This whitepaper is for historical reference only. Some content might be outdated and some links might not be available.
Web application hosting in the cloud using AWS
The first question you should ask concerns the value of moving a classic web application hosting solution into the AWS Cloud. If you decide that the cloud is right for you, you’ll need a suitable architecture. This section helps you evaluate an AWS Cloud solution. It compares deploying your web application in the cloud to an on-premises deployment, presents an AWS Cloud architecture for hosting your application, and discusses the key components of the AWS Cloud Architecture solution.
How AWS can solve common web application hosting issues
If you’re responsible for running a web application, you could face a variety of infrastructure and architectural issues for which AWS can provide seamless and cost-effective solutions. The following are some of the benefits of using AWS over a traditional hosting model.
A scalable solution to handling unexpected traffic peaks
A more dire consequence of the slow provisioning associated with a traditional hosting model is the inability to respond in time to unexpected traffic spikes. There are a number of stories about web applications becoming unavailable because of an unexpected spike in traffic after the site is mentioned in popular media. In the AWS Cloud, the same on-demand capability that helps web applications scale to match regular traffic spikes can also handle an unexpected load. New hosts can be launched and are readily available in a matter of minutes, and they can be taken offline just as quickly when traffic returns to normal.
An on-demand solution for test, load, beta, and reproduction environments
The hardware costs of building and maintaining a traditional hosting environment for a production web application don’t stop with the production fleet. Often, you need to create preproduction, beta, and testing fleets to ensure the quality of the web application at each stage of the development lifecycle. While you can make various optimizations to ensure the highest possible use of this testing hardware, these parallel fleets are not always used optimally, and a lot of expensive hardware sits unused for long periods of time.
In the AWS Cloud, you can provision testing fleets as and when you need them. This not only eliminates the need for pre-provisioning resources days or months prior to the actual usage, but gives you the flexibility to tear down the infrastructure components when you do not need them. Additionally, you can simulate user traffic on the AWS Cloud during load testing. You can also use these parallel fleets as a staging environment for a new production release. This enables quick switchover from current production to a new application version with little or no service outages.
An AWS Cloud architecture for web hosting
The following figure provides another look at that classic web application architecture and how it can leverage the AWS Cloud computing infrastructure.
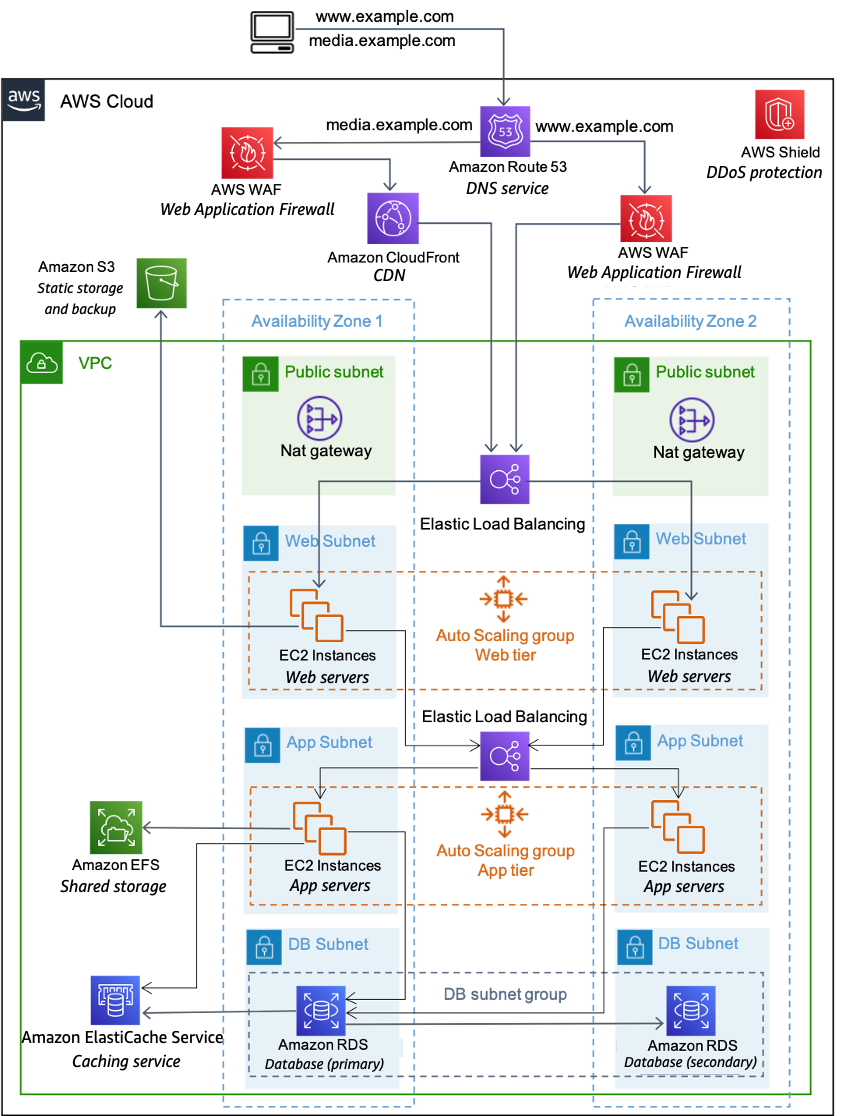
An example of a web hosting architecture on AWS
-
DNS services with Amazon Route 53
– Provides DNS services to simplify domain management. -
Edge caching with Amazon CloudFront
– Edge caches high-volume content to decrease the latency to customers. -
Edge security for Amazon CloudFront with AWS WAF
– Filters malicious traffic, including cross site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection via customer-defined rules. -
Load balancing with ELB
(ELB) – Enables you to spread load across multiple Availability Zones and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling groups for redundancy and decoupling of services. -
DDoS protection with AWS Shield
– Safeguards your infrastructure against the most common network and transport layer DDoS attacks automatically. -
Firewalls with security groups – Moves security to the instance to provide a stateful, host-level firewall for both web and application servers.
-
Caching with Amazon ElastiCache
– Provides caching services with Redis or Memcached to remove load from the app and database, and lower latency for frequent requests. -
Managed database with Amazon Relational Database Service
(Amazon RDS) – Creates a highly available, multi-AZ database architecture with six possible DB engines. -
Static storage and backups with Amazon Simple Storage Service
(Amazon S3) – Enables simple HTTP-based object storage for backups and static assets like images and video.