Using a custom vocabulary filter
Once your custom vocabulary filter is created, you can include it in your transcription requests; refer to the following sections for examples.
The language of the custom vocabulary filter you're including in your request must match the language code you specify for your media. If you use language identification and specify multiple language options, you can include one custom vocabulary filter per specified language. If the languages of your custom vocabulary filters don't match the language identified in your audio, your filters are not applied to your transcription and there are no warnings or errors.
Using a custom vocabulary filter in a batch transcription
To use a custom vocabulary filter with a batch transcription, see the following for examples:
-
Sign in to the AWS Management Console
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Transcription jobs, then select Create job (top right). This opens the Specify job details page.

Name your job and specify your input media. Optionally include any other fields, then choose Next.
-
On the Configure job page, in the Content removal panel, toggle on Vocabulary filtering.
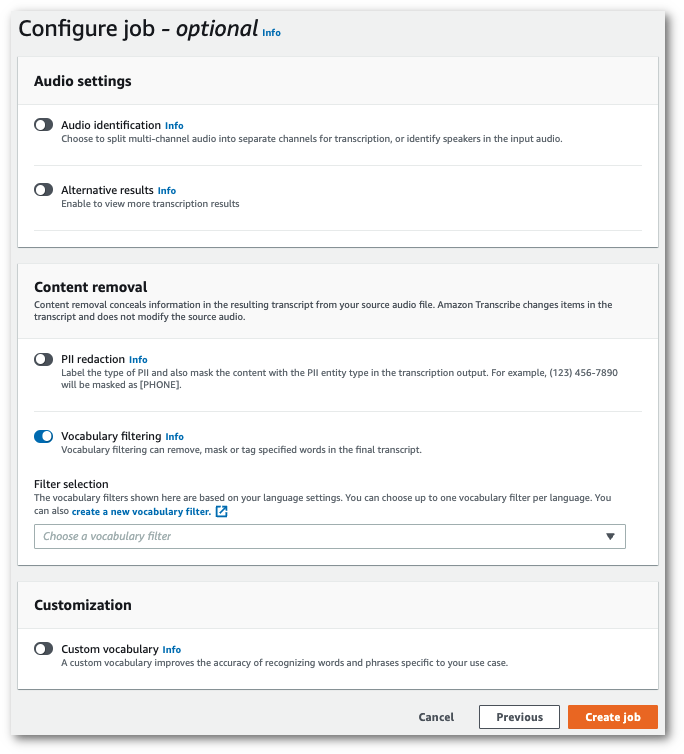
-
Select your custom vocabulary filter from the dropdown menu and specify the filtration method.
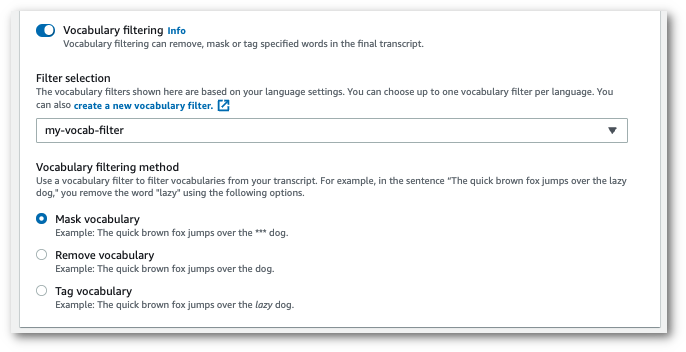
-
Select Create job to run your transcription job.
This example uses the start-transcription-jobSettings parameter with the VocabularyFilterName
and VocabularyFilterMethod sub-parameters. For more information, see
StartTranscriptionJob and
Settings.
aws transcribe start-transcription-job \ --regionus-west-2\ --transcription-job-namemy-first-transcription-job\ --media MediaFileUri=s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-input-files/my-media-file.flac\ --output-bucket-nameamzn-s3-demo-bucket\ --output-keymy-output-files/ \ --language-codeen-US\ --settings VocabularyFilterName=my-first-vocabulary-filter,VocabularyFilterMethod=mask
Here's another example using the start-transcription-job
aws transcribe start-transcription-job \ --regionus-west-2\ --cli-input-json file://my-first-vocabulary-filter-job.json
The file my-first-vocabulary-filter-job.json contains the following request body.
{ "TranscriptionJobName": "my-first-transcription-job", "Media": { "MediaFileUri": "s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-input-files/my-media-file.flac" }, "OutputBucketName": "amzn-s3-demo-bucket", "OutputKey": "my-output-files/", "LanguageCode": "en-US", "Settings": { "VocabularyFilterName": "my-first-vocabulary-filter", "VocabularyFilterMethod": "mask" } }
This example uses the AWS SDK for Python (Boto3) to include a custom vocabulary filter using the
Settings argument for the
start_transcription_jobStartTranscriptionJob and
Settings.
For additional examples using the AWS SDKs, including feature-specific, scenario, and cross-service examples, refer to the Code examples for Amazon Transcribe using AWS SDKs chapter.
from __future__ import print_function import time import boto3 transcribe = boto3.client('transcribe', 'us-west-2') job_name = "my-first-transcription-job" job_uri = "s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-input-files/my-media-file.flac" transcribe.start_transcription_job( TranscriptionJobName = job_name, Media = { 'MediaFileUri': job_uri }, OutputBucketName = 'amzn-s3-demo-bucket', OutputKey = 'my-output-files/', LanguageCode = 'en-US', Settings = { 'VocabularyFilterName': 'my-first-vocabulary-filter', 'VocabularyFilterMethod': 'mask' } ) while True: status = transcribe.get_transcription_job(TranscriptionJobName = job_name) if status['TranscriptionJob']['TranscriptionJobStatus'] in ['COMPLETED', 'FAILED']: break print("Not ready yet...") time.sleep(5) print(status)
Using a custom vocabulary filter in a streaming transcription
To use a custom vocabulary filter with a streaming transcription, see the following for examples:
-
Sign into the AWS Management Console
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Real-time transcription. Scroll down to Content removal settings and expand this field if it is minimized.
