Starting a real-time Call Analytics transcription
Before starting a real-time Call Analytics transcription, you must create all the categories you want Amazon Transcribe to match in your call.
Note
Call Analytics transcripts can't be retroactively matched to new categories. Only the categories you create before starting a Call Analytics transcription can be applied to that transcription output.
If you've created one or more categories, and your audio matches all the rules within at least one of your categories, Amazon Transcribe flags your output with the matching categories. If you choose not to use categories, or if your audio doesn't match the rules specified in your categories, your transcript isn't flagged.
To include post-call analytics with your real-time Call Analytics transcription, you must provide an
Amazon S3 bucket in your request using the OutputLocation
parameter. You must also include a DataAccessRoleArn that has write permissions
to the specified bucket. A separate transcript is produced and stored in the specified bucket upon
completion of your real-time Call Analytics streaming session.
With real-time Call Analytics, you also have the option to create real-time category alerts; refer to Creating real-time alerts for category matches for instructions.
To start a real-time Call Analytics transcription, you can use the AWS Management Console, HTTP/2, or WebSockets; see the following for examples:
Important
Currently, the AWS Management Console only offers a demo for real-time Call Analytics with pre-loaded audio examples. If you want to use your own audio, you must use the API (HTTP/2, WebSockets, or an SDK).
Use the following procedure to start a Call Analytics request. The calls that match all characteristics defined by a category are labeled with that category.
Note
Only a demo is available in the AWS Management Console. To start a custom real-time analytics transcription, you must use the API.
-
In the navigation pane, under Amazon Transcribe Call Analytics, choose Analyze a real-time call.

-
For Step 1: Specify input audio, choose a demo test file from the dropdown menu.
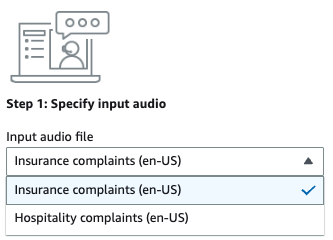
-
For Step 2: Review call categories, you have the option to review the real-time Call Analytics categories you previously created. All real-time Call Analytics categories are applied to your transcription.
Choosing View categories opens a new pane that shows your existing real-time Call Analytics categories and provides a link to create new ones.
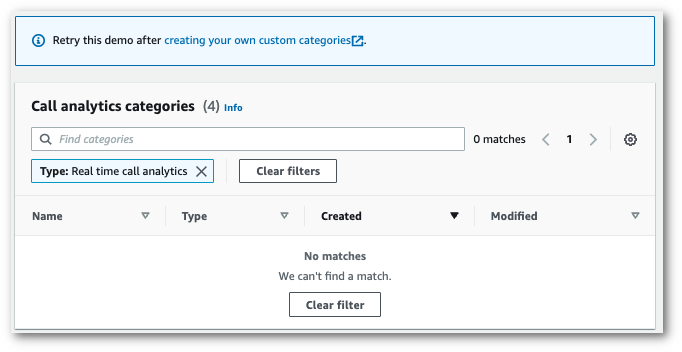
-
For Step 3: Configure input and output, you have the option to apply additional settings.
Choosing Configure advanced settings opens a new pane where you can specify content redaction settings.
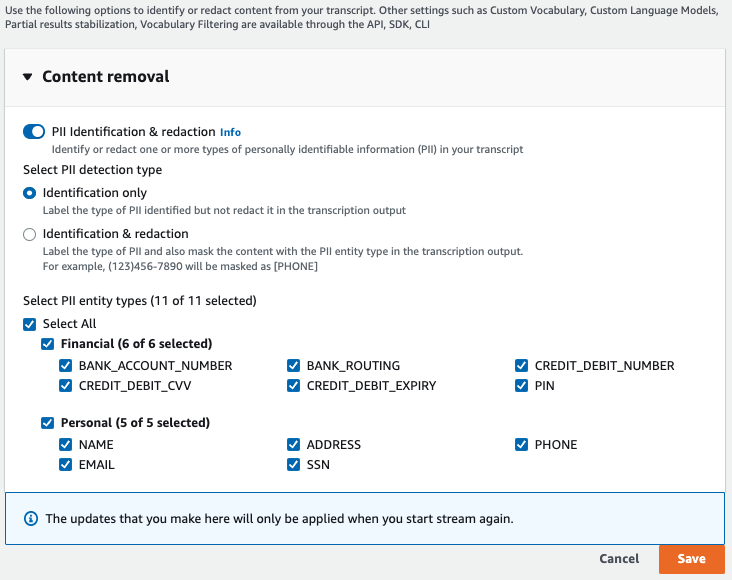
Once you've made all your selections, choose Save to return to the main page.
