High availability and security best practices for AWS Launch Wizard for SQL Server
The application architecture created by AWS Launch Wizard supports AWS best practices for high
availability and security as promoted by the AWS Well-Architected Framework
High availability
Using Amazon EC2, you can set the location of instances in multiple locations composed of AWS Regions and Availability Zones. Regions are dispersed and located in separate geographic areas. Availability Zones are distinct locations within a Region that are engineered to be isolated from failures in other Availability Zones. Availability Zones provide inexpensive, low-latency network connectivity to other Availability Zones in the same Region.
When you launch your instances in different Regions, you can set your SQL Server Always On application to be closer to specific customers, or to meet legal or other requirements. When you launch your instances in different Availability Zones, you can protect your SQL Server Always On applications from the failure of a single location.
Automatic failover
When you deploy AWS Launch Wizard with the default parameters, it configures a two-node, automatic failover cluster with a file share witness. An Always On Availability Group is deployed on this cluster with two availability replicas, as shown in the following diagram.
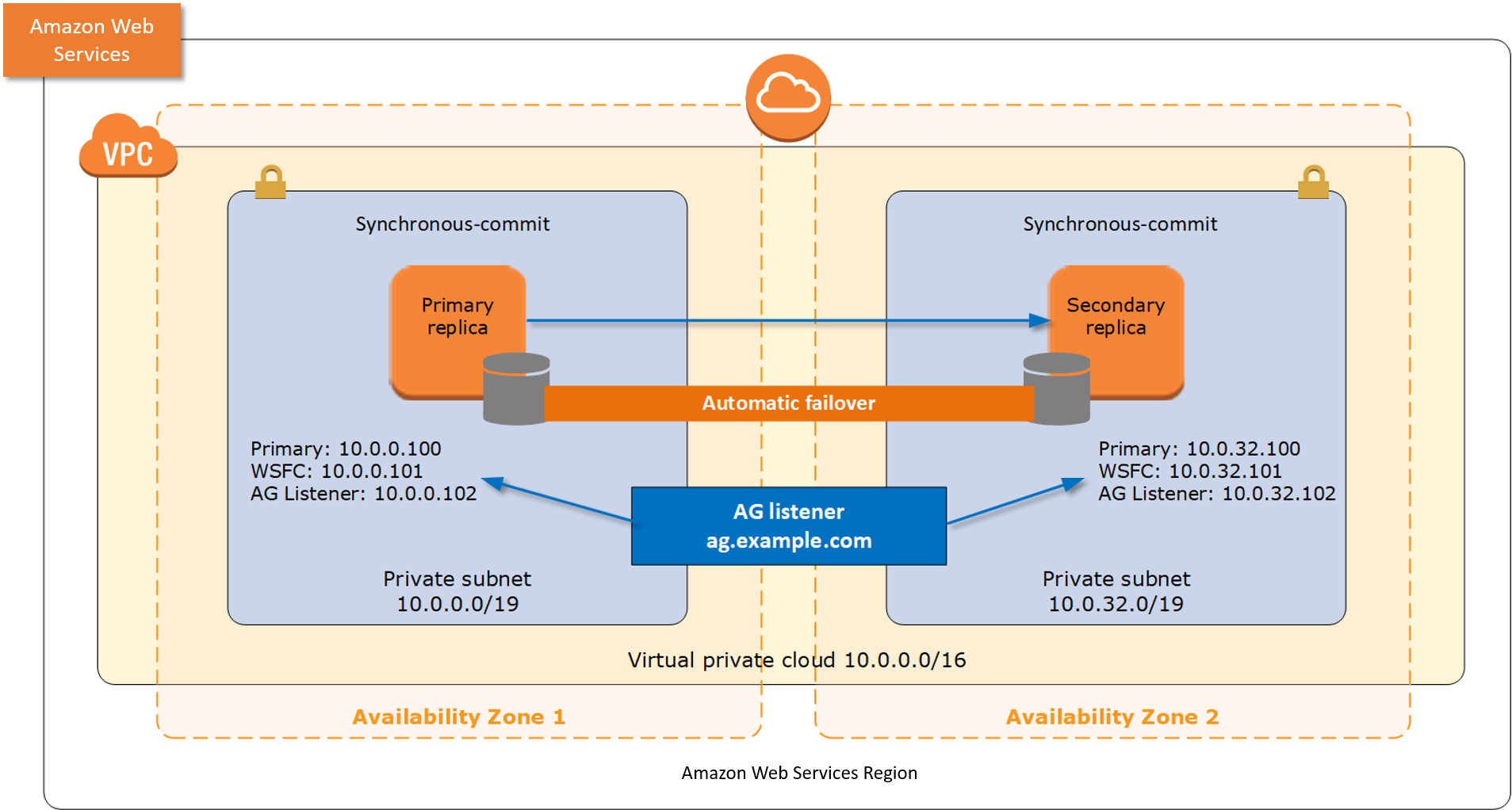
Launch Wizard implementation supports the following scenarios:
-
Protection from the failure of a single instance
-
Automatic failover between the cluster nodes
-
Automatic failover between Availability Zones
The default implementation of Launch Wizard does not provide automatic failover in every case.
For example, the failure of Availability Zone 1, which contains the primary node and
file share witness, would prevent automatic failover to Availability Zone 2 because the
cluster would fail as it loses quorum. In this scenario, you could follow manual
disaster recovery steps that include restarting the cluster service and forcing quorum
on the second cluster node (for example, WSFCNode2) to restore application availability.
Launch Wizard also provides an option to deploy to three Availability Zones. This deployment
option can mitigate the loss of quorum if a single node fails. However, you can select
this option only in AWS Regions that include three or more Availability Zones. For a
current list of supported Regions, see AWS Global
Infrastructure
Security groups and firewalls
Launch Wizard creates a number of security groups and rules for you. When Amazon EC2 instances are launched, they must be associated with a security group, which acts as a stateful firewall. You have complete control over the network traffic entering or leaving the security group. You can also build granular rules that are scoped by protocol, port number, and source or destination IP address or subnet. By default, all outbound traffic from a security group is permitted. Inbound traffic, on the other hand, must be configured to allow the appropriate traffic to reach your instances.
The Securing the Microsoft Platform on Amazon Web Services
Domain controllers and member servers require several security group rules to allow traffic for services such as AD DS replication, user authentication, Windows Time services, and Distributed File System (DFS), among others. The WSFC nodes running SQL Server must permit several additional ports to communicate with each other. Finally, instances launched into the application server tier must establish SQL client connections to the WSFC nodes.
In addition to security groups, the Windows Firewall must also be modified on the SQL Server instances. During the bootstrapping process, a script runs on each instance that opens the TCP ports 1433, 1434, 4022, 5022, 5023, and 135 on the Windows Firewall.