Coding agents
Coding agents can reason about programming tasks, generate or modify code, and interact with developer environments, such as IDEs and CLIs. These agents combine natural-language understanding with structured reasoning to assist, augment, and automate software development, ranging from function generation to bug fixing and test authoring.
Unlike autocomplete tools, coding agents actively interpret user goals, query the development environment for context (for example, it opens files and traces errors), identify requirements, and then propose and perform actions.
Architecture
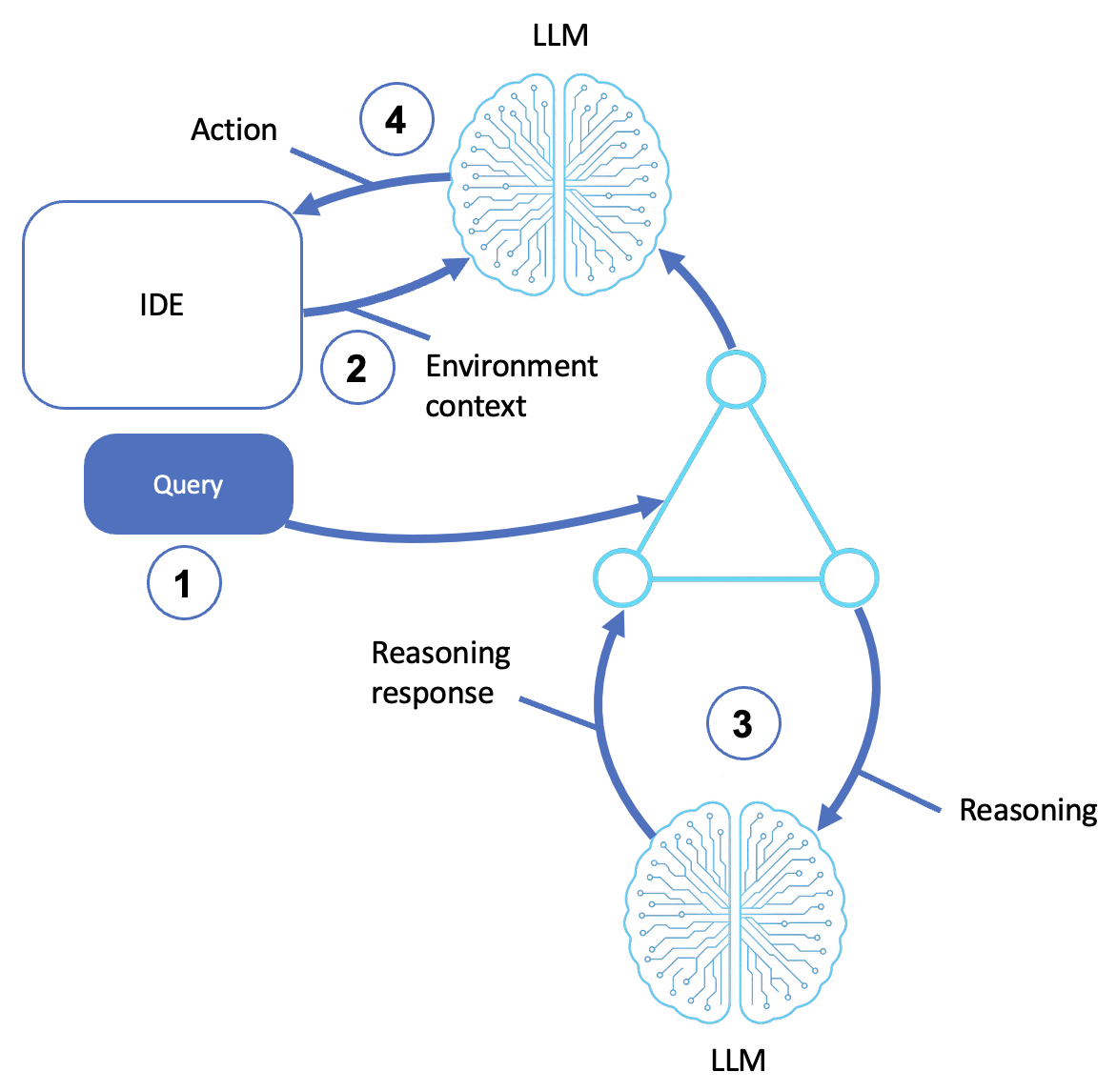
A coding-agent pattern is shown in the following diagram:
Description
-
Receives query
-
The user provides natural-language instructions through a command palette, chat window, or CLI (for example, "Add logging to this function" or "Refactor for readability").
-
-
Extracts environment context
-
The agent gathers context from the IDE, including active files, cursor position, code snippets and symbol tables.
-
It outputs error messages, test results, and outputs from other agents.
-
-
LLM reasoning
-
The agent sends a prompt, including the query and environmental context, to an LLM.
-
The LLM performs a reasoning pass to determine the following:
-
What needs to change
-
How to generate a solution
-
Any refactoring, rewriting, or coding steps
-
-
-
Executes actions
-
The LLM returns the output to the agent and imports it into the IDE or runtime environment.
-
This may include inserting or modifying code, generating comments or documentation, and triggering downstream build, test, and linting tasks.
-
Capabilities
-
High-contextual awareness (for example, IDE state, cursor, and syntax tree)
-
Iterative reasoning of goals and feedback
-
Optional code planning and action separation (for example, first reason and then act)
-
Works in synchronous or asynchronous developer workflows
Common use cases
-
Code generation from task descriptions
-
Code refactoring and optimization
-
Test-case generation and validation
-
Error explanations and debugging
-
Documentation assistants
-
Paired programming copilots
Implementation guidance
-
You can build this pattern using the following tools and AWS services:
-
Amazon Bedrock for LLM-driven generation and reasoning
-
Amazon Q Developer for coding suggestions and completions
-
AWS Lambda or Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) for running and testing sandbox environments
-
AWS Cloud9, VS Code extensions, or custom IDE integrations to host and evaluate context
-
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) for storing intermediate prompts, responses, and revision history
Summary
Coding agents are new AI-powered development tools that are capable of interpreting natural language, analyzing context, generating multistep code changes, and integrating with the software development lifecycle.