-
To apply additional analytics, you can toggle on Post-call Analytics. This provides you with the same analytics as a post-call analytics transcription, including interruptions, loudness, non-talk time, talk speed, talk time, issues, action items, and outcomes. Post-call analytics output is stored in a separate file from your real-time Call Analytics transcript.

If you apply post-call analytics, you must specify an Amazon S3 output file destination and an IAM role. You can optionally choose to encrypt your output.
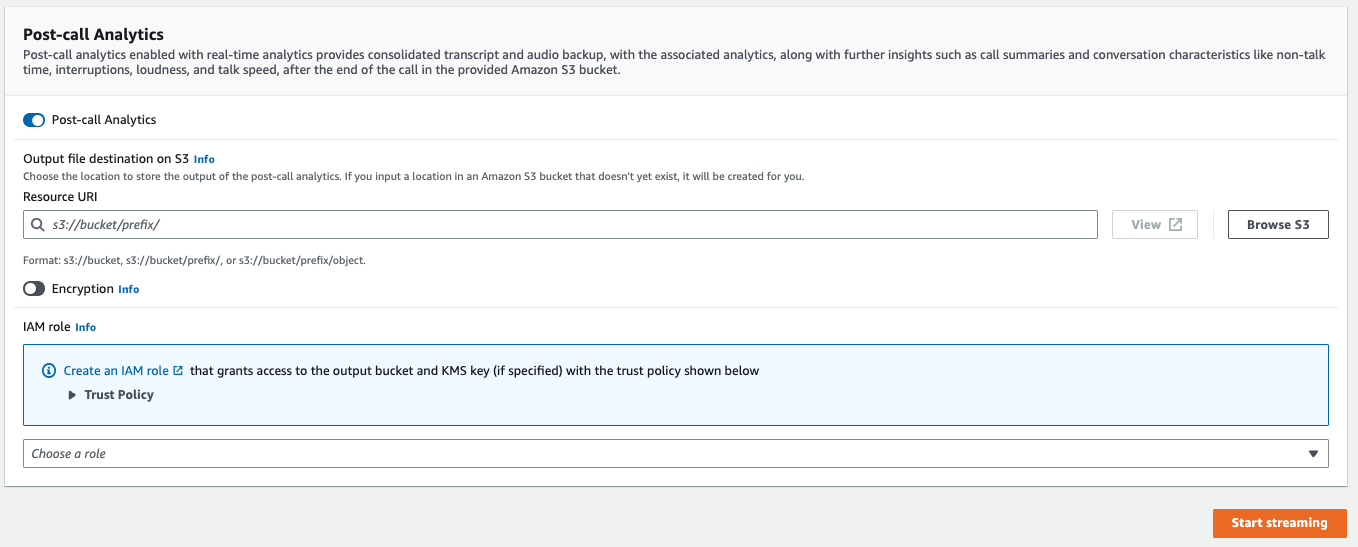
-
Choose Start streaming.
This example creates an HTTP/2 request with Call Analytics enabled. For
more information on using HTTP/2 streaming with Amazon Transcribe, see
Setting up an HTTP/2 stream. For more detail on
parameters and headers specific to Amazon Transcribe, see StartCallAnalyticsStreamTranscription.
This example includes post-call analytics. If you
don't want post-call analytics, remove the PostCallAnalyticsSettings section from
the request.
Note that the configuration event shown in the following example needs to be passed as the first event in the stream.
