SQL query processing in Amazon Redshift
Amazon Redshift routes a submitted SQL query through the parser and optimizer to develop a query plan. The execution engine then translates the query plan into code and sends that code to the compute nodes for execution. Before you design a query plan, it's critical to understand how query processing works.
Query planning and execution workflow
The following diagram provides a high-level view of the query planning and execution workflow.

The diagram shows the following workflow:
-
The leader node in the Amazon Redshift cluster receives the query and parses the SQL statement.
-
The parser produces an initial query tree that's a logical representation of the original query.
-
The query optimizer takes the initial query tree and evaluates it, analyzes table statistics to determine join order and predicate selectivity, and, if necessary, rewrites the query to maximize its efficiency. Sometimes a single query can be written as several dependent statements in the background.
-
The optimizer generates a query plan (or several, if the previous step resulted in multiple queries) for the execution with the best performance. The query plan specifies execution options such as execution order, network operations, join types, join order, aggregation options, and data distributions.
-
A query plan contains information on the individual operations required to run a query. You can use the
EXPLAINcommand to view the query plan. The query plan is a fundamental tool for analyzing and tuning complex queries. -
The query optimizer sends the query plan to the execution engine. The execution engine checks the compiled plan cache for a query plan match and uses the compiled cache (if found). Otherwise, the execution engine translates the query plan into steps, segments, and streams:
-
Steps are individual operations that take place during query execution. Steps are identified by a label (for example,
scan,dist,hjoin, ormerge). A step is the smallest unit. You can combine steps so that compute nodes can perform a query, join, or another database operation. -
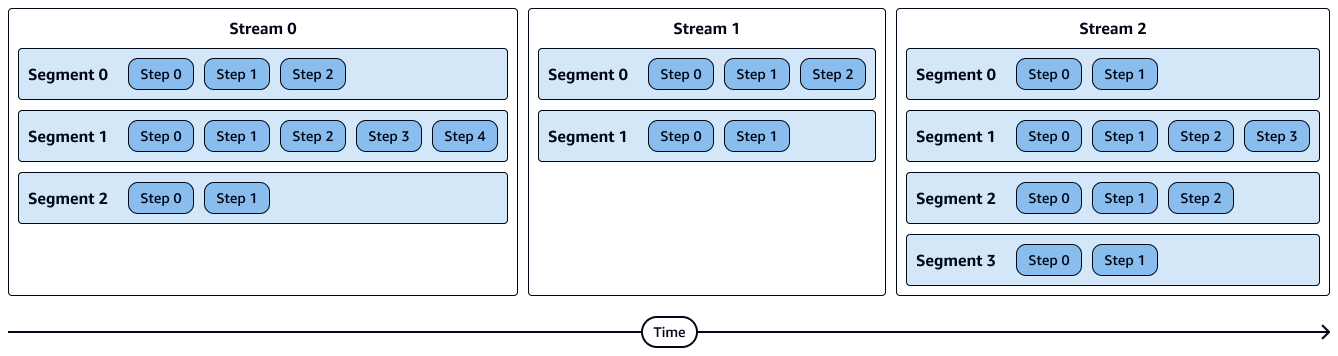
A segment refers to a segment of a query and combines several steps that can be done by a single process. A segment is the smallest compilation unit executable by a compute node slice. A slice is the unit of parallel processing in Amazon Redshift.
-
A stream is a collection of segments to be parceled out over the available compute node slices. The segments in a stream run in parallel across node slices. Therefore, the same step from the same segment is also executed in parallel in multiple slices.
-
-
The code generator receives the translated plan and generates a C++ function for each segment.
-
The generated C++ function gets compiled by the GNU Compiler Collection and converted to an O (
.o) file. -
The compiled code (O file) runs. Compiled code runs faster than interpreted code and uses less compute capacity.
-
The compiled O file is then broadcasted to the compute nodes.
-
Each compute node consists of several compute slices. The compute slices run the query segments in parallel. Amazon Redshift takes advantage of optimized network communication, memory, and disk management to pass intermediate results from one query plan step to the next. This also helps to speed up query execution. Consider the following:
-
Steps 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11 happen once for each stream.
-
The engine creates the executable segments for one stream and sends these segments to the compute nodes.
-
After the segments of a prior stream are completed, the engine generates the segments for the next stream. In this way, the engine can analyze what happened in the prior stream (for example, whether operations were disk-based) to influence the generation of segments in the next stream.
-
-
After the compute nodes are done, they return the query results to the leader node for final processing. The leader node merges the data into a single result set and addresses any required sorting or aggregation.
