AWS DMS
AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) provides ongoing replication of data, keeping the source and target databases in sync. By using AWS DMS as a DR option, you can establish synchronous replication with minimal recovery point objective (RPO). The RPO depends on redo or transaction log generation and network transfer time.
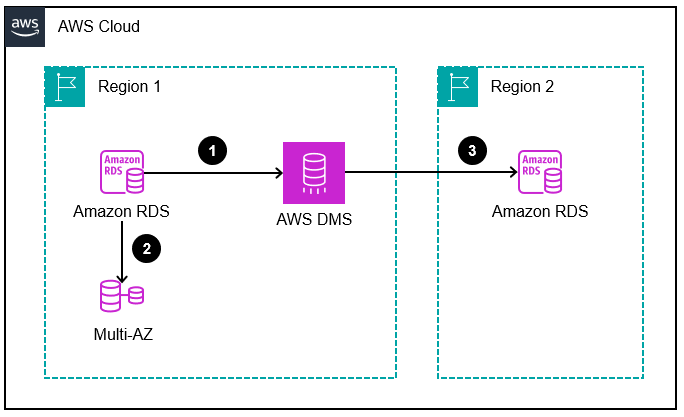
The following diagram shows the ongoing replication of data from the primary Region to the standby Region by using AWS DMS.
-
In the primary Region, data is copied from the Amazon RDS DB instance to AWS DMS.
-
The Amazon RDS database in the primary Region also uses a Multi-AZ deployment.
-
From AWS DMS, data is loaded onto the standby Amazon RDS database in the secondary Region.
When choosing AWS DMS as a DR option, take note of the following considerations:
-
This is a cost-intensive-solution. The cost associated mainly depends on the type of replication instance that you choose and the storage allocated. There is also a small cost for data transfer.
-
AWS DMS replicates only a limited amount of data definition language (DDL) statements. AWS DMS doesn't propagate items such as indexes, users, privileges, stored procedures, and other database changes not directly related to table data.
-
Before you deploy AWS DMS as your DR solution, consider the data type involved. AWS DMS has limitations for some data types. Also consider the types of transactions happening on the primary RDS DB instance. For more information, see the AWS DMS documentation:
-
Ongoing maintenance is required for schema changes.
-
The failover using AWS DMS is manual and not transparent. You must modify the application connection settings after failover.