Private NAT Gateway
Teams often work independently and they might create a new VPC for a project, which may have overlapping classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) blocks. For integration, they might want to enable communication between networks with overlapping CIDRs, which is not achievable through features such as VPC peering and Transit Gateway. A private NAT gateway can help with this use case. Private NAT gateway uses a unique private IP address to perform source NAT for the overlapping source IP address, and ELB does the destination NAT for the overlapping destination IP address. You can route traffic from your private NAT gateway to other VPCs or on-premises networks using Transit Gateway or a virtual private gateway.
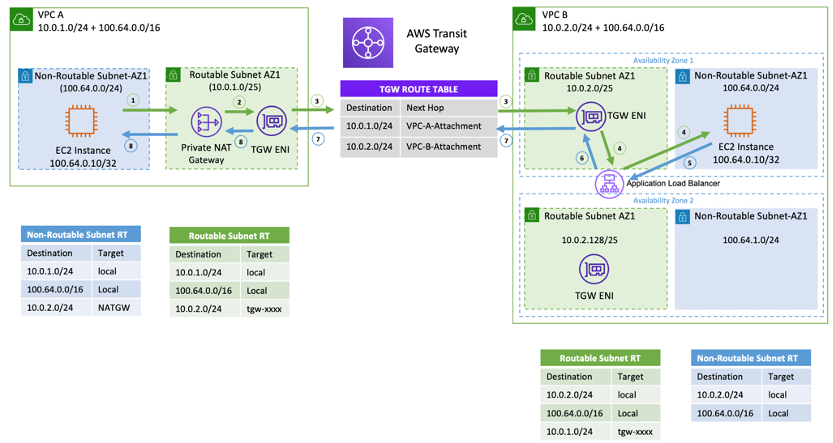
Example setup – Private NAT gateway
The preceding figure shows two non-routable (overlapping CIDRs, 100.64.0.0/16)
subnets in VPC A and B. To establish a connection between them, you can add secondary
non-overlapping/routable CIDRs (routable subnets, 10.0.1.0/24 and
10.0.2.0/24) to VPC A and B, respectively. The routable CIDRs should be
allocated by the network management team responsible for IP allocation. A private NAT gateway
is added to the routable subnet in VPC A with an IP address of 10.0.1.125.
The private NAT gateway performs source network address translation on requests from instances in
non-routable subnet of VPC A (100.64.0.10) as 10.0.1.125, the ENI of
the private NAT gateway. Now traffic can be pointed to a routable IP address assigned to the
Application Load Balancer (ALB) in VPC B (10.0.2.10), which has a target of
100.64.0.10. Traffic is routed through Transit Gateway. Return traffic is processed by the
private NAT gateway back to the original Amazon EC2 instance requesting the connection.
The private NAT gateway can also be used when your on-premises network restricts access to
approved IPs. The on-premises networks of few customers are required by compliance to
communicate only with private networks (no IGW) only through a limited contiguous block of
approved IPs owned by the customer. Instead of allocating each instance a separate IP from
the block, you can run large workloads on AWS VPCs behind each allow-listed IP using private
NAT gateway. For details, refer to the How to solve Private IP exhaustion with Private NAT Solution
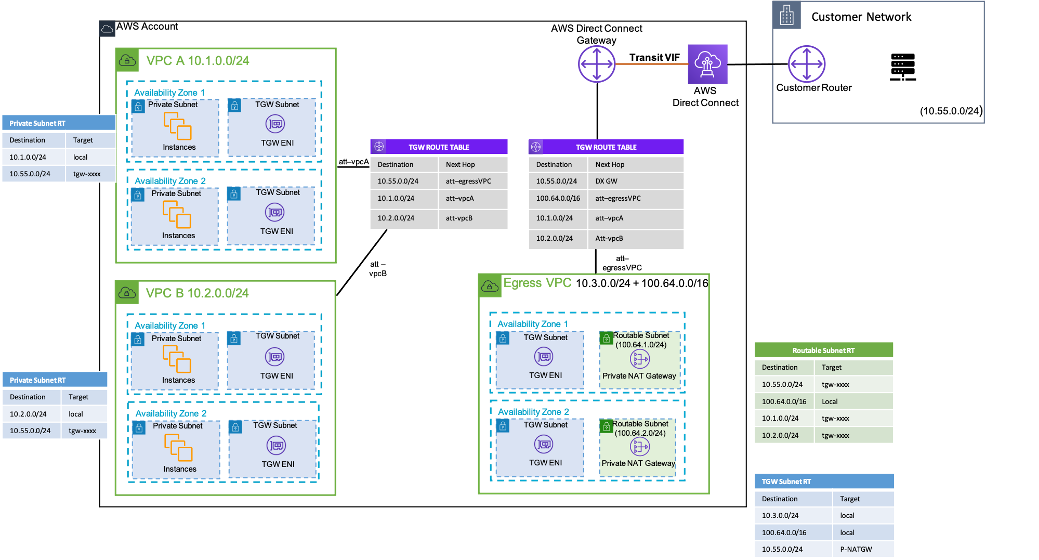
Example setup – How to use Private NAT gateway to provide approved IPs for on-premises network