An AWS Cloud architecture for web hosting
The following figure provides another look at that classic web application architecture and how it can leverage the AWS Cloud computing infrastructure.
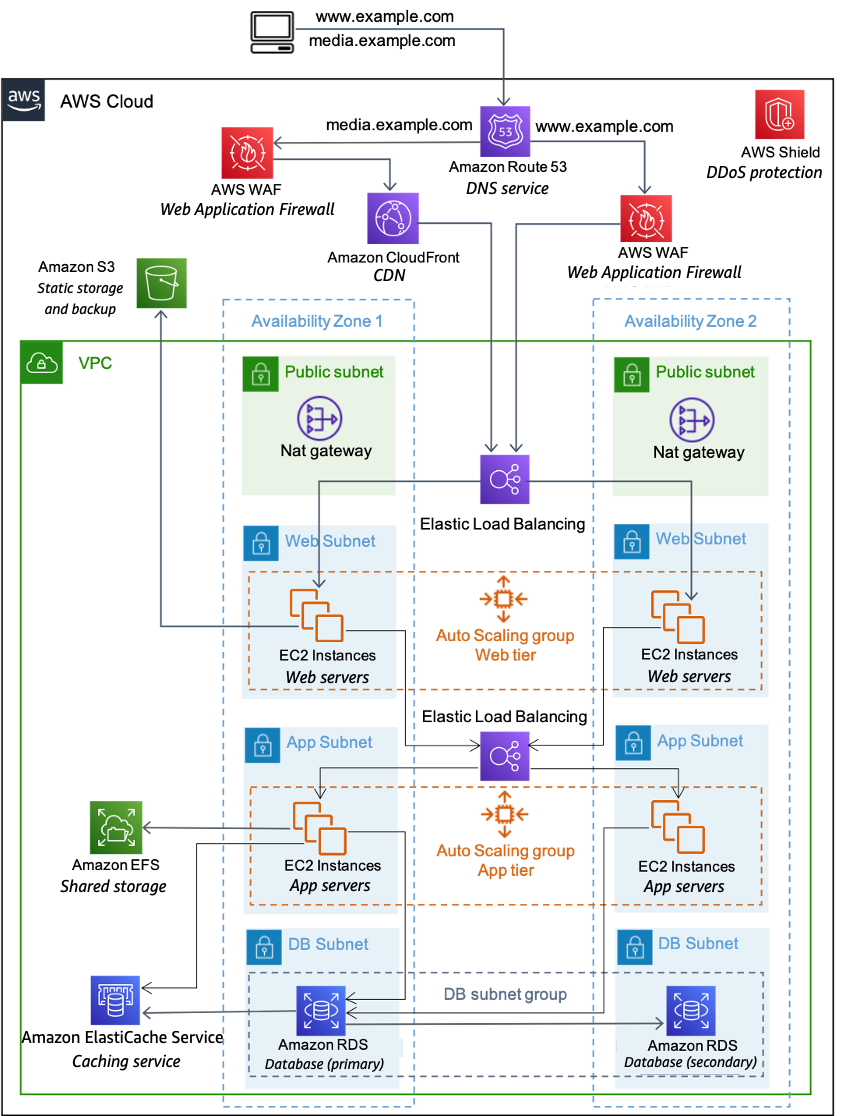
An example of a web hosting architecture on AWS
-
DNS services with Amazon Route 53
– Provides DNS services to simplify domain management. -
Edge caching with Amazon CloudFront
– Edge caches high-volume content to decrease the latency to customers. -
Edge security for Amazon CloudFront with AWS WAF
– Filters malicious traffic, including cross site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection via customer-defined rules. -
Load balancing with Elastic Load Balancing
(ELB) – Enables you to spread load across multiple Availability Zones and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling groups for redundancy and decoupling of services. -
DDoS protection with AWS Shield
– Safeguards your infrastructure against the most common network and transport layer DDoS attacks automatically. -
Firewalls with security groups – Moves security to the instance to provide a stateful, host-level firewall for both web and application servers.
-
Caching with Amazon ElastiCache
– Provides caching services with Redis or Memcached to remove load from the app and database, and lower latency for frequent requests. -
Managed database with Amazon Relational Database Service
(Amazon RDS) – Creates a highly available, multi-AZ database architecture with six possible DB engines. -
Static storage and backups with Amazon Simple Storage Service
(Amazon S3) – Enables simple HTTP-based object storage for backups and static assets like images and video.