Network function deployment and configuration
The pipeline created in the previous stage enables both ISVs and providers to decentralize and optimize the deployment of network functions. The pipeline is connected and listens to changes in the application repository, which is configured in the JSON file in step 1 of the preceding figure.
To vet the images that are published by third parties, a vulnerability scanning solution
that assists in identifying software vulnerabilities in container images is deployed and
configured. The scanning solution automatically checks all new images pushed to Amazon ECR
The following figure demonstrates the architecture of the Image Vulnerability Scanning solution.
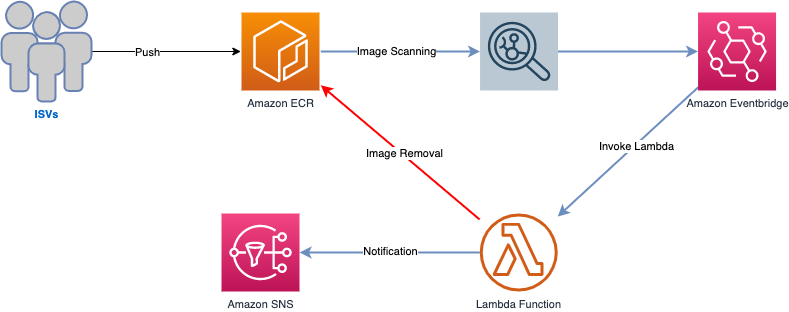
Architecture of the Image Vulnerability Scanning solution
The application pipeline can be configured to be triggered by changes in the image after the scanning result, or by direct changes in the repository. For example, when a new Helm image is created.
The following list is the sequence that creates/upgrades the network function, as represented in the following figure:
ISVs publish new images to Amazon ECR. (If the image is approved, the application pipeline is triggered.
CodePipeline pulls the new image from Amazon ECR and uses CodeBuild to deploy the image to Kubernetes. Helm commands can be used to upgrade the network function.
After the image is deployed, Test as Service (TaS) is triggered. TaS validates the new deployment and centralizes data and metrics about the network functions’ performance under stress.
Logs and metrics are collected and centralized in OpenSearch and Grafana. Third
parties such as Datadog
A MANO that can coordinate network resources can also be deployed and integrated with the solution. It uses the data collected to take automated actions such as network slicing and Quality of Service (QoS) auto scaling.

Application pipeline