SageMaker Operators for Kubernetes
SageMaker Operators for Kubernetes make it easier for developers and data scientists using
Kubernetes to train, tune, and deploy machine learning (ML) models in SageMaker. You can install
these SageMaker Operators on your Kubernetes cluster in Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) to create SageMaker jobs
natively using the Kubernetes API and command-line Kubernetes tools such as
kubectl. This guide shows how to set up and use the operators to run model
training, hyperparameter tuning, or inference (real-time and batch) on SageMaker from a Kubernetes
cluster. The procedures and guidelines in this chapter assume that you are familiar with
Kubernetes and its basic commands.
Important
We are stopping the development and technical
support of the original version of
SageMaker Operators for Kubernetes
If you are currently using version v1.2.2
or below of
SageMaker Operators for Kubernetes
For information on the migration steps, see Migrate resources to the latest Operators.
For answers to frequently asked questions on the end of support of the original version of SageMaker Operators for Kubernetes, see Announcing the End of Support of the Original Version of SageMaker Operators for Kubernetes
Note
There is no additional charge to use these operators. You do incur charges for any SageMaker resources that you use through these operators.
What is an operator?
A Kubernetes operator is an application controller managing applications on behalf of a
Kubernetes user. Controllers of the control plane encompass various control loops listening to
a central state manager (ETCD) to regulate the state of the application they control. Examples
of such applications include the Cloud-controller-managerkube-controller-manager. Operators typically provide a higher-level
abstraction than raw Kubernetes API, making it easier for users to deploy and manage
applications. To add new capabilities to Kubernetes, developers can extend the Kubernetes API
by creating a custom resource that contains their
application-specific or domain-specific logic and components. Operators in Kubernetes allow
users to natively invoke these custom resources and automate associated workflows.
How does AWS Controllers for Kubernetes (ACK) work?