-
The leader node returns the results to the client.
The following diagram shows the execution workflow of streams, segments, steps, and compute node slices. Keep in mind the following:
-
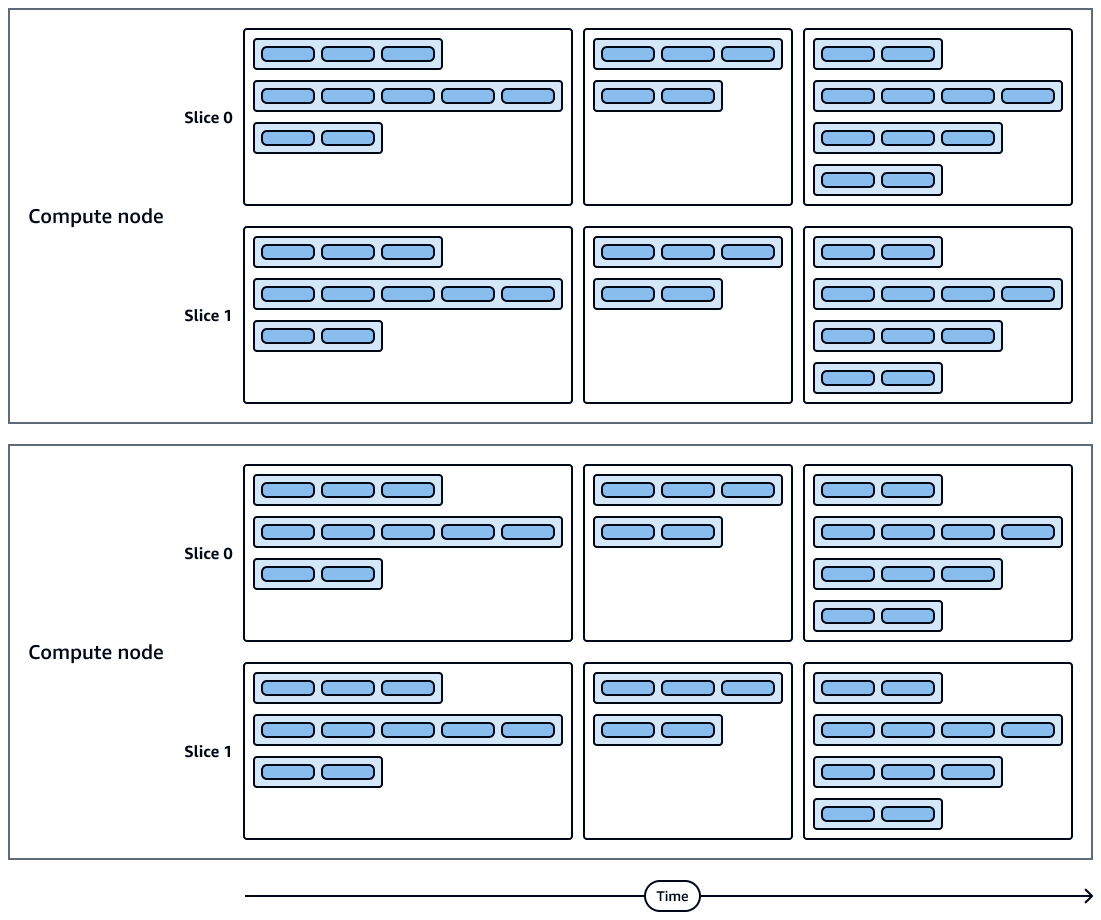
Steps in a segment run sequentially.
-
Segments in a stream run in parallel.
-
Streams run sequentially.
-
Compute node slices run in parallel.
The following diagram shows a visual representation of streams, segments, and steps. Each segment contains multiple steps, and each stream contains multiple segments.
The following diagram shows a visual representation of query executions and compute node slices. Each compute node contains multiple slices, streams, segments, and steps.
Additional considerations
We recommend that you consider the following in regard to query processing:
-
Cached compiled code is shared across sessions on the same cluster, so subsequent executions of the same query will be faster, often even with different parameters.
-
When you benchmark your queries, we recommend that you always compare the times for the second execution of a query, because the first execution time includes the overhead of compiling the code. For more information, see Query performance factors in the Query best practices for Amazon Redshift guide.
-
The compute nodes could return some data to the leader node during query execution if necessary. For example, if you have a subquery with a
LIMITclause, the limit is applied on the leader node before data is redistributed across the cluster for further processing.