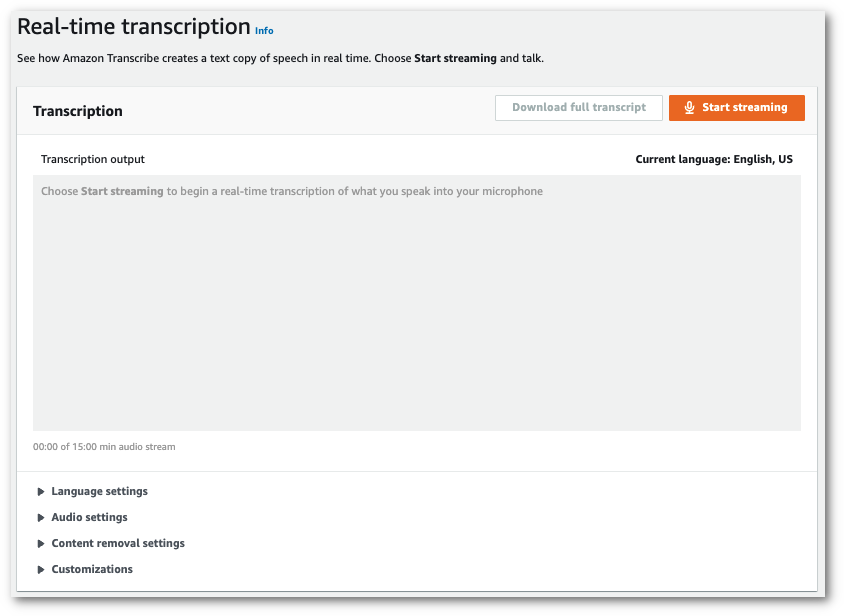
-
Toggle on Vocabulary filtering. Select a custom vocabulary filter from the dropdown menu and specify the filtration method.
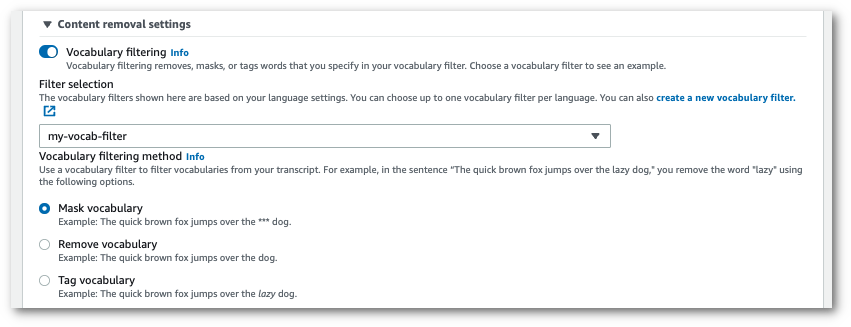
Include any other settings you want to apply to your stream.
-
You're now ready to transcribe your stream. Select Start streaming and begin speaking. To end your dictation, select Stop streaming.
This example creates an HTTP/2 request that includes your custom vocabulary filter and filter method.
For more information on using HTTP/2 streaming with Amazon Transcribe, see
Setting up an HTTP/2 stream. For more detail on parameters
and headers specific to Amazon Transcribe, see StartStreamTranscription.
POST /stream-transcription HTTP/2 host: transcribestreaming.us-west-2.amazonaws.com X-Amz-Target: com.amazonaws.transcribe.Transcribe.StartStreamTranscriptionContent-Type: application/vnd.amazon.eventstream X-Amz-Content-Sha256:stringX-Amz-Date:20220208T235959Z Authorization: AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 Credential=access-key/20220208/us-west-2/transcribe/aws4_request, SignedHeaders=content-type;host;x-amz-content-sha256;x-amz-date;x-amz-target;x-amz-security-token, Signature=stringx-amzn-transcribe-language-code:en-USx-amzn-transcribe-media-encoding:flacx-amzn-transcribe-sample-rate:16000x-amzn-transcribe-vocabulary-filter-name:my-first-vocabulary-filterx-amzn-transcribe-vocabulary-filter-method:masktransfer-encoding: chunked
Parameter definitions can be found in the API Reference; parameters common to all AWS API operations are listed in the Common Parameters section.
This example creates a presigned URL that applies your custom vocabulary filter to a WebSocket stream.
Line breaks have been added for readability. For more information on using WebSocket streams with
Amazon Transcribe, see Setting up a WebSocket stream.
For more detail on parameters, see StartStreamTranscription.
GET wss://transcribestreaming.us-west-2.amazonaws.com:8443/stream-transcription-websocket? &X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 &X-Amz-Credential=AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE%2F20220208%2Fus-west-2%2Ftranscribe%2Faws4_request &X-Amz-Date=20220208T235959Z &X-Amz-Expires=300&X-Amz-Security-Token=security-token&X-Amz-Signature=string&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=content-type%3Bhost%3Bx-amz-date &language-code=en-US&media-encoding=flac&sample-rate=16000&vocabulary-filter-name=my-first-vocabulary-filter&vocabulary-filter-method=mask
Parameter definitions can be found in the API Reference; parameters common to all AWS API operations are listed in the Common Parameters section.