This whitepaper is for historical reference only. Some content might be outdated and some links might not be available.
Amazon Web Services concepts
This section describes the AWS infrastructure and services that are part of the reference architecture for running Oracle E-Business Suite on AWS.
Regions and Availability Zones
Each
Region
An AWS account provides multiple Regions so you can launch your application in locations that meet your requirements. For example, you might want to launch your application in Europe to be closer to your European customers, or to meet legal requirements.
Each Region has multiple, isolated locations known as Availability Zones. Each Availability Zone runs on its own physically distinct, independent infrastructure, and is engineered to be highly reliable. Common points of failure, such as generators and cooling equipment, are not shared across Availability Zones. Because Availability Zones are physically separate, even extremely uncommon disasters such as fires, tornados or flooding would only affect a single Availability Zone. Each Availability Zone is isolated, but the Availability Zones in a Region are connected through low-latency links. The following figure illustrates the relationship between Regions and Availability Zones.
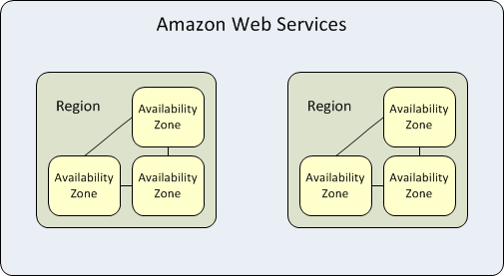
Relationship between AWS Regions and Availability Zones
The following figure shows the Regions and the number of
Availability Zones in each Region provided by an AWS account at
the time of this publication. For the most current list of Regions
and Availability Zones, see
Global
Infrastructure
Note
You can’t describe or access additional Regions from the AWS GovCloud (US) Region or China (Beijing) Region.
Map of AWS Regions and Availability Zones
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2)
Amazon EC2
Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle
Amazon RDS
Custom
Elastic Load Balancing
Elastic Load Balancing
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
Amazon EBS
Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is simply a packaged-up environment that includes all the necessary bits to set up and boot your instance. Your AMIs are your unit of deployment. Amazon EC2 uses Amazon EBS and Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) to provide reliable, scalable storage of your AMIs so they can boot when you need them.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
Amazon S3
Amazon Route 53
Amazon Route 53
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC)
Amazon VPC
You can use multiple layers of security, including security groups and network access control lists, to help control access to EC2 instances in each subnet. Additionally, you can create a Hardware Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection between your corporate data center and your VPC and use the AWS Cloud as an extension of your corporate data center.
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS)
Amazon EFS
AWS security and compliance
The AWS Cloud security infrastructure has been architected to be
one of the most flexible and secure cloud computing environments
available today. Security on AWS is very similar to security in
your on-premises data center—but without the costs and
complexities involved in protecting facilities and hardware. AWS
provides a secure global infrastructure, plus a range of features
that you can use to help secure your systems and data in the
cloud. To learn more, see
AWS Cloud
Security
AWS compliance enables customers to understand the robust controls in place at AWS to maintain security and data protection in the cloud. AWS engages with external certifying bodies and independent auditors to provide customers with extensive information regarding the policies, processes, and controls established and operated by AWS.
To learn more, see
AWS Compliance