Access virtual appliances through AWS PrivateLink
You can use a Gateway Load Balancer to distribute traffic to a fleet of network virtual appliances. The appliances can be used for security inspection, compliance, policy controls, and other networking services. You specify the Gateway Load Balancer when you create a VPC endpoint service. Other AWS principals access the endpoint service by creating a Gateway Load Balancer endpoint.
Pricing
You are billed for each hour that your Gateway Load Balancer endpoint is provisioned in each Availability Zone.
You are also billed per GB of data processed. For more information, see
AWS PrivateLink Pricing
Contents
For more information, see Gateway Load Balancers.
Overview
The following diagram shows how application servers access security appliances through AWS PrivateLink. The application servers run in a subnet of the service consumer VPC. You create a Gateway Load Balancer endpoint in another subnet of the same VPC. All traffic entering the service consumer VPC through the internet gateway is first routed to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint for inspection and then routed to the destination subnet. Similarly, all traffic leaving the application servers is routed to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint for inspection before it is routed back through the internet gateway.
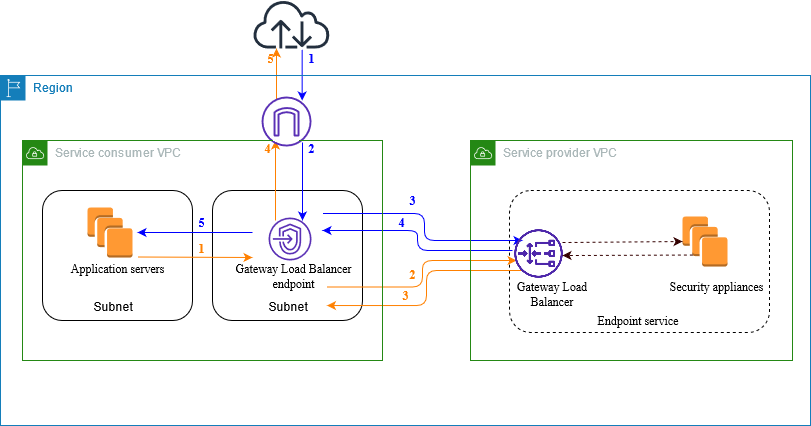
Traffic from the internet to the application servers (blue arrows):
-
Traffic enters the service consumer VPC through the internet gateway.
-
Traffic is sent to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint, based on route table configuration.
-
Traffic is sent to the Gateway Load Balancer for inspection through the security appliance.
-
Traffic is sent back to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint after inspection.
-
Traffic is sent to the application servers, based on route table configuration.
Traffic from the application servers to the internet (orange arrows):
-
Traffic is sent to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint, based on route table configuration.
-
Traffic is sent to the Gateway Load Balancer for inspection through the security appliance.
-
Traffic is sent back to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint after inspection.
-
Traffic is sent to the internet gateway based on the route table configuration.
-
Traffic is routed back to the internet.
IP address types
Service providers can make their service endpoints available to service consumers over IPv4, IPv6, or both IPv4 and IPv6, even if their security appliances support only IPv4. If you enable dualstack support, existing consumers can continue to use IPv4 to access your service and new consumers can choose to use IPv6 to access your service.
If a Gateway Load Balancer endpoint supports IPv4, the endpoint network interfaces have IPv4 addresses. If a
Gateway Load Balancer endpoint supports IPv6, the endpoint network interfaces have IPv6 addresses. The IPv6 address
for an endpoint network interface is unreachable from the internet. If you describe an
endpoint network interface with an IPv6 address, notice that denyAllIgwTraffic
is enabled.
Requirements to enable IPv6 for an endpoint service
-
The VPC and subnets for the endpoint service must have associated IPv6 CIDR blocks.
-
The Gateway Load Balancer for the endpoint service must use the dualstack IP address type. The security appliances do not need to support IPv6 traffic.
Requirements to enable IPv6 for a Gateway Load Balancer endpoint
-
The endpoint service must have an IP address type that includes IPv6 support.
-
The IP address type of a Gateway Load Balancer endpoint must be compatible with the subnet for the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint, as described here:
-
IPv4 – Assign IPv4 addresses to your endpoint network interfaces. This option is supported only if all selected subnets have IPv4 address ranges.
-
IPv6 – Assign IPv6 addresses to your endpoint network interfaces. This option is supported only if all selected subnets are IPv6 only subnets.
-
Dualstack – Assign both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to your endpoint network interfaces. This option is supported only if all selected subnets have both IPv4 and IPv6 address ranges.
-
-
The route tables for the subnets in the service consumer VPC must route IPv6 traffic and the network ACLs for these subnets must allow IPv6 traffic.
Routing
To route traffic to the endpoint service, specify the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint as a target in your route tables, using its ID. For the diagram above, add routes to the route tables as follows. When using a Gateway Load Balancer endpoint as a target, you cannot specify a prefix list as a destination. In these tables, IPv6 routes are included for a dualstack configuration.
Route table for the internet gateway
This route table must have a route that sends traffic destined for the application servers to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint.
| Destination | Target |
|---|---|
VPC IPv4 CIDR |
Local |
VPC IPv6 CIDR |
Local |
Application subnet IPv4 CIDR |
vpc-endpoint-id |
Application subnet IPv6 CIDR |
vpc-endpoint-id |
Route table for the subnet with the application servers
This route table must have a route that sends all traffic from the application servers to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint.
| Destination | Target |
|---|---|
VPC IPv4 CIDR |
Local |
VPC IPv6 CIDR |
Local |
| 0.0.0.0/0 | vpc-endpoint-id |
| ::/0 | vpc-endpoint-id |
Route table for the subnet with the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint
This route table must send traffic that is returned from inspection to its final destination. For traffic that originated from the internet, the local route sends the traffic to the application servers. For traffic that originated from the application servers, add a route that sends all traffic to the internet gateway.
| Destination | Target |
|---|---|
VPC IPv4 CIDR |
Local |
VPC IPv6 CIDR |
Local |
| 0.0.0.0/0 | internet-gateway-id |
| ::/0 | internet-gateway-id |