Speech and voice agents
Speech and voice agents interact with users through spoken dialogue. These agents integrate speech recognition, natural-language understanding, and speech synthesis to enable conversational AI across telephony, mobile, web, and embedded platforms.
Voice agents are particularly effective in hands-free, real-time, or accessibility-driven environments. By combining streaming interfaces with LLM-powered reasoning, they facilitate rich, dynamic interactions that feel natural to users.
Architecture
A speech and voice agent is shown in the following diagram:
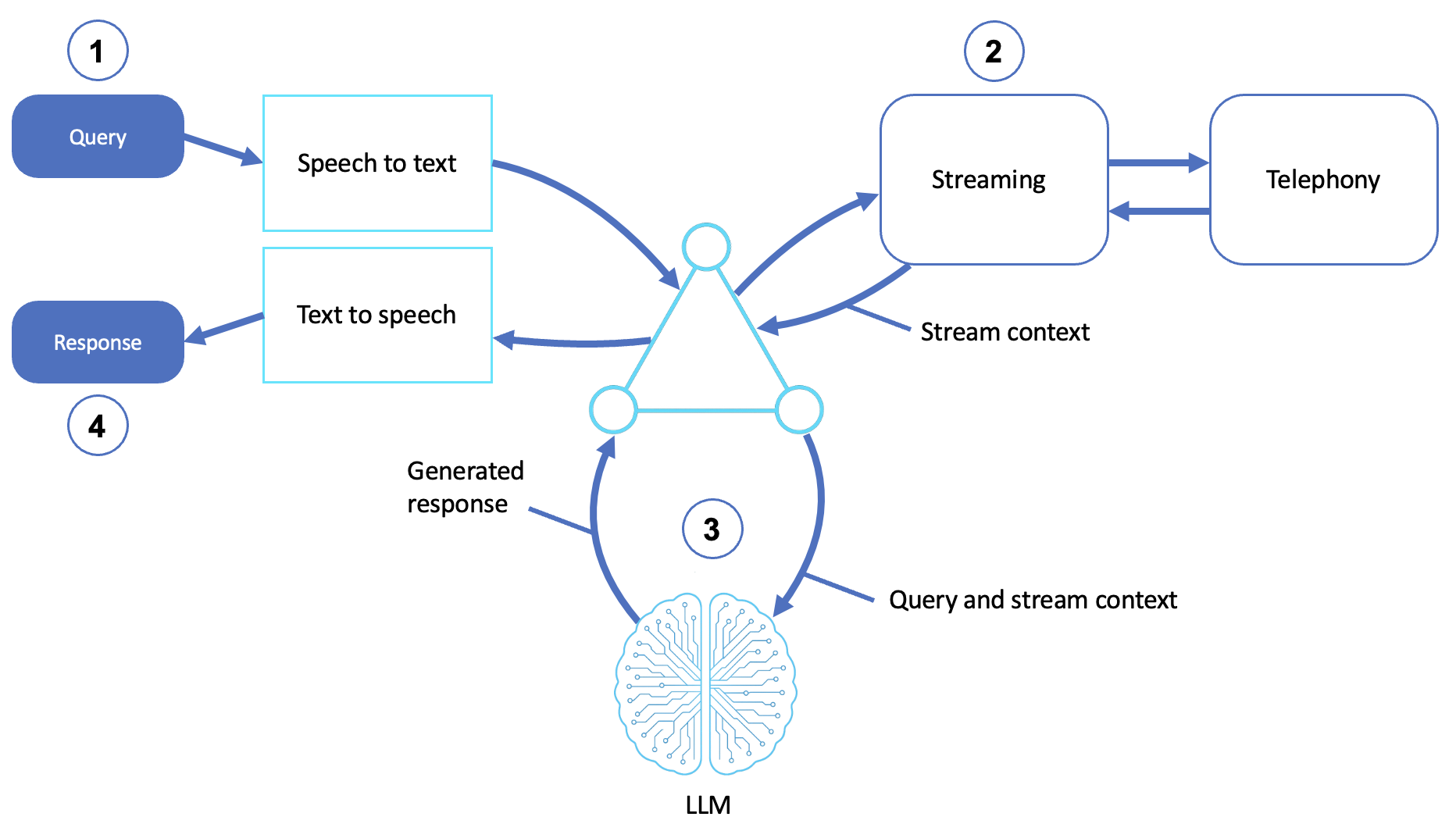
Description
-
Receives a voice query
-
The user voices a request to a phone, microphone, or embedded system.
-
A speech-to-text (STT) module converts the audio to text.
-
-
Integrates streaming and telephony context
-
The agent uses a streaming interface to manage audio I/O in real time.
-
If it's deployed in a contact center or telecom context, telephony integration handles session routing, dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) input, and media transport.
-
Note: DTMF refers to the tones generated when you press buttons on a telephone keypad. In the context of streaming and telephony context integration within voice agents, DTMF is used as a signal input mechanism during a phone call, especially in interactive voice response (IVR) systems. DTMF inputs enable the agent to:
-
Recognize menu selections (for example, "Press 1 for billing. Press 2 for support.")
-
Collect numeric inputs (for example, account numbers, PINs, and confirmation numbers)
-
Trigger workflows or state transitions in call flows
-
Revert from speech to touch-tone when necessary
-
Reasons through LLM stream context
-
The query is sent to the agent, which passes it, along with any session metadata (for example, caller ID, prior context), to an LLM.
-
The LLM generates a response, possibly using a chain-of-thought strategy or multiturn memory if the interaction is ongoing.
-
-
Returns a voice response
-
The agent converts its response to speech using text-to-speech (TTS).
-
It returns audio to the user through a voice channel.
-
Capabilities
-
Real-time speech understanding and generation
-
Multilingual I/O with STT and TTS support
-
Integration with telephony or streaming APIs
-
Session awareness and memory handoff between turns
Common use cases
-
Conversational IVR systems
-
Virtual receptionists and appointment schedulers
-
Voice-driven helpdesk agents
-
Wearable voice assistants
-
Voice interfaces for smart homes and accessibility tools
Implementation guidance
You can build this pattern using the following tools and AWS services:
-
Amazon Lex V2 or Amazon Transcribe for STT
-
Amazon Polly for TTS
-
Amazon Chime SDK, Amazon Connect, or Amazon Interactive Video Service (Amazon IVS) for streaming and telephony
-
Amazon Bedrock for reasoning with Anthropic, AI21, or other foundation models
-
AWS Lambda to connect STT, LLM, TTS, and session context
(Optional) Additional enhancements may include the following:
-
Amazon Kendra or OpenSearch for context-aware RAG
-
Amazon DynamoDB for session memory
-
Amazon CloudWatch Logs and AWS X-Ray for traceability
Summary
Speech and voice agents are intelligent systems that interact through natural conversations. By integrating speech interfaces with LLM reasoning and real-time streaming infrastructure, voice agents enable seamless, accessible, and scalable interactions.