Tool-based agents for calling functions
Tool-based agents extend the capabilities of reasoning agents by invoking external functions or APIs to complete tasks that go beyond language-only reasoning. This pattern uses an LLM to decide which tool to use and then generates call arguments and incorporates a tool's output into its reasoning loop.
This pattern enables agents to act rather than just providing responses. The tool interface represents any callable capability, ranging from arithmetic calculations and database lookups to external APIs and cloud services.
Architecture
A tool-based agent for calling functions is shown in the following diagram:
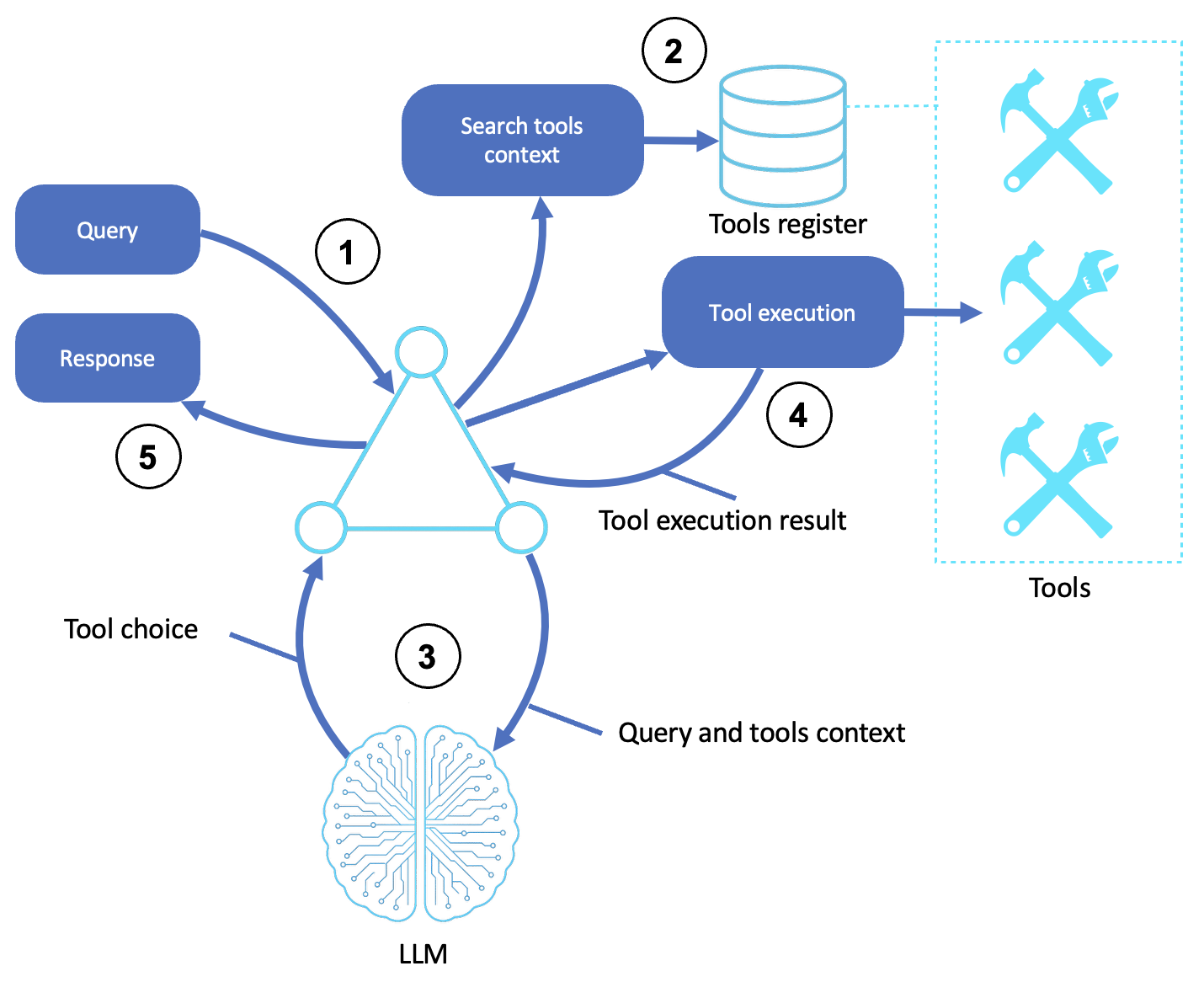
Description
-
Receives query
-
The agent receives a natural-language query or task from the user or calling system.
-
-
Searches for tools
-
The agent uses internal metadata or a tool registry to search for available tools, schemas, and relevant capabilities.
-
-
Selects and invokes tools
-
The LLM receives the query and tool metadata (for example, function names, input types, and descriptions) in its prompt.
-
It chooses the most relevant tool, constructs input arguments, and returns a structured function call.
-
-
Runs the chosen tool
-
The agent shell or tool runner executes the selected function and returns the result (for example, an API output, database value, or computation).
-
-
Returns a response
-
The LLM passes results to the agent, either directly or as part of an updated prompt. It then returns a natural-language result.
-
Capabilities
-
Dynamic tool selection based on task context
-
Schema-based prompting (OpenAPI, JSON schema, AWS function interface)
-
Results interpretation and chaining of outputs into reasoning
-
Stateless or session-aware operations
Common use cases
-
Virtual assistants with external data access
-
Financial calculators and estimators
-
API-based knowledge workers
-
LLMs that invoke AWS Lambda, Amazon SageMaker endpoints, and SaaS services
Implementation guidance
Use the following to create tool-based agents for calling functions:
-
Amazon Bedrock with function-calling support (Anthropic Claude)
-
AWS Lambda as a tool-execution backend
-
Amazon API Gateway or AWS Step Functions for tool orchestration
-
Amazon DynamoDB or Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) for context-aware tool metadata
-
Amazon EventBridge pipelines or AWS Step Functions that map states to route outputs
Summary
Tool-based function-calling agents represent a shift from understanding language to performing actions. These agents invoke dynamic, context-aware tools while maintaining LLM reasoning, transforming passive assistants into systems that complete tasks, access services, and integrate business operations. This pattern is an important component of agentic AI in enterprise settings, especially when combined with declarative schemas, authorization frameworks, and multi-agent systems.