The SageMaker Operators for Kubernetes allow you to manage jobs in SageMaker from your Kubernetes cluster. The latest version of SageMaker Operators for Kubernetes is based on AWS Controllers for Kubernetes (ACK). ACK includes a common controller runtime, a code generator, and a set of AWS service-specific controllers, one of which is the SageMaker controller.
The following diagram illustrates how ACK works.
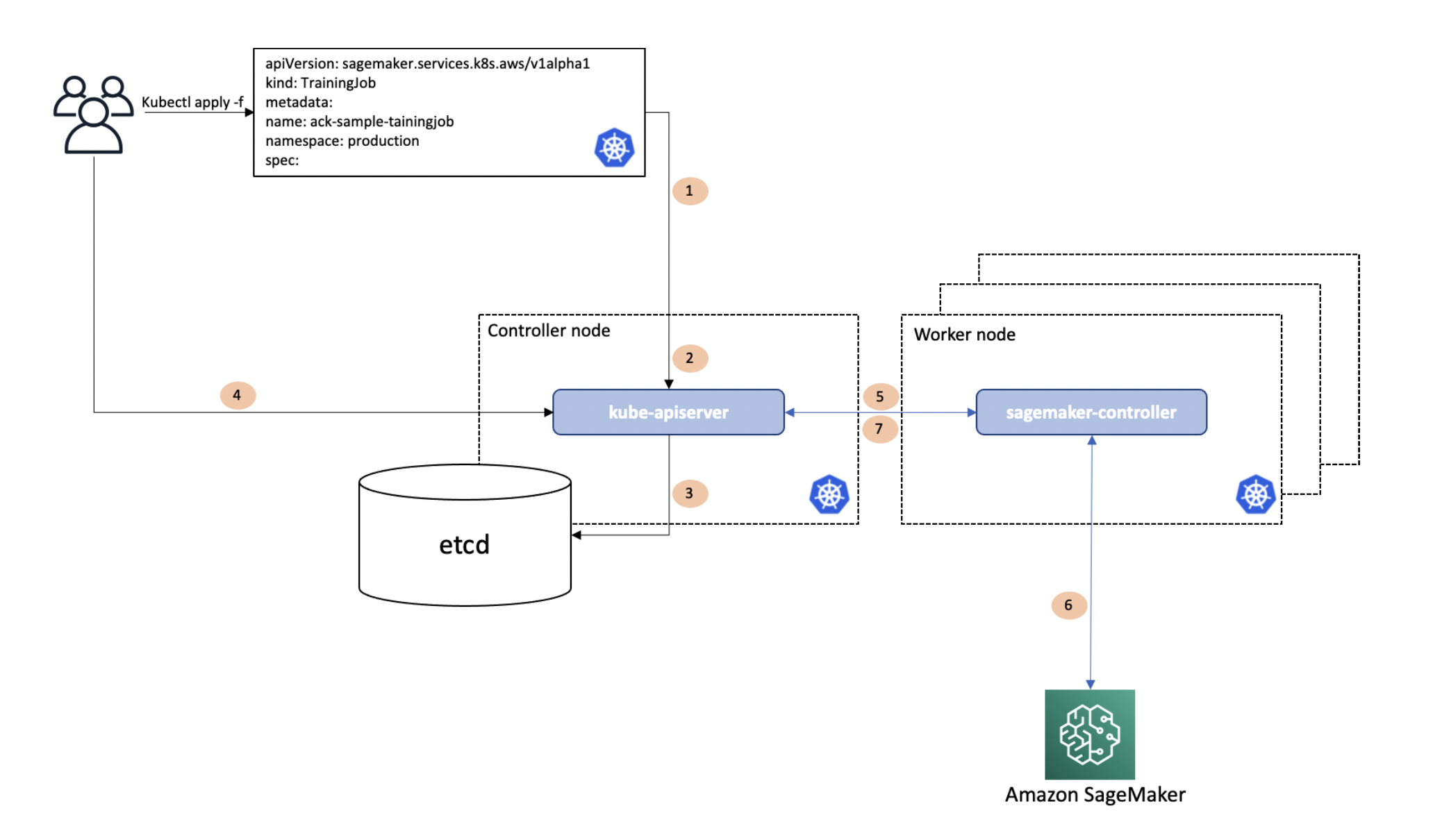
In this diagram, a Kubernetes user wants to run model training on SageMaker from within the
Kubernetes cluster using the Kubernetes API. The user issues a call to kubectl
apply, passing in a file that describes a Kubernetes custom resource describing the
SageMaker training job. kubectl apply passes this file, called a manifest, to the
Kubernetes API server running in the Kubernetes controller node (Step 1 in the workflow diagram). The Kubernetes API server
receives the manifest with the SageMaker training job specification and determines whether the
user has permissions to create a custom resource of kind
sageMaker.services.k8s.aws/TrainingJob, and whether the custom resource is
properly formatted (Step 2). If the user is
authorized and the custom resource is valid, the Kubernetes API server writes (Step
3) the custom resource to its etcd data store and
then responds back (Step 4) to the user that the
custom resource has been created. The SageMaker controller, which is running on a Kubernetes
worker node within the context of a normal Kubernetes Pod, is notified (Step 5) that a new custom resource of kind
sageMaker.services.k8s.aws/TrainingJob has been created. The SageMaker controller
then communicates (Step 6) with the SageMaker API,
calling the SageMaker CreateTrainingJob API to create the training job in AWS.
After communicating with the SageMaker API, the SageMaker controller calls the Kubernetes API server
to update (Step 7) the custom resource’s status
with information it received from SageMaker. The SageMaker controller therefore provides the same
information to the developers that they would have received using the AWS SDK.
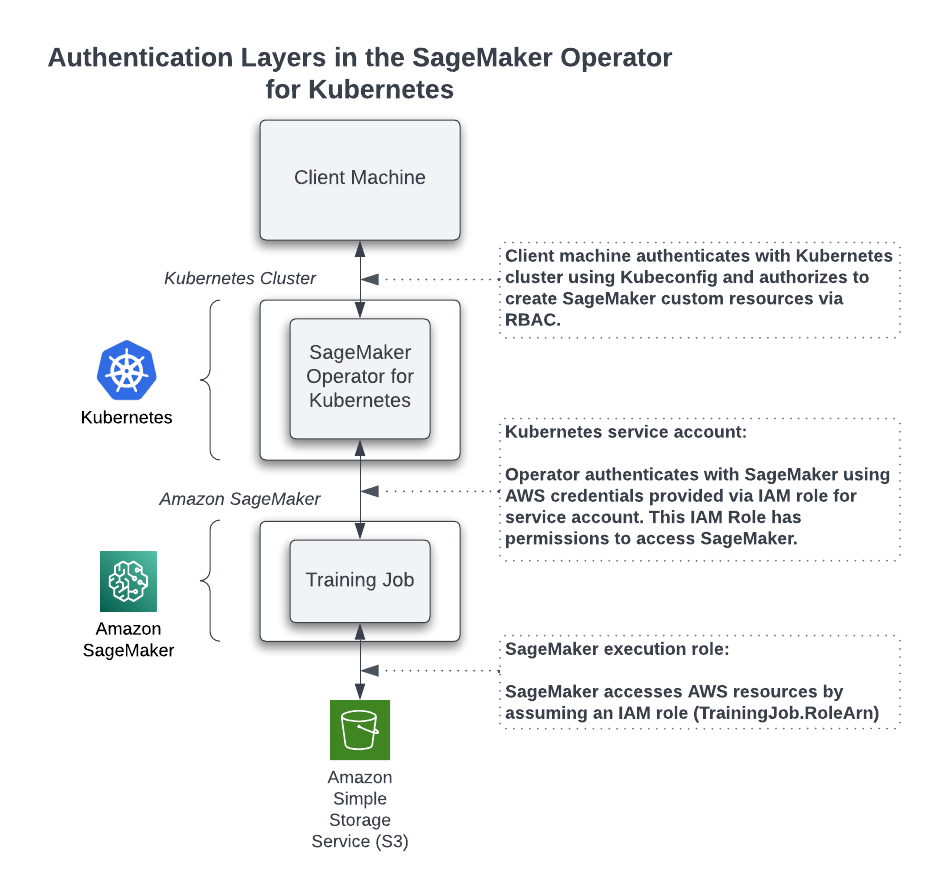
Permissions overview
The operators access SageMaker resources on your behalf. The IAM role that the operator assumes to interact with AWS resources differs from the credentials you use to access the Kubernetes cluster. The role also differs from the role that AWS assumes when running your machine learning jobs.
The following image explains the various authentication layers.