Workflow orchestration agents
Workflow orchestration agents manage and coordinate multistep tasks, processes, and services across distributed systems. Rather than reasoning and acting in isolation, these agents delegate work to subagents or other systems, maintain execution context, and adapt based on intermediate results.
These agents are a fundamental part of automation flows. They are particularly useful when handling long-running tasks, multi-agent compositions, and cross-domain integrations where various agents and tools must be called in sequence or conditionally.
Architecture
A workflow orchestration agent is shown in the following diagram:
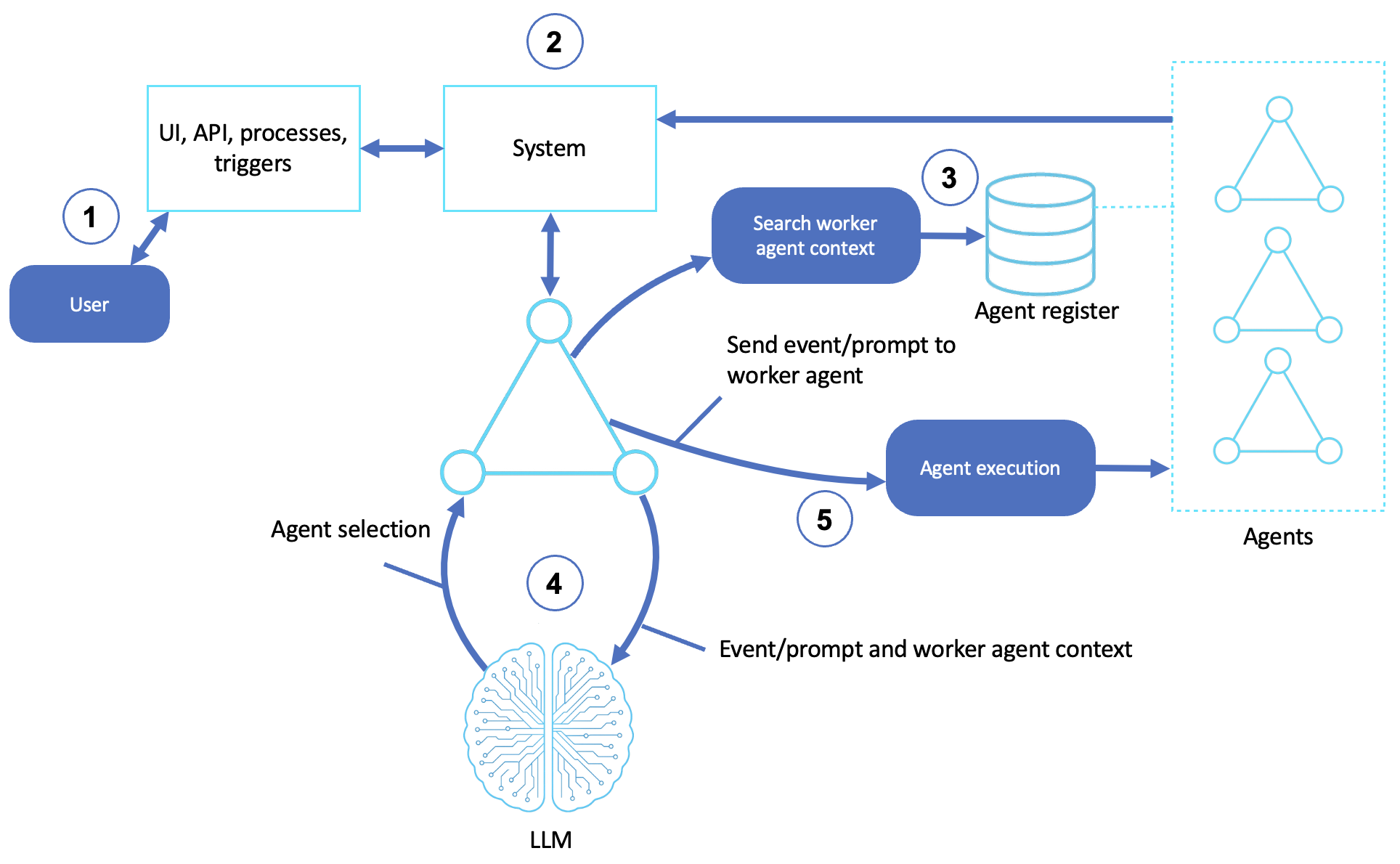
Description
-
Receives user input
-
A user (or external trigger) initiates a task through a UI, API, or system event.
-
-
Handles system events
-
A system component receives the request and emits an event or command that requires orchestration.
-
-
Retrieves context
-
The workflow agent queries knowledge bases and agent registries to find the right worker agent for the task based on metadata, domain, and prior success rate.
-
-
Selects an LLM agent
-
An LLM helps to select the best agent or workflow plan by analyzing the task description and available options.
-
It may also formulate task-specific prompts to send to a selected agent.
-
-
Delegates and executes
-
The chosen worker agent receives the event or prompt and begins running commands.
-
It can track execution state, retry on failure, and pass intermediate results to the next agent in the sequence.
-
Capabilities
-
Agent composition (for example, supervisors, collaborator agents, and tools)
-
Event-driven or scheduled execution
-
Memory and state tracking over time
-
Hierarchical or parallel task orchestration (synchronous compared with asynchronous workflows)
-
Dynamic agent selection and chaining
Common use cases
-
Multistep automation (for example, data ingestion and reporting)
-
Customer service routing and escalation (for example, agent-as-coordinator)
-
AI agents coordinate with humans and bots within the same loop
-
Automates enterprise processes using LLM-powered logic
-
Hybrid systems combine AI agents and traditional orchestration tools
Implementation guidance
You can build this pattern using the following tools and AWS services:
-
Amazon Bedrock for reasoning and agent selection
-
AWS Step Functions or Amazon EventBridge for workflow composition
-
AWS Lambda as execution units or task runners
-
Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), or Amazon RDS to track states and results
-
AWS AppFabric or Amazon AppFlow for cross-system coordination
-
(Optional) Use Amazon SageMaker run agent to host domain-specific worker agents
Summary
Workflow agents coordinate, adapt, and align goals in multi-agent environments. This means that AI agents can collaborate, adapt to runtime conditions, and deliver complex outcomes through modular, explainable workflows.