POST /stream-transcription HTTP/2 host: transcribestreaming.us-west-2.amazonaws.com X-Amz-Target: com.amazonaws.transcribe.Transcribe.StartCallAnalyticsStreamTranscriptionContent-Type: application/vnd.amazon.eventstream X-Amz-Content-Sha256:stringX-Amz-Date:20220208T235959Z Authorization: AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 Credential=access-key/20220208/us-west-2/transcribe/aws4_request, SignedHeaders=content-type;host;x-amz-content-sha256;x-amz-date;x-amz-target;x-amz-security-token, Signature=stringx-amzn-transcribe-language-code:en-USx-amzn-transcribe-media-encoding:flacx-amzn-transcribe-sample-rate:16000transfer-encoding: chunked { "AudioStream": { "AudioEvent": { "AudioChunk": blob }, "ConfigurationEvent": { "ChannelDefinitions": [ { "ChannelId":0, "ParticipantRole": "AGENT" }, { "ChannelId":1, "ParticipantRole": "CUSTOMER" } ], "PostCallAnalyticsSettings": { "OutputLocation": "s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-output-files/", "DataAccessRoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/ExampleRole" } } } }
Parameter definitions can be found in the API Reference; parameters common to all AWS API operations are listed in the Common Parameters section.
This example creates a presigned URL that uses Call Analytics in a WebSocket stream. Line
breaks have been added for readability. For more information on using WebSocket streams with
Amazon Transcribe, see Setting up a WebSocket stream. For more detail on parameters, see
StartCallAnalyticsStreamTranscription.
This example includes post-call analytics. If you
don't want post-call analytics, remove the PostCallAnalyticsSettings section from
the request.
Note that the configuration event shown in the following example needs to be passed as the first event in the stream.
GET wss://transcribestreaming.us-west-2.amazonaws.com:8443/call-analytics-stream-transcription-websocket? &X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 &X-Amz-Credential=AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE%2F20220208%2Fus-west-2%2Ftranscribe%2Faws4_request &X-Amz-Date=20220208T235959Z &X-Amz-Expires=300&X-Amz-Security-Token=security-token&X-Amz-Signature=string&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=content-type%3Bhost%3Bx-amz-date &language-code=en-US&media-encoding=flac&sample-rate=16000{ "AudioStream": { "AudioEvent": { "AudioChunk": blob }, "ConfigurationEvent": { "ChannelDefinitions": [ { "ChannelId":0, "ParticipantRole": "AGENT" }, { "ChannelId":1, "ParticipantRole": "CUSTOMER" } ], "PostCallAnalyticsSettings": { "OutputLocation": "s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-output-files/", "DataAccessRoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/ExampleRole" } } } }
Parameter definitions can be found in the API Reference; parameters common to all AWS API operations are listed in the Common Parameters section.
Tip
The above HTTP/2 and WebSocket examples include post-call analytics. If you don't want
post-call analytics, remove the PostCallAnalyticsSettings section from the
request.
If you enable PostCallAnalyticsSettings, you must send a configuration event as
the first event. Your configuration event includes settings for ChannelDenifitions and
PostStreamAnalyticsSettings, as shown in the preceding examples.
Binary data are passed as a binary message with
content-type application/octet-stream and the configuration event is passed as a
text message with content-type application/json.
For more information, see Setting up a streaming transcription.
Creating real-time alerts for category matches
To set up real-time alerts, you must first create a TranscriptFilterType
category with the REAL_TIME flag. This flag allows your category to be applied to
real-time Call Analytics transcriptions.
For instructions on creating a new category, see Creating categories for real-time transcriptions.
When you start your real-time Call Analytics transcription, all categories that have the
REAL_TIME flag are automatically applied to your transcription output at a segment level. If a
TranscriptFilterType match occurs, it appears under the CategoryEvent
section of your transcript. You can then use this parameter and its sub-parameters,
MatchedCategories and MatchedDetails, to set up custom real-time
alerts.
Here's an example of real-time Call Analytics transcription output for a
CategoryEvent match:
"CategoryEvent": { "MatchedCategories": [ "shipping-complaint" ], "MatchedDetails": { "my package never arrived" : { "TimestampRanges": [ { "BeginOffsetMillis":19010, "EndOffsetMillis":22690} ] } } },
The previous example represents an exact text match to the speech "my package never arrived," which represents a rule within the 'shipping-complaint' category.
You can set up your real-time alert to include any combination of the listed parameters. For
example, you could set your alert to include only the phrase that was matched
(MatchedDetails) or only the category name (MatchedCategories). Or
you could set your alert to include all parameters.
How you set up your real-time alerts depends on your organization's interfaces and your
desired alert type. For example, you could set a CategoryEvent match to send a
pop-up notification, an email, a text, or any other alert your system can accept.