Layer 3: Security and governance for generative AI platforms on AWS
A robust security and governance framework is essential for scaling generative AI adoption across the enterprise. We recommend a platform-centric approach. This approach makes sure that all generative AI powered applications, irrespective of which team builds them, benefit from a default set of security and responsible AI guardrails.
This section contains the following topics:
Core security disciplines
OWASP top 10 for LLM applications
-
Governance and compliance – Create the necessary policies, procedures, and reporting to empower the business while minimizing risk. For generative AI applications, this encompasses guidelines for model selection, data usage, and output validation.
-
Legal and privacy – Meet the specific regulatory, legal, and privacy requirements for using or creating generative AI solutions. Organizations must carefully consider data protection laws, intellectual property rights, and industry-specific regulations when implementing generative AI solutions.
-
Risk management – Identify potential threats to generative AI solutions and recommended mitigations. This includes addressing risks such as data poisoning, prompt injection attacks, or unintended biases in model outputs.
-
Controls – Implement security controls that mitigate risk. For generative AI applications, this includes input sanitization, output filtering, and access controls for model usage. For more information, see Recommended security controls in this guide.
-
Resilience – Architect generative AI solutions to maintain availability and meet business service-level agreements (SLAs). This includes considerations for model redundancy, fallback mechanisms, and scalability under varying load conditions.
Recommended security controls
Defense-in-depth is a cybersecurity approach that uses layers of security controls to protect a system, network, or workload. Different layers help detect and stop attacks if one layer fails. At the minimum, we recommend the following controls to adopt a defense-in-depth approach for generative AI workloads and their environments:
-
Identity and access management – AWS services, including Amazon Bedrock and Amazon SageMaker AI, natively integrate with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). IAM provides granular control over who can perform actions on your AWS accounts and resources, such as subscribing to foundation models or running inference on a model. We recommend that you create multiple IAM roles with granular permissions. For example, you might create the following roles:
-
Evaluation role – Users with this role can evaluate foundation models in a sandbox environment as new models are added to Amazon Bedrock. These users should coordinate with your legal and procurement teams before activating subscriptions that allow broader access.
-
General access role – Users with this role can access foundational models for standard usage.
-
Fine-tuned model access role – Users with this role can access models that are fine-tuned with your proprietary data.
-
Specialized model access role – Users with this role can access to cutting-edge, high-cost models for specific use cases.
-
-
Private network access through AWS PrivateLink – Use AWS PrivateLink with Amazon Bedrock and Amazon SageMaker AI to invoke models from within your VPC and on-premises network. This helps keep sensitive data within your private network.
-
Guardrails for Amazon Bedrock – Implement guardrails to manage and filter the requests and responses to and from foundation models. This adds an additional layer of control.
-
Securely store invocation logs – To make sure that use meets your compliance needs, you can store all requests and responses to an Amazon S3 bucket or to Amazon CloudWatch Logs. For more information, see Monitor model invocation using CloudWatch Logs and Amazon S3 in the Amazon Bedrock documentation.
-
Audit and track access to foundation models – Use Amazon CloudWatch, a service that records actions taken by a user, role, or an AWS service. CloudTrail captures all API calls for Amazon Bedrock as events. For more information, see Monitor Amazon Bedrock API calls using CloudTrail and Logging Amazon SageMaker AI API calls using AWS CloudTrail.
-
Follow OWASP top 10 for LLM security – Adhere to OWASP's top 10 security risks for LLM applications, and make sure that you have clearly identified strategies and security controls to architect layered defenses. For more information, see Architect defense-in-depth security for generative AI applications using the OWASP Top 10 for LLMs
(AWS blog post).
Security scoping matrix
The specific security controls that you need depends on the nature of your generative
AI application. The AWS Generative AI Security Scoping Matrix
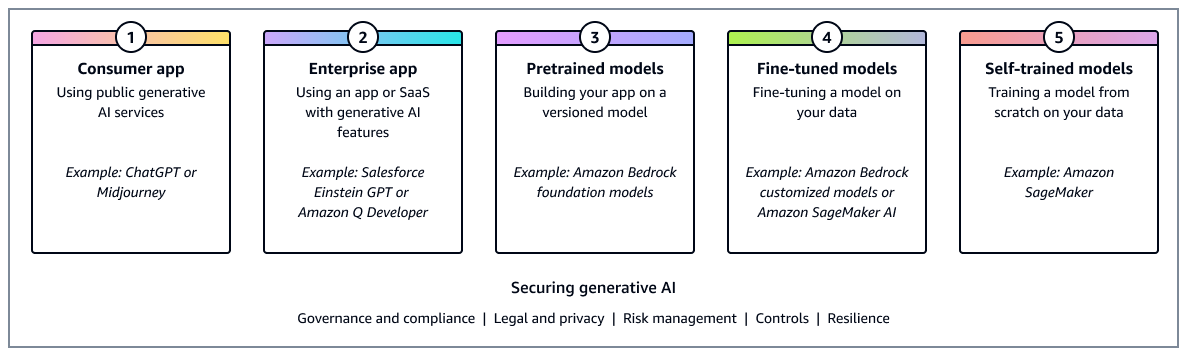
The matrix helps organizations identify the appropriate security controls based on factors such as:
-
Whether the application is consumer-facing or internal to the enterprise
-
The use of pretrained models compared to fine-tuning
-
The sensitivity of the data being processed
-
The criticality of the application to business operations
Implementation recommendations
To implement a comprehensive security and governance framework for your generative AI workloads, consider the following recommendations:
-
Establish clear policies and procedures for model access and usage.
-
Implement security controls at multiple layers, such as at the network, application, and data layers.
-
Perform regular security assessments and compliance audits.
-
Maintain detailed documentation for security measures and controls.
-
Provide security awareness training for teams that work with generative AI.
-
Regularly review and update security controls as threats evolve.