Workflow for routing
In the routing pattern, a classifier or router agent uses an LLM to interpret the intent or category of a query, then routes the input to a specialized downstream task or agent.
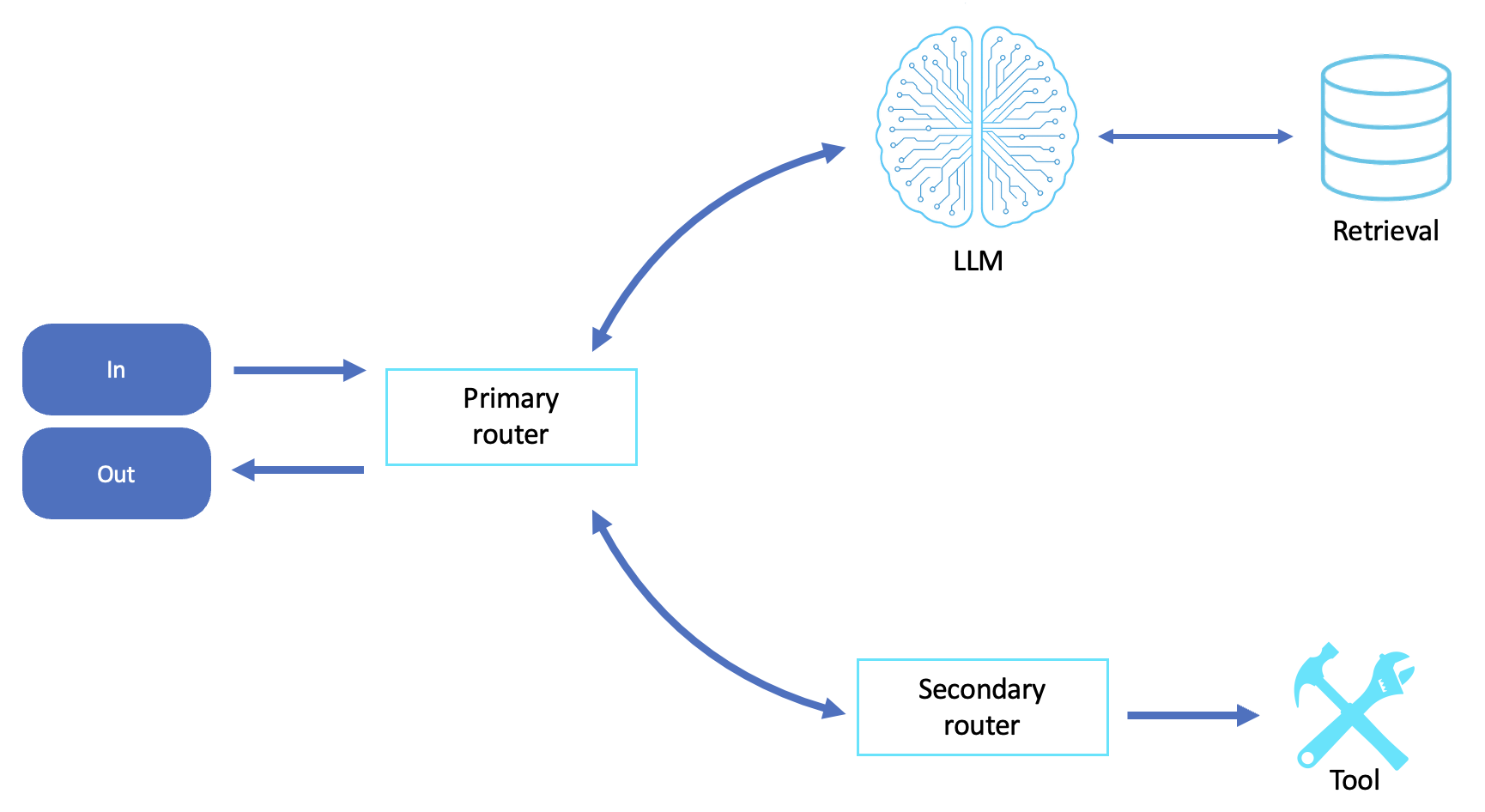
The Routing workflow is used in scenarios where an agent must quickly classify input intent, task type, or domain, and then delegate the request to a specialized subagent, tool, or workflow. It is especially useful in capability agents, such as those that serve as general assistants, front doors to enterprise functions, or user-facing AI interfaces that span domains.
Routing is particularly effective when:
-
Triaging requests across a variety of tasks (for example, search, summarization, booking, calculations).
-
Inputs must be preprocessed or normalized before entering more specialized workflows.
-
Different input types (for example, images vs. text, structured vs. unstructured queries) require custom handling.
-
An agent is acting as a conversational switchboard, delegating tasks to specialized agents or microservices.
-
This workflow is common in domain-specific copilots, customer-support bots, enterprise service routers, and multimodal agents, where intelligent dispatching determines both the quality and efficiency of agent behavior.
Capabilities
-
A first-pass LLM acts as a dispatcher
-
Routes can invoke distinct workflows or even other agent patterns
-
Supports modular expansion of capabilities
Common use cases
-
Multidomain assistants ("is this a legal, medical, or financial question?")
-
Decision trees enhanced with LLM reasoning
-
Dynamic tool selection (for example, search vs. code generation)