This whitepaper is for historical reference only. Some content might be outdated and some links might not be available.
Compliance Auditing and Security Analytics
With AWS CloudTrail
CloudTrail logs can be aggregated from multiple Regions and multiple AWS accounts into a single Amazon S3 bucket. AWS recommends that you write logs--especially AWS CloudTrail logs--to an Amazon S3 bucket with restricted access in an AWS account designated for logging (Log Archive). The permissions on the bucket should prevent deletion of the logs, and they should also be encrypted at rest using Server-Side Encryption with Amazon S3-managed encryption keys (SSE-S3) or AWS KMS–managed keys (SSE-KMS). CloudTrail log file integrity validation can be used to determine whether a log file was modified, deleted, or unchanged after CloudTrail delivered it. This feature is built using industry standard algorithms: SHA-256 for hashing and SHA-256 with RSA for digital signing. This makes it computationally hard to modify, delete, or forge CT; log files without detection. You can use the AWS command line interface (AWS CLI) to validate the files in the location where CloudTrail delivered them.
CloudTrail logs aggregated in an Amazon S3 bucket can be analyzed for auditing purposes or for
troubleshooting activities. Once the logs are centralized, you can integrate with Security
Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions or use AWS services, such as Amazon Athena
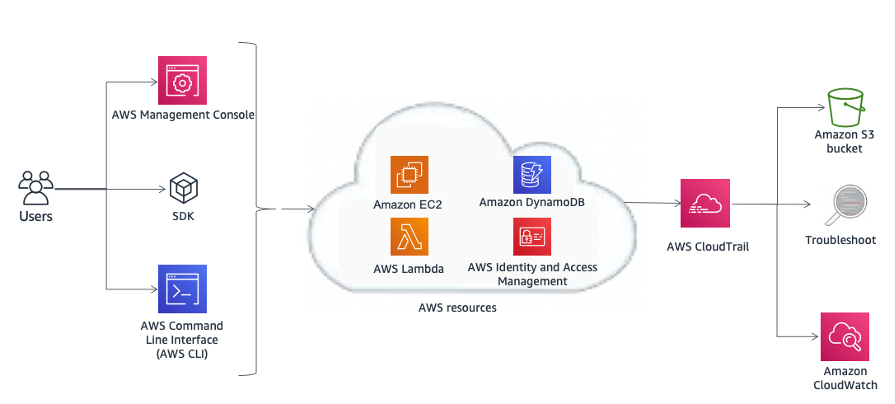
Figure 2 – Example architecture for compliance auditing and security analytics with AWS CloudTrail
AWS CloudTrail logs can also trigger preconfigured Amazon CloudWatch events. You can use these events to notify users or systems that an event has occurred, or for remediation actions. For example, if you want to monitor activities on your Amazon EC2 instances, you can create a CloudWatch Event rule. When a specific activity happens on the Amazon EC2 instance and the event is captured in the logs, the rule triggers an AWS Lambda function, which sends a notification email about the event to the administrator. (See Figure 3.) The email includes details such as when the event happened, which user performed the action, Amazon EC2 details, and more. The following diagram shows the architecture of the event notification.

Figure 3 – Example of AWS CloudTrail event notification