AWS Optimization and Licensing Assessment
Overview
An AWS
Optimization and Licensing Assessment (AWS OLA)
-
Understand existing deployments, application performance, and contracts.
-
Right size your resources.
-
Develop a roadmap to the AWS Cloud.
-
Reduce or eliminate costs by using existing investments and paying only for what you use.
We recommend that you make an AWS OLA the first step on your cost optimization journey. You can work with the AWS Partner Network to complete an AWS OLA. They will help you gather assessment data and provide you with recommendations for optimizing your licensing and instance costs.
The following diagram provides an overview of the assessment process.

Assessment options
You can choose from two AWS OLA options for your Microsoft workloads on AWS:
-
Lite version – In this use case, all of your workloads are on VMware. You can provide AWS with an output from RVTools
. Then, AWS can offer a turnaround time of 1–5 days. This approach uses point-in-time information pulled directly from VMware vCenter to develop sizing recommendations and offer on-demand pricing options. -
Full version – In this use case, you have a mixed environment running in different cloud providers, physical servers, and virtual servers. AWS uses operating system agents to collect usage data from 14 to 30 days. This allows AWS to make informed instance sizing decisions based on your application usage patterns. AWS uses several third-party tools, such as Cloudamize, to complete the analysis. AWS works with its AWS Partner Network to help deliver the final total cost of ownership (TCO) assessment with multiple pricing options that factor in pricing models and different architectures.
Full assessment
The full AWS OLA assessment is kicked off with a one-hour phone call. During this call, AWS helps you to determine the most optimal AWS infrastructure to support your migration, choose a data collection method, and establish a timeline for completion. Implementing discovery tooling in your organization depends on the data collection method, the size of your organization, and the tooling that your organization uses to manage its fleet of servers. It typically takes two weeks to collect usage data.
The full AWS OLA process takes between 30–45 days and consists of the following phases:
-
Scope workloads
-
Collect data
-
Analyze data
-
Plan next steps
Scope workloads
First, AWS works with you and your team to determine the scope of the assessment. This is usually broken down by environment type (for example, non-production and production). The scope includes the location of the workloads. This could be workloads that you're migrating to AWS, workloads that are already running on AWS (for example, AWS OLA for Amazon EC2), or workloads running in other cloud providers.
Collect data
Next, AWS deploys tooling to help with resource discovery and collect performance data from your servers. This tooling comes in four deployment options:
-
Tools that can query the hypervisor (requires only VMware vCenter or Hyper-V credentials)
-
Agents that can be deployed on physical or virtual machines
-
Agentless discovery by using SSH, Windows Remote Management (WinRM), or Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) depending on your environment and operating system
-
Flat file data collection and analysis
For your tooling deployment, you can mix and match each option and consolidate results. It's crucial to ensure that whatever option you choose doesn't strain your IT resources. AWS strives to make the assessment process as turnkey as possible. Beyond a brief phone call to assist with setup, the AWS OLA team and Microsoft specialist solutions architects will prep the total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis and recommendations for review.
Data collection usually takes two to three weeks when CPU utilization, RAM utilization, storage throughput, IOPS, and network throughput are analyzed. Ideally, this collection takes place during the peak times of your business month (for example, during end-of-month financial reporting). AWS wants to capture the peak usage because this gives good statistical samples for what the right-sized AWS instance should be, while still guaranteeing the performance can exceed what's available on premises. AWS merges utilization metrics with performance heuristics of various processor generations to target exactly how much CPU and RAM a given workload requires. These targets are usually less than what's allocated on premises. This not only reduces the compute cost for size of the instance but also optimizes licensing costs.
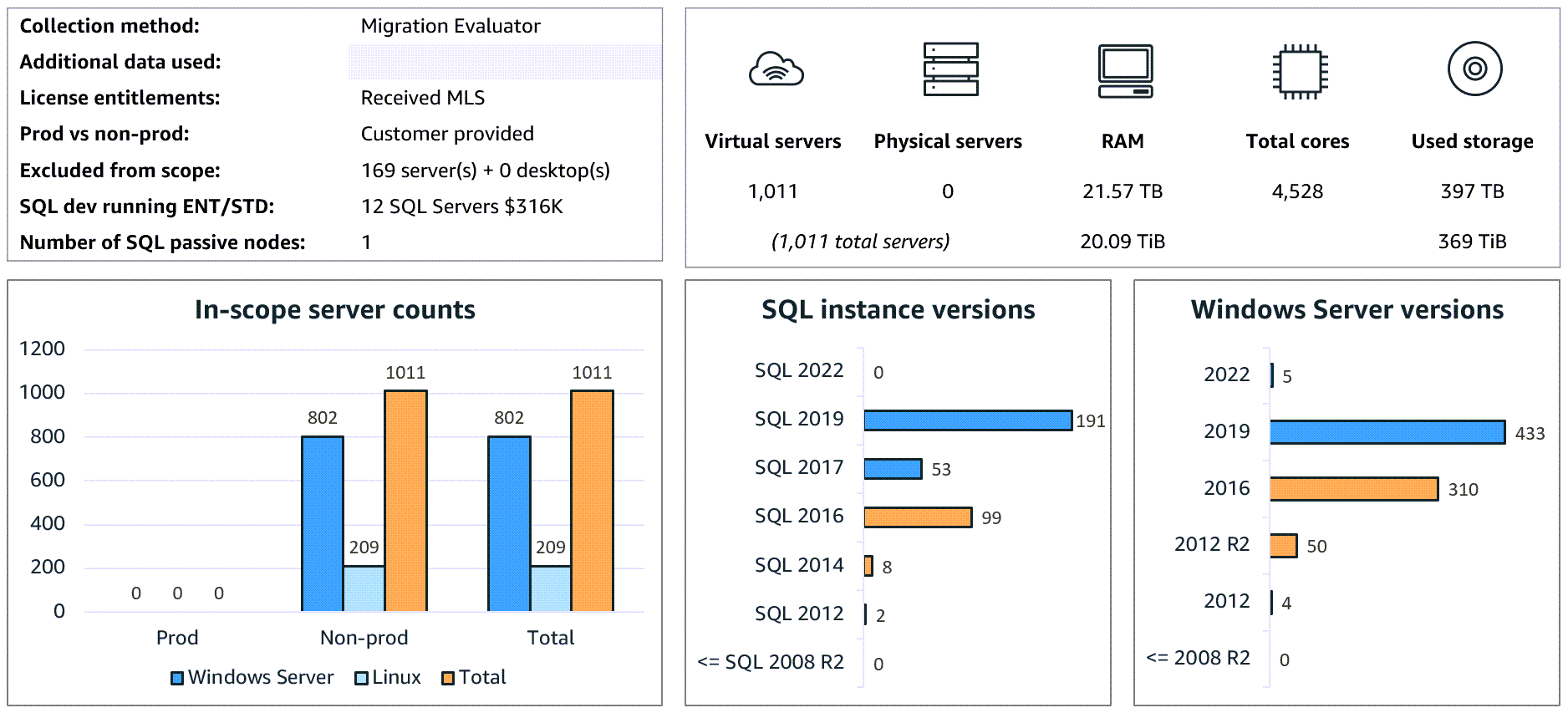
The following dashboard view shows an example of infrastructure costs that can be captured by an assessment.

Analyze data
AWS delivers a debrief presentation after the data collection is completed. AWS reviews the data, summarizes findings, and then makes recommendations for on-premises usage and cloud migration. You can reduce compute and licensing costs by examining consolidation opportunities, elasticity gains (where workloads can be turned off or seasonally adjusted), right-SKU opportunities (for example, SQL Server Enterprise edition is in use, but resource requirements and feature usage suggest SQL Server Standard edition is suitable). For products like SQL Server which are licensed by the core, it often makes financial sense to place workloads in a more expensive compute instance. That is, if the CPU profile and ratio of RAM to vCPU serves a net effect to reduce the number of licensed cores for both license-included and Bring Your Own License (BYOL) use cases.
The following shows an example analysis based on the data collected by the assessment.
Common optimization scenarios include identifying both AWS resource optimization opportunities and third-party license savings.
Examples of AWS resource optimization opportunities:
-
Avoid overprovisioning for peak usage.
-
Avoid over-specifying and underusing resources.
-
Right size your instances and migrate to the newest generations of EC2 instances.
-
Save on operations costs by moving to managed databases.
Examples of third-party license savings:
-
Reduce required cores to run the same workload.
-
Get rid of unnecessary SQL Server Enterprise edition and add-on packs.
-
Remove zombie servers and replace outdated hardware.
-
Use BYOL and license-included options to reduce future commercial agreements.
-
Modernize to open-source and cloud-native solutions.
Plan next steps
Finally, AWS uses the collected performance data to estimate specific workload sizing and cost. AWS can also look in aggregate at your scoped environment and provide a quantitative analysis. This can help you determine if the best option is an on-premises refresh or a migration to AWS. You can build a cloud economic business case by using the TCO analysis summary (as shown in the following example) provided at the end of an AWS OLA.

An AWS OLA also provides insight into the impact that modernization can have on your existing workloads by making suggestions such as the following:
-
Move to a Linux operating system.
-
Add application support for ARM processors (AWS Graviton).
-
Move SQL Server workloads to Amazon Aurora.
-
Remove software assurance by moving Windows and SQL Server workloads to open-source technologies.
The following diagram shows the cost savings that can be achieved through modernization techniques such as moving from Windows to Linux or from SQL Server to Aurora.

The full AWS OLA process takes roughly 45 days from start to finish. The following diagram shows an example timeline.

If you have a pure VMware environment and can provide output from RVTools, then you can reduce this timeline to one business week. Additionally, AWS can analyze a flat file that includes asset and utilization data, such as CPU average, CPU peak, RAM average, and RAM peak.
Assessment impact
The average customer typically experiences a 20–30 percent cost reduction from the right-sizing effort. Right sizing matches the source workload to the best sized AWS instances based on usage data. These right-sizing adjustments not only reduce the monthly cost of the AWS environment, but frequently result in savings elsewhere in the organization. For example, a 20–30 percent gain of Windows or SQL Server licensing can reduce the next true-up with Microsoft, or free up licensing for additional line-of-business applications. Consolidation and right sizing of SQL Server workloads is commonly where the most dramatic financial gains are realized.
AWS can help you categorize systems into modernization buckets. Some systems are legacy and are not financially viable to touch, while others may be modernized into containers or serverless applications where the most significant savings are realized. The conversation with your AWS team moves from generalized topics of what the cloud enables to more specific discussions of how and why specific workloads should be modernized. AWS also helps you explore potential innovation opportunities.
Next steps
If you're beginning your cost optimization journey for Microsoft workloads that are
running in on-premises environments or on AWS, engage with your AWS account team and
request an AWS OLA. AWS team members can answer your questions and help you decide
if an AWS OLA is ultimately the right choice for you and your organization.
Alternatively, you can request an AWS OLA online