Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle
If you're unable to move to a fully managed service such as Amazon RDS because of customization requirements, you can migrate to Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle. With Amazon RDS Custom, you can retain administrative rights to the database and its underlying operating system.
When to choose Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle
Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle is a good migration option when:
-
You have legacy, custom, and packaged applications that require access to the underlying operating system and database environment.
-
You need access to SYS or SYSTEM user to meet vendor-based application deployment requirements.
-
You need access to the underlying operating system to configure settings, install patches, and enable native features to meet the dependent application's requirements.
-
You want to access and customize the database environment (by applying custom database patches or modifying operating system packages) to meet your database and application needs.
How it works
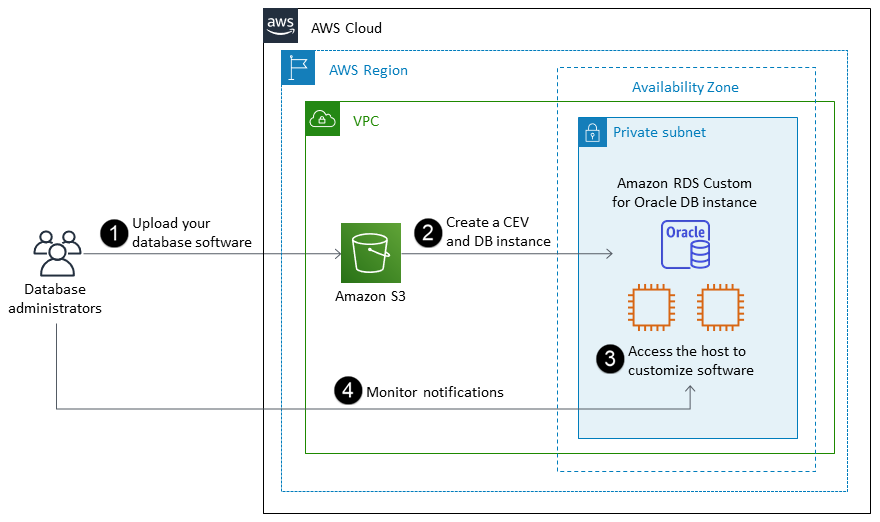
To use Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle, you follow these steps, which are illustrated in the following diagram:
-
Upload your database software to an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket.
-
Create a custom engine version (CEV) and DB instance.
-
Connect your application to the DB instance endpoint and access the host to customize your software.
-
Monitor the notifications generated by Amazon RDS Custom automation.
For more information about these steps, see the Amazon RDS Custom documentation.
To provision your Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle DB instance, review the requirements in the Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle documentation.
In Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle, you use your own media, patches, and Oracle licenses. When you create a custom engine version (CEV), Amazon RDS Custom installs the media that you provide. You have access to the underlying EC2 instance that hosts the DB engine. You can access the EC2 instance by using Secure Shell (SSH) or AWS Systems Manager and perform your customizations.
You can also install software to run custom applications and agents. Because you have privileged access to the host, you can modify file systems to support legacy applications. You can also apply custom database patches or modify operating system packages on your Amazon RDS Custom DB instances.
Amazon RDS Custom automatically provides monitoring, backups, and instance recovery, and ensures that your DB instance uses a supported AWS infrastructure, operating system, and database. If you want to customize your instance, you can pause Amazon RDS Custom automation for up to 24 hours and then resume it when your customization work is complete. Pausing the automation prevents Amazon RDS automation from directly interfering with your customizations.
When you resume automation, the support perimeter determines whether your customization of the database or operating system environment interferes with, or breaks, Amazon RDS Custom automation. Amazon RDS Custom supports your customization of the host and database environment as long as your changes don't put the DB instance outside the support perimeter. The support perimeter checks are performed every 30 minutes by default, and also occur after events such as snapshot deletions or uninstalling the Amazon RDS Custom agent, which monitors the DB instance. The Amazon RDS Custom agent is a critical component for ensuring Amazon RDS Custom functionality. If you uninstall the agent, Amazon RDS Custom runs the support perimeter check after one minute and moves the DB instance outside the support perimeter.
Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle is available on the Oracle Linux operating system and supports Oracle Database Enterprise Edition and Standard Edition on the BYOL model. For specifics, see Feature availability and support for RDS Custom for Oracle and RDS Custom for Oracle requirements and limitations in the AWS documentation.
For additional information, see the following resources:
-
Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle – New Control Capabilities in Database Environment
(AWS News blog) -
Using Amazon RDS for Oracle cross-Region automated backups to enhance your DR capabilities:
-
Migrating from an on-premises or self-managed Oracle database to Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle by using native tools:
-
Physical migration of Oracle databases to Amazon RDS Custom using Data Guard
(AWS Database blog) -
Physical migration of Oracle databases to Amazon RDS Custom using RMAN duplication
(AWS Database blog)
-
-
Integrating an Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) shared file system with Amazon RDS for Oracle to share files between the database and application servers or as a staging location to keep backups and data loads: Integrate Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle with Amazon EFS
(AWS Database blog)