Troubleshoot AWS Site-to-Site VPN connectivity when using Border Gateway Protocol
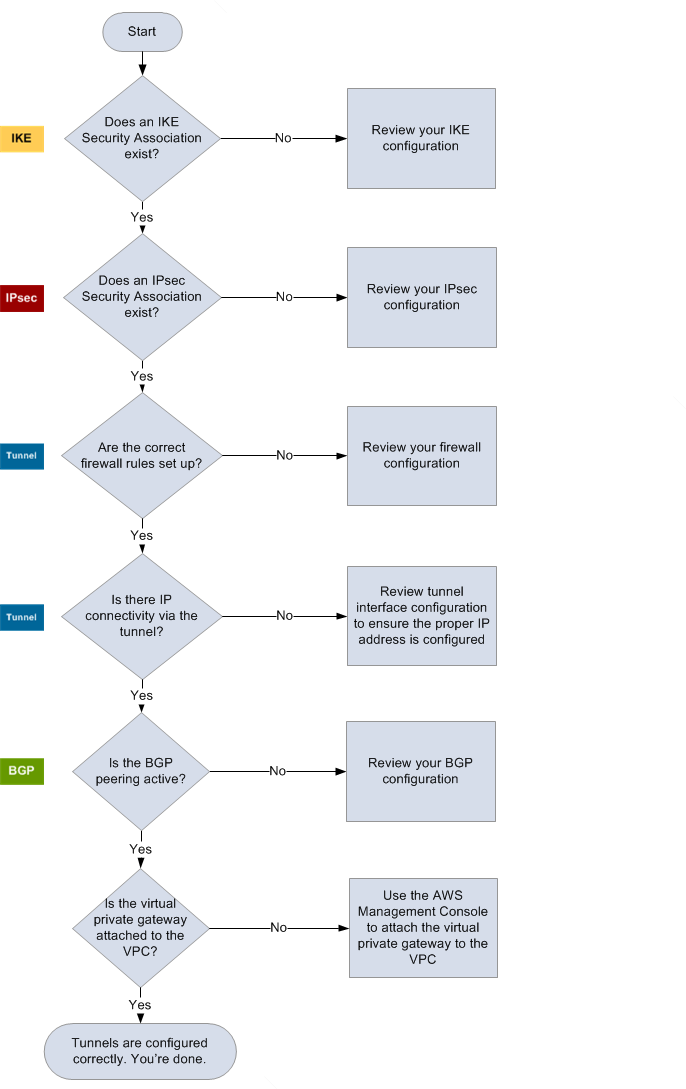
The following diagram and table provide general instructions for troubleshooting a customer gateway device that uses Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). We also recommend that you enable the debug features of your device. Consult your gateway device vendor for details.
| IKE |
Determine if an IKE security association exists. An IKE security association is required to exchange keys that are used to establish the IPsec security association. If no IKE security association exists, review your IKE configuration settings. You must configure the encryption, authentication, perfect forward secrecy, and mode parameters as listed in the configuration file. If an IKE security association exists, move on to 'IPsec'. |
| IPsec |
Determine if an IPsec security association (SA) exists. An IPsec SA is the tunnel itself. Query your customer gateway device to determine if an IPsec SA is active. Ensure that you configure the encryption, authentication, perfect forward secrecy, and mode parameters as listed in the configuration file. If no IPsec SA exists, review your IPsec configuration. If an IPsec SA exists, move on to 'Tunnel'. |
| Tunnel |
Confirm that the required firewall rules are set up (for a list of the rules, see Firewall rules for an AWS Site-to-Site VPN customer gateway device). If they are, move forward. Determine if there is IP connectivity through the tunnel. Each side of the tunnel has an IP address as specified in the configuration file. The virtual private gateway address is the address used as the BGP neighbor address. From your customer gateway device, ping this address to determine if IP traffic is being properly encrypted and decrypted. If the ping isn't successful, review your tunnel interface configuration to make sure that the proper IP address is configured. If the ping is successful, move on to 'BGP'. |
| BGP |
Determine if the BGP peering session is active. For each tunnel, do the following:
If the tunnels are not in this state, review your BGP configuration. If the BGP peering is established, you are receiving a prefix, and you are advertising a prefix, your tunnel is configured correctly. Make sure that both tunnels are in this state. |