Planning and operations
Supply chain planning and operations involve managing the flow of goods, services, and information from suppliers to end customers. This complex process encompasses demand forecasting, inventory management, procurement, production scheduling, warehousing, transportation, and distribution activities. Organizations use supply chain planning to optimize their resources, reduce costs, minimize risks, and make timely delivery of products to customers. Effective supply chain operations require careful coordination among various stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and logistics providers.
AWS offers a powerful combination of Amazon SageMaker AI's machine learning capabilities and Amazon Bedrock's generative AI models to revolutionize supply chain planning and operations. In demand planning and forecasting, while SageMaker AI processes historical sales data and market trends to create statistical forecasting models, Bedrock's Claude or Titan models analyze unstructured data sources like news articles, social media trends, and market reports to identify emerging patterns that might impact demand. This combined approach provides more comprehensive and nuanced demand predictions than traditional forecasting methods alone.
In manufacturing operations, Amazon SageMaker AI builds predictive maintenance models that analyze equipment sensor data to forecast potential failures days or weeks in advance, reducing unplanned downtime. Amazon Bedrock enhances these insights by generating equipment-specific maintenance procedures, step-by-step troubleshooting guides, and repair documentation tailored to detected anomalies.
Anthropic's Claude analyzes historical maintenance logs alongside technical documentation to identify recurring issues and suggest optimization opportunities, such as modified maintenance intervals or alternative replacement parts, resulting in a more proactive maintenance program that extends equipment lifespan.
For capacity planning, SageMaker AI algorithms optimize production schedules by analyzing historical throughput data, labor constraints, and material availability, while Bedrock generates detailed production scenarios for various demand patterns, equipment configurations, and workforce levels.
This enables manufacturing planners to evaluate multiple operational strategies through intuitive natural language interfaces where they can conversationally query complex scheduling scenarios, such as What happens to our production capacity if supplier X delays deliveries by two weeks?
In logistics and distribution, SageMaker AI powers route optimization models that reduce transportation costs and inventory management systems that decrease holding costs while maintaining service levels.
Bedrock complements these capabilities by generating comprehensive logistics execution plans containing carrier-specific handling instructions, temperature control requirements, customs documentation checklists, and contingency procedures for disruptions like port congestion or weather events.
Claude analyzes complex shipping documentation against constantly changing customs regulations for different countries, identifying compliance issues before shipment and suggesting corrective actions that significantly reduce the risk of costly delays and regulatory penalties.
For supply chain risk management, SageMaker AI analyzes quantifiable risk factors such as historical supplier performance, lead time variability, and demand volatility, while Bedrock continuously monitors news feeds, weather forecasts, labor disputes, and geopolitical developments affecting key trade routes or production regions.
This combined approach enables the generation of comprehensive risk reports with financial impact assessments, probability ratings, and prioritized mitigation recommendations tailored to specific business constraints.
Supplier relationship management benefits significantly from SageMaker AI's ability to evaluate comprehensive supplier performance metrics including quality, on-time delivery, responsiveness, and cost competitiveness, creating segmentation models that identify which suppliers require closer partnership versus transactional relationships.
Bedrock assists procurement teams by generating professional correspondence such as RFP documents, contract amendment requests, and negotiation position summaries based on specific business requirements and supplier history.
Claude analyzes complex supplier proposals and contract language to identify favorable terms, potential risks, hidden costs, and negotiation opportunities, improving overall supplier governance and relationship management.
Implementation of these supply chain solutions follows a structured approach in Amazon SageMaker AI Studio: setting up the environment with appropriate IAM permissions; integrating supply chain data from ERP systems, IoT devices, and external sources; developing and training appropriate models for specific use cases; connecting to Bedrock services for natural language capabilities; creating automated pipelines for ongoing operations; deploying models as scalable endpoints; and integrating these intelligent capabilities into existing supply chain workflows and systems through well-documented APIs and user interfaces.
The integration of SageMaker AI's machine learning capabilities with Bedrock's generative AI creates a more comprehensive supply chain management solution. This combination enables organizations to handle both quantitative analysis and qualitative insights, while providing natural language interfaces that make complex supply chain operations more accessible to users across the organization. The system can continuously learn and adapt to new conditions while generating actionable insights and recommendations in human-readable formats. This integrated approach helps organizations maintain optimal inventory levels, respond quickly to market changes, verify product quality, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction while maximizing operational efficiency and profitability.
Reference architecture
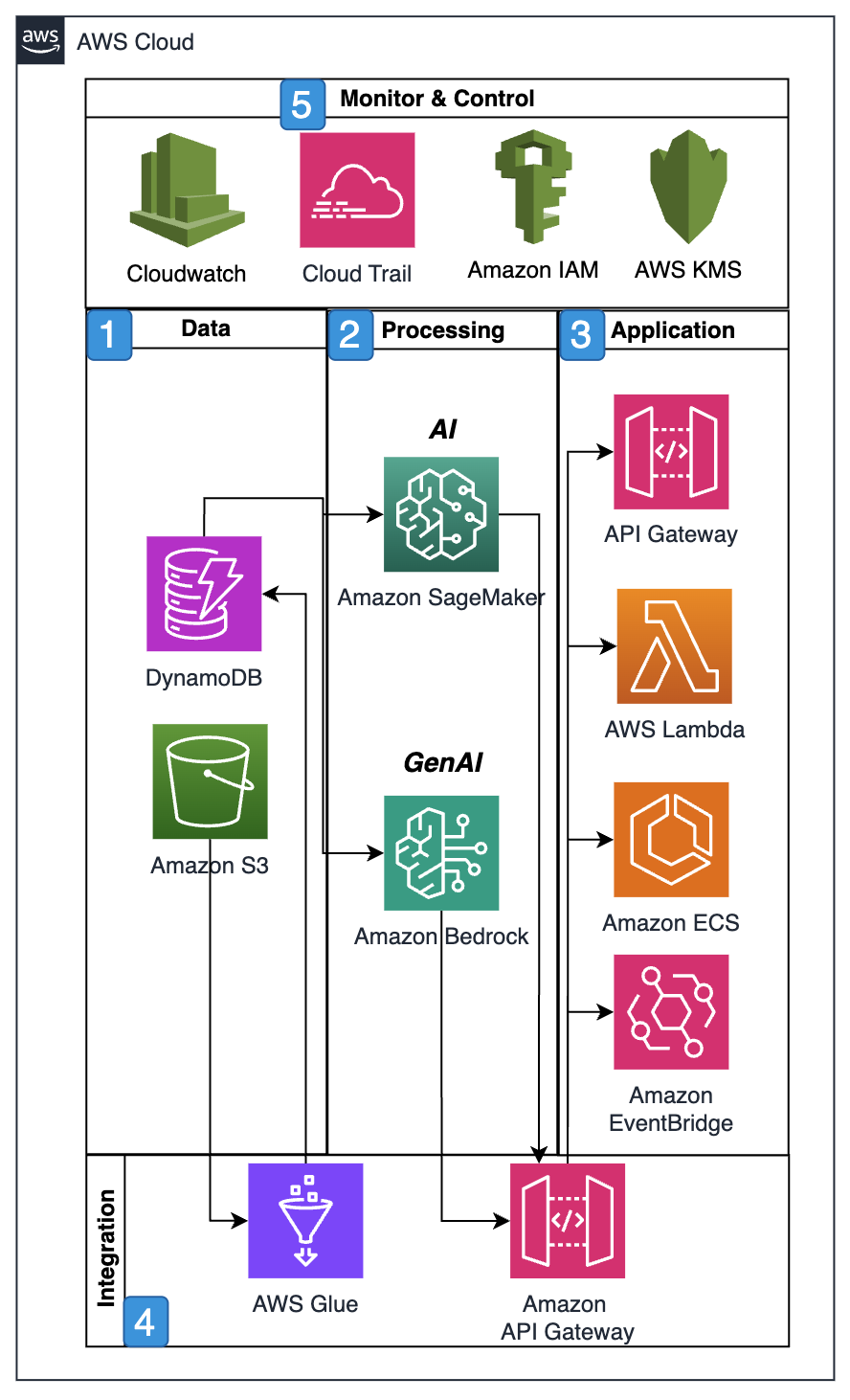
Architecture description
Data ingestion from various sources.
Processing through ML models and AI services.
Real-time analysis and prediction.
API-based service delivery.
Continuous monitoring and optimization.
Architecture objectives
-
Scalable processing of supply chain data.
-
Real-time insights and predictions.
-
Secure and compliance-aligned operations.
-
Integration with existing systems.
-
Monitoring and optimization capabilities.
Metrics
Based on the supply chain planning and operations scenario, the three recommended metrics for an AWS Well-Architected Framework analysis, along with their rationale are:
-
Simulation accuracy:
-
Metric: Percentage accuracy of simulations predicting the impact of changes in transportation strategies.
-
Rationale: This directly measures the reliability and effectiveness of the combined SageMaker AI and Bedrock solution in making accurate predictions, which is fundamental to the entire system's value proposition.
-
Target: Over or equal to 90% accuracy in predictions when compared to actual outcomes.
-
Well-Architected pillars: Performance efficiency and reliability.
-
-
Route optimization savings:
-
Metric: Dollar savings achieved through last-mile and middle-mile route optimizations.
-
Rationale: Provides concrete financial validation of the system's effectiveness and demonstrates clear business value.
-
Target: Minimum 15% reduction in transportation costs.
-
Well-Architected pillars: Cost optimization and performance efficiency.
-
-
Frequency of emergency responses:
-
Metric: Number of emergency responses or corrective actions triggered by the application. For Example:
-
Supply chain disruptions like weather, political, labor or other developments impacting logistics or trade routes.
-
Equipment Failures flagged as imminent requiring immediate intervention.
-
Compliance issues impacting customs processing time or penalties.
-
Inventory shortages impending based on plan including supplier performance issues or unexpected demand spikes.
-
Quality control failures requiring immediate corrective action.
-
-
Rationale: Indicates the system's effectiveness in proactive risk management and its ability to prevent disruptions.
-
Target: Over or equal to 30% reduction in emergency incidents year-over-year.
-
Well-Architected pillars: Reliability and operational excellence.
-
These metrics were selected because they:
-
Directly align with core AWS Well-Architected Framework pillars.
-
Provide measurable evidence of system effectiveness.
-
Cover both technical performance and business outcomes.
-
Address key aspects of the scenario: prediction accuracy, cost optimization, and risk management.