Auditing
You can use the Db2 audit facility to generate and maintain an audit trail for a series of predefined database events. The records generated from this facility are kept in an audit log file, which helps to provide insights into who did what, when, and where.
Auditing can be set up and configured at the instance level and in each database within the instance. The audit files are written and maintained separately for the instance and for each database.
The following diagram illustrates the Db2 audit facility that can be configured at the instance level and at each database level within the instance.
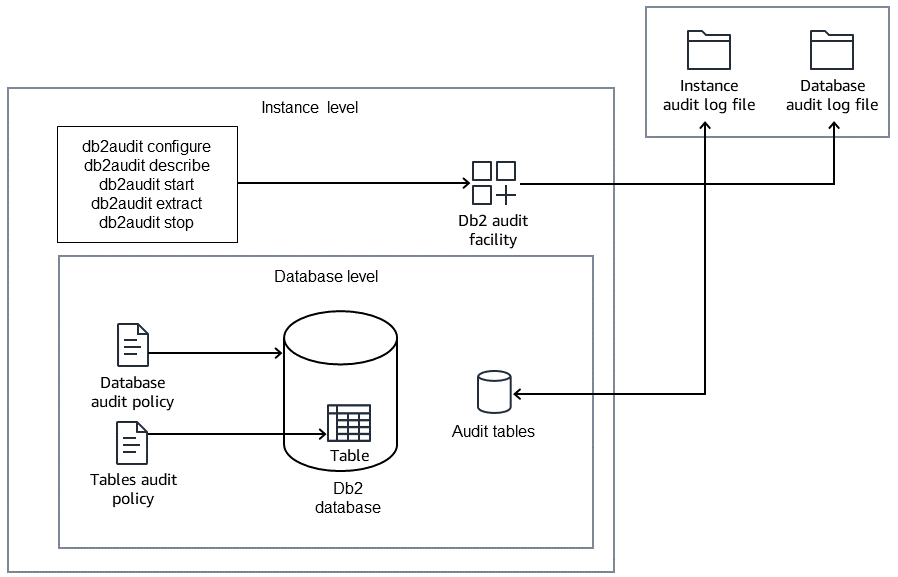
A database audit is defined by using audit policies that are associated with specific
objects using the AUDIT statement. Audit policies can be associated with
different database objects such as databases, tables, users, groups, roles, and
authorizations to control what requires an audit. Configuration can specify whether to
audit one or more of the defined event categories:
-
AUDIT– Change in audit settings or audit log access -
CHECKING– Authorization checks -
OBJMAINT– Objects created or dropped (some but not all alter actions) -
SECMAINT– Changes to security controls -
SYSADMIN– Use ofSYSADM,SYSMAINT, orSYSCTRLauthority -
VALIDATE– Authentication or access of system security information -
CONTEXT– Contextual information for a database operation -
EXECUTE– The running of SQL statements