single Active Directory site and define Active Directory subnets accordingly. This configuration ensures all of your clients will correctly select the closest available domain controller.
-
Ensure robust inter-Region connectivity exists between all of the Regions. Within AWS, you can leverage cross-Region VPC peering to achieve highly available private connectivity between the Regions. You can also leverage the Transit VPC solution to interconnect multiple regions.
Designing Active Directory sites and services topology
It’s important to define Active Directory sites and subnets
correctly to avoid clients from using domain controllers that are
located far away as this would cause increased latency. See
How
Domain Controllers are Located in Windows
Follow these best practices for configuring sites and services:
-
Configure one Active Directory site per AWS Region. If you are operating in multiple AWS Regions, we recommend configuring one Active Directory site for each of these Regions.
-
Define the entire VPC as a subnet and assign it to the Active Directory site defined for this Region.
-
If you have multiple VPCs in the same Region, define each of these VPCs as separate subnets and assign it to the single Active Directory site set up for this Region. This setup allows you to use domain controllers in that Region to service all clients in that region.
-
If you have enabled IPv6 in your Amazon VPC, create the necessary IPv6 subnet definition and assign it to this Active Directory site.
-
Define all IP address ranges. If clients exist in undefined IP address ranges, the clients might not be associated with the correct Active Directory site.
-
If you have reliable high-speed connectivity between all of the sites, you can use a single site link for all of your AD sites and maintain a single replication configuration.
-
Use consistent sites names in all AD forests connected by trusts.