Observer and monitoring agents
Observer and monitoring agents passively observe systems, environments, and interactions to detect patterns, generate insights, and trigger actions. As intelligent watchers, they enhance alerts, diagnostics, and audits without directly initiating behavior.
These agents excel where traditional monitoring lacks adaptability or reasoning, particularly for AI-in-the-loop monitoring, anomaly detection, compliance oversight, and security intelligence. Observer agents are event listeners that continuously monitor system telemetry and user interactions. The agent depends on perception, interpretation, and conditional escalation or reporting.
Architecture
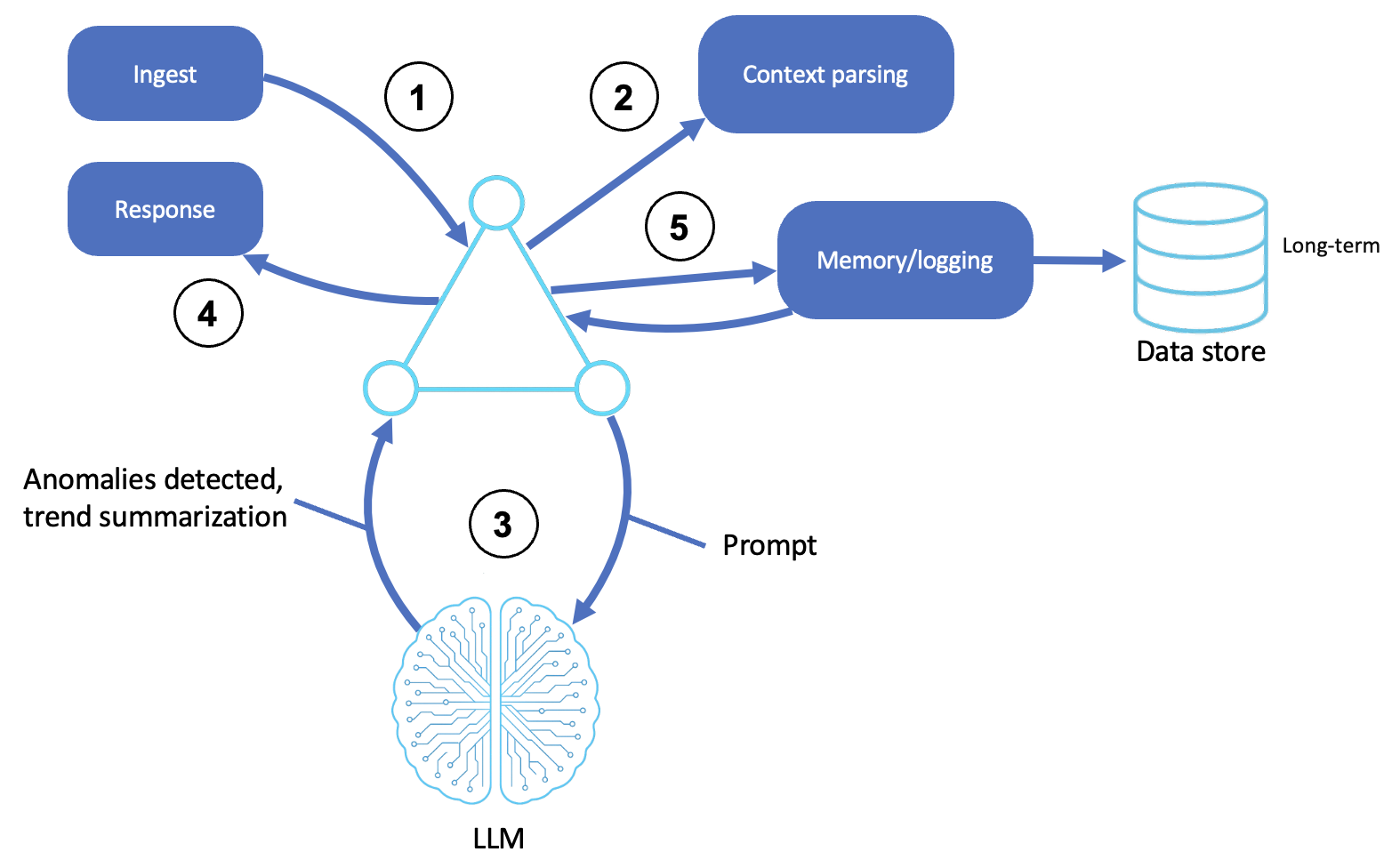
Description
-
Ingest telemetry
-
The agent receives input from one or more system sources, such as the following:
-
Logs (application, infrastructure, security)
-
Metrics (performance, latency, usage)
-
Events (API calls, user actions, sensor data)
-
-
-
Parse context
-
Raw input is parsed, structured, and enriched with metadata, such as a timestamp, actor identity, system state, and trace ID.
-
-
Reasons using LLM
-
The agent uses an LLM or logic module to interpret parsed inputs by identifying anomalies, summarizing trends, and correlating across distributed traces or time windows.
-
-
Classify or alert
-
The agent determines if the observed behavior warrants the following:
-
An alert or escalation
-
A report or dashboard update
-
A response trigger (for example, automatic remediation and policy enforcement)
-
-
-
Log memory or feedback loops
-
The agent stores events and decisions for long-term learning, audits, or future reference for other agents.
-
Capabilities
-
Passive and noninvasive (agent doesn't directly act)
-
Highly scalable and asynchronous
-
AI-driven correlation across noisy or distributed signals
-
Supports audit, compliance, and real-time insight
-
Can feed downstream agents or human workflows
Common use cases
-
AI-augmented observability for microservices and APIs
-
Monitoring for model drift, policy violation, or out-of-band behavior
-
Customer activity analysis or interaction summaries
-
Code review agents that monitor commits or deployments
-
Security or compliance log monitoring using LLM reasoning
Implementation guidance
You can build an observer and monitoring agent using the following tools and AWS services:
Component |
AWS service |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Event ingestion |
Amazon EventBridge, Amazon CloudWatch Logs, Amazon Kinesis, Amazon S3 |
Ingest structured and unstructured telemetry |
Preprocessing |
AWS Lambda, AWS Glue, AWS Step Functions |
Transform raw data into structured prompts |
Reasoning engine |
Amazon Bedrock, Amazon SageMaker, AWS Lambda |
Analyze events, classify behavior, generate insights |
Storage and memory |
Amazon S3, Amazon DynamoDB, OpenSearch |
Persistent observations, summaries, and outputs |
Alerting and escalation |
Amazon SNS, AWS AppFabric, Amazon EventBridge |
Trigger downstream systems or agents |
The following are additional applications:
-
AWS Security Hub for security log monitoring
-
Amazon QuickSight
for visualizing agent outputs
Summary
Observer and monitoring agents track systems and behaviors in real time. They detect anomalies, audit security, and gather operations intelligence by identifying patterns that humans or rules might overlook. This capability helps create systems that can adapt to changing conditions and make decisions based on comprehensive data